At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
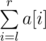 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space:a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 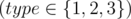 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 5 4
3 3 5
1 2 5
2 1 3 3
1 1 3
8
5
10 10
6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5
1 3 9
2 7 10 9
2 5 10 8
1 4 7
3 3 7
2 7 9 9
1 2 4
1 6 6
1 5 9
3 1 10
49
15
23
1
9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
-
/* 多校被虐>_<。一些题题解都看不懂,只有默默来写CF了。。。 题意很好理解, 解法:对于维护区间最大值mx和区间sum,当 x > mx时不再更新下去, 否则一直更新到根节点 总结:遇到一个居间的数按照某种方式改变时,我们更新的时候,要抓住什么 什么不更新下去是不影响最后结果的,就像本题,如果孩子的最大值mx < x 更新是没有意思的。 */ #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<ctime> #include<map> #include<set> #include<stack> #include<list> #define maxn 100010 #define LL long long using namespace std ; struct node { LL sum ; int mx,mod ; }tree[maxn*3]; int ql ,qr; LL v ; void pushup( int L ,int R,int o) { tree[o].mx = max(tree[o<<1].mx,tree[o<<1|1].mx) ; tree[o].sum = tree[o<<1].sum+tree[o<<1|1].sum ; tree[o].mod = 0 ; } void insert( int L ,int R ,int o ) { if(L==R) { tree[o].sum = v; tree[o].mx = v ; tree[o].mod = 0 ; return ; } int mid = (L+R)>>1 ; if(ql <=mid) insert(L,mid,o<<1) ; else insert(mid+1,R,o<<1|1) ; pushup(L,R,o) ; } void update( int L,int R,int o) { if(L==R) { tree[o].mx %= v ; tree[o].sum = tree[o].mx; return ; } int mid = (L+R)>>1 ; if(ql <= mid && tree[o<<1].mx >= v) update(L,mid,o<<1) ; if(qr > mid && tree[o<<1|1].mx >= v ) update(mid+1,R,o<<1|1) ; pushup(L,R,o) ; } void find( int L ,int R ,int o ) { if(ql <= L && qr >= R) { v += tree[o].sum ; return ; } int mid = (L+R)>>1 ; if(ql <= mid) find(L,mid,o<<1) ; if(qr > mid) find(mid+1,R,o<<1|1) ; pushup(L,R,o) ; } int main() { int i , n , m ,j , k; while( scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) != EOF) { for( ql = 1 ; ql <= n ;ql++) { scanf("%I64d",&v) ; insert(1,n,1) ; } while(m--) { scanf("%d",&k) ; if(k==1) { scanf("%d%d",&ql,&qr) ; v = 0 ; find(1,n,1) ; printf("%I64d ",v) ; } else if(k==2) { scanf("%d%d%I64d",&ql,&qr,&v) ; update(1,n,1) ; } else{ scanf("%d%I64d",&ql,&v) ; insert(1,n,1) ; } } } return 0 ; }