Mojtaba and Arpa are playing a game. They have a list of n numbers in the game.
In a player's turn, he chooses a number pk (where p is a prime number and k is a positive integer) such that pk divides at least one number in the list. For each number in the list divisible by pk, call it x, the player will delete x and add 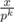 to the list. The player who can not make a valid choice of p and k loses.
to the list. The player who can not make a valid choice of p and k loses.
Mojtaba starts the game and the players alternatively make moves. Determine which one of players will be the winner if both players play optimally.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of elements in the list.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the elements of the list.
If Mojtaba wins, print "Mojtaba", otherwise print "Arpa" (without quotes).
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
4
1 1 1 1
Arpa
4
1 1 17 17
Mojtaba
4
1 1 17 289
Arpa
5
1 2 3 4 5
Arpa
In the first sample test, Mojtaba can't move.
In the second sample test, Mojtaba chooses p = 17 and k = 1, then the list changes to [1, 1, 1, 1].
In the third sample test, if Mojtaba chooses p = 17 and k = 1, then Arpa chooses p = 17 and k = 1 and wins, if Mojtaba chooses p = 17and k = 2, then Arpa chooses p = 17 and k = 1 and wins.
思路:分析出每个数不是独立的游戏,但对于每个质因子是互不相关的。所以对每个质因子进行状态压缩,类似状压dp求出sg值,复杂度瓶颈好像在质因子分解,可以做到O(n * sqrt(MAX_A[i]) / log(MAX_A[i])。
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #include <cctype> #include <cassert> #include <bitset> #include <ctime> using namespace std; #define pau system("pause") #define ll long long #define pii pair<int, int> #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define clr(a, x) memset(a, x, sizeof(a)) const double pi = acos(-1.0); const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; const double EPS = 1e-9; int n, a[105], cnt_prim; map<int, int> sg; map<int, int> prim; set<int> ss[1015]; int cal_sg(int x) { if (sg.count(x)) { return sg[x]; } set<int> mex; for (int i = 0; i <= 30; ++i) { mex.insert(i); } for (int i = 1; i <= 29; ++i) { if ((1 << i) > x) { break; } int y = x; int mask = y >> i; y ^= mask << i; mask |= y; int res = cal_sg(mask); mex.erase(res); } return sg[x] = *mex.begin(); } int main() { sg[1] = 0; scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { scanf("%d", &a[i]); int d = sqrt(a[i] + 0.5); for (int j = 2; j <= d && j <= a[i]; ++j) { if (a[i] % j == 0) { int tmp = 0; if (!prim.count(j)) { prim[j] = ++cnt_prim; } while (a[i] % j == 0) { ++tmp; a[i] /= j; } ss[prim[j]].insert(tmp); } } if (1 != a[i]) { if (!prim.count(a[i])) { prim[a[i]] = ++cnt_prim; } ss[prim[a[i]]].insert(1); } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= cnt_prim; ++i) { int tmp = 0; for (set<int>::iterator it = ss[i].begin(); it != ss[i].end(); ++it) { int x = *it; tmp |= 1 << x; } ans ^= cal_sg(tmp); } puts(ans ? "Mojtaba" : "Arpa"); return 0; }