本节主要介绍 json是什么以及jsoncpp库的使用。
(1)JSON是什么
json 是一种轻量级的文本数据交换格式;
json 独立于语言、平台,使用java script语法来描述对象;
json 解析器和json库对多种不同语言均提供了支持;
json (JavaScript Object Notation) 指的是javascript对象表示方法.
(2)c++JSON书写范例
1.书写c++代码:
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "json/reader.h"
#include "json/value.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
Json::Value person;
person["name"] = "MenAngel";
person["sex"] = "男";
person["age"] = 23;
person["height"] = 178;
cout<<person.toStyledString()<<endl;
return 0;
}
2.头文件及库文件所在路径如下:
头文件:/data01/bm80/ob_rel/include/3rd
库文件:/data01/bm80/ob_rel/lib
库名:libjsoncppD.so
3.使用g++编译链接:
g++ main.cpp -ljsoncppD -I /data01/bm80/ob_rel/include/3rd -L /data01/bm80/ob_rel/lib -o test
4.执行结果如下:
{
"name" : "MenAngel",
"sex" : "男",
"age" : 23,
"height" : 178
}
(3)html中使用javascript脚本创建java对象
1.书写html:
<html>
<body>
<h2>在 JavaScript 中创建 JSON 对象</h2>
<p>
Name: <span id="jname"></span><br />
sex: <span id="jage"></span><br />
age: <span id="jstreet"></span><br />
</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
var JSONObject= {
"name":"MenAngel",
"sex":"男",
"age":23};
document.getElementById("jname").innerHTML=JSONObject.name
document.getElementById("jage").innerHTML=JSONObject.sex
document.getElementById("jstreet").innerHTML=JSONObject.age
</script>
</body>
</html>
用浏览器打开结果如下:

(4)几个重要的jsoncpp的类
Json::Value 可以表示所有的类型,int、uint、string、object、array,boolean等;
Json::Reader 将json文件流或字符串解析到Json::Value, 主要函数有Parse;
Json::Writer 将Json::Value转化成字符串流,
Json::FastWriter 输出不带格式的json
Json::StyleWriter 输出带格式的json
(5)jsoncpp使用详细范例:
1.从字符串中解析json:
// main.cpp
#include "json/reader.h"
#include "json/value.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//创建json value 并转化为字符串
Json::Value person;
person["name"] = "MenAngel";
person["isMarriged"] = false;
person["age"] = 23;
person["height"] = "178";
string strJson = person.toStyledString();
//解析字符串
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
string name;
bool isMarriged;
int age;
int height,weight;
if(reader.parse(strJson,root))
{
if(!root["name"].isNull())
name = root["name"].asString();
if(!root["isMarriged"].isNull())
isMarriged = root["isMarriged"].asBool();
if(!root["age"].isNull())
age = root["age"].asInt();
if(!root["height"].isNull())
height = atoi(root["height"].asString().c_str());
weight = root["weight"].asInt();
}
cout<<"name = " << name <<" "<< root["name"].isString() <<endl
<<"isMarriged = " << isMarriged <<" "<< root["isMarriged"].isBool() <<endl
<<"age = " << age <<" "<< root["age"].isInt() <<endl
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isObject() <<endl //当key不存在时,返回nullValue ,isObject() is 1
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isInt() <<endl
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isArray() <<endl
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isNumeric() <<endl
<<"weight = " << weight <<" "<< root["weight"].isObject() <<endl;
return 0;
}
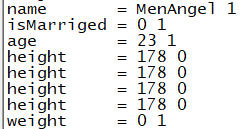
2.从文件中解析json
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "json/reader.h"
#include "json/value.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//创建json value 并转化为字符串
Json::Value person;
person["name"] = "MenAngel";
person["isMarriged"] = false;
person["age"] = 23;
person["height"] = "178";
string strJson = person.toStyledString();
const char * filename = "./json.txt";
//将json字符串写入文件
ofstream ofile;
ofile.open(filename);
ofile<<strJson<<endl;
ofile.flush();
ofile.close();
//从文件中解析json字符串
ifstream ifile;
ifile.open(filename,ios::binary);
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
string name;
bool isMarriged;
int age;
int height,weight;
if(reader.parse(ifile,root))
{
if(!root["name"].isNull())
name = root["name"].asString();
if(!root["isMarriged"].isNull())
isMarriged = root["isMarriged"].asBool();
if(!root["age"].isNull())
age = root["age"].asInt();
if(!root["height"].isNull())
height = atoi(root["height"].asString().c_str());
weight = root["weight"].asInt();
}
cout<<"name = " << name <<" "<< root["name"].isString() <<endl
<<"isMarriged = " << isMarriged <<" "<< root["isMarriged"].isBool() <<endl
<<"age = " << age <<" "<< root["age"].isInt() <<endl
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isObject() <<endl //当key不存在时,返回nullValue ,isObject() is 1
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isInt() <<endl
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isArray() <<endl
<<"height = " << height <<" "<< root["height"].isNumeric() <<endl
<<"weight = " << weight <<" "<< root["weight"].isObject() <<endl;
//remove(filename);
return 0;
}
//json.txt
{
"name" : "MenAngel",
"isMarriged" : false,
"age" : 23,
"height" : "178"
}
3.FastWriter将一个Value对象格式化为JSON格式的字符串 (FastWriter、StyledWriter、StyledStreamWriter)
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <json/json.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
Json::Value person;
person["name"] = "MenAngel";
person["sex"] = "男";
person["age"] = 23;
person["height"] = 178;
Json::Writer *writer1 = new Json::FastWriter();
Json::Writer *writer2 = new Json::StyledWriter();
string str1 = writer1->write(person);
string str2 = writer2->write(person);
string str3 = person.toStyledString();//Json::StyledStreamWriter();
cout<<"str1 : "<<endl
<<str1<<endl;
cout<<"str2 : "<<endl
<<str2<<endl;
cout<<"str3 : "<<endl
<<str3<<endl;
cout<<"str4 : "<<endl
<<person<<endl;
return 0;
}
str1 :
{"name":"MenAngel","sex":"男","age":23,"height":178}
str2 :
{
"name" : "MenAngel",
"sex" : "男",
"age" : 23,
"height" : 178
}
str3 :
{
"name" : "MenAngel",
"sex" : "男",
"age" : 23,
"height" : 178
}
str4 :
{
"name" : "MenAngel",
"sex" : "男",
"age" : 23,
"height" : 178
}
4.在JsonCpp中对Json:value对象中array、object、member、number、int的操作
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <json/json.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//构建json对象
Json::Value family;
Json::Value members;
family["family_id"] = 1314;
family["single_parent"] = false;
family["age"] = 20;
family["money"] = 13.14;
for(int i = 0 ;i < 4; ++i)
{
Json::Value member;
member["id"] = i + 1;
member["name"] = "name";
members.append(member);
}
family["members"] = members;
//打印json value
string strJson = family.toStyledString();
cout<<family<<endl;
//解析json value
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
if(reader.parse(strJson,root))
{
std::vector<std::string> list_strMembers;
if(!root.isNull() && root.isObject())
list_strMembers = root.getMemberNames();
for(auto str:list_strMembers)
{
if(!root.isMember(str))
continue;
cout<<str<<" : ";
if(!root[str].isNull())
{
if(root[str].isInt())
{
int tempInt = root[str].asInt();
cout<<" is Int,value = "<<tempInt<<endl;
}
if(root[str].isBool())
{
bool tempBool = root[str].asBool();
cout<<"is Bool,value = "<<tempBool<<endl;
}
if(root[str].isString())
{
string tempString = root[str].asString();
cout<<"is String,value = "<<tempString<<endl;
}
if(root[str].isObject())
{
Json::Value tempValue = root[str];
cout<<"is Object,value = "<<tempValue<<endl;
}
if(root[str].isArray())
{
Json::Value tempMember = root[str];
cout<<"is Array,size = "<<tempMember.size()<<endl;
for(int j = 0;j < tempMember.size();j++)
{
Json::Value tempValue = tempMember[j];
cout<<" person "<<j+1<<":"<<endl;
cout<<" id = "<<tempValue["id"];
cout<<" name = "<<tempValue["name"];
}
}
if(root[str].isNumeric() && !root[str].isBool())
{ //布尔值在使用[]获取时返回的即是整型又是数值类型,其中整型是数值类型的一种
double tempDouble = root[str].asDouble();
cout<<"is Double,value = "<<tempDouble<<endl;
}
}
}
}
//解析
return 0;
}
{
"family_id" : 1314,
"single_parent" : false,
"age" : 20,
"money" : 13.140,
"members" :
[
{
"id" : 1,
"name" : "name"
},
{
"id" : 2,
"name" : "name"
},
{
"id" : 3,
"name" : "name"
},
{
"id" : 4,
"name" : "name"
}
]
}
family_id : is Int,value = 1314
single_parent : is Bool,value = 0
age : is Int,value = 20
money : is Double,value = 13.14
members : is Array,size = 4
person 1:
id = 1
name = "name"
person 2:
id = 2
name = "name"
person 3:
id = 3
name = "name"
person 4:
id = 4
name = "name"
在main.cpp中使用了c++11的特性因此编译时要进行指定 -std=c++11
g++ main.cpp -std=c++11 -ljsoncppD -I /data01/bm80/ob_rel/include/3rd -L /data01/bm80/ob_rel/lib -o test
5.对json value的修改,删除
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <json/json.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//构建json对象
Json::Value family;
Json::Value members;
family["family_id"] = 1314;
family["single_parent"] = false;
family["age"] = 20;
family["money"] = 13.14;
for(int i = 0 ;i < 4; ++i)
{
Json::Value member;
member["id"] = i + 1;
member["name"] = "name";
members.append(member);
}
family["members"] = members;
//打印json value
string strJsonBefore = family.toStyledString();
cout<<strJsonBefore<<endl;
family.removeMember("age");
family["money"] = 521;
//Json::Value tempDelete; //新版本中删除json数组中元素的方法
//family["members"].removeIndex(3,tempDelete);
string strJsonAfter = family.toStyledString();
cout<<strJsonAfter<<endl;
return 0;
}
{ "family_id" : 1314, "single_parent" : false, "age" : 20, "money" : 13.140, "members" : [ { "id" : 1, "name" : "name" }, { "id" : 2, "name" : "name" }, { "id" : 3, "name" : "name" }, { "id" : 4, "name" : "name" } ] } { "family_id" : 1314, "single_parent" : false, "money" : 521, "members" : [ { "id" : 1, "name" : "name" }, { "id" : 2, "name" : "name" }, { "id" : 3, "name" : "name" }, { "id" : 4, "name" : "name" } ] }
6.处理不合法的json字符串时
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <json/json.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
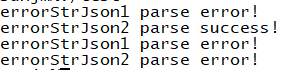
string errorStrJson1 = "{"key1":"value1","}";
string errorStrJson2 = "1111 {}";
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
if(!reader.parse(errorStrJson1,root))
{
cout<<"errorStrJson1 parse error!"<<endl;
}
if(!reader.parse(errorStrJson2,root))
{
cout<<"errorStrJson2 parse error!"<<endl;
}else
{
cout<<"errorStrJson2 parse success!"<<endl;
//root.getMemberNames();会core掉
}
//启用严格模式,让非法的json解析时直接返回false,不自动容错。这样,在调用parse的时候就会返回false。
Json::Reader *pJsonParser = new Json::Reader(Json::Features::strictMode());
if(!pJsonParser->parse(errorStrJson1,root))
{
cout<<"errorStrJson1 parse error!"<<endl;
}
if(!pJsonParser->parse(errorStrJson2,root))
{
cout<<"errorStrJson2 parse error!"<<endl;
}else
{
cout<<"errorStrJson2 parse success!"<<endl;
//root.getMemberNames();会core掉
}
return 0;
}