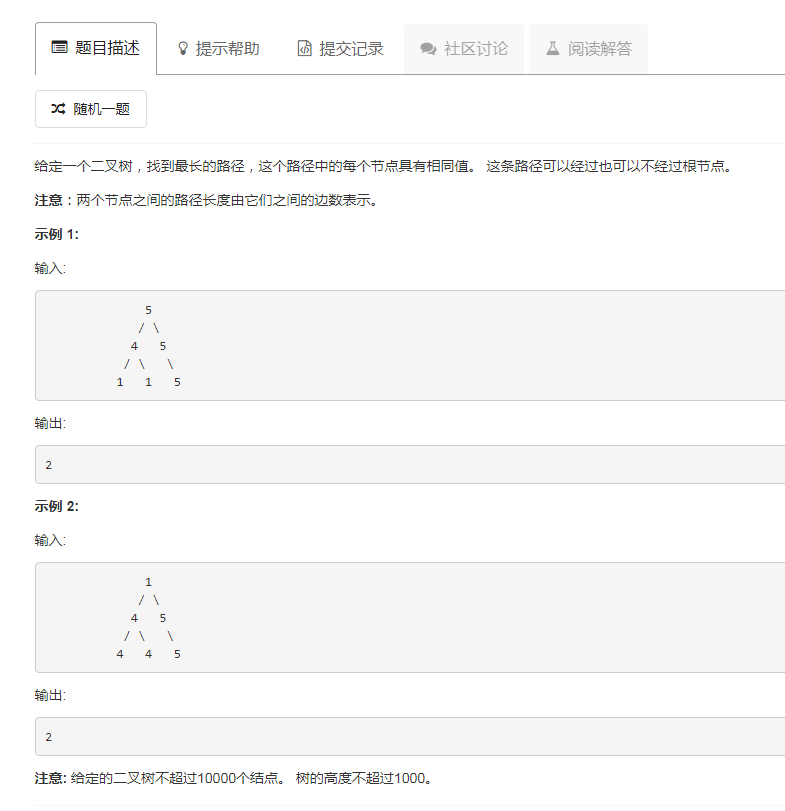
这个路径可能存在从子节点经过父节点,再到子节点的情况,所有从当前节点构成的路径需要考虑左右两条路径相加,用递归,求得左右的最长路径,相加,即为所求
// Study.cpp: 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define INT_MAX 2147483647 // maximum (signed) int value
#define INT_MIN (-2147483647 - 1) // minimum (signed) int value
;
using namespace std;
int Max(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int Min(int a, int b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
int rmax = 0;
int find_depth(TreeNode* p, int value)
{
if (p == nullptr || p->val != value)
return 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
left = find_depth(p->left,value);
right = find_depth(p->right,value);
return 1 + Max(left, right);
}
void solution(TreeNode* p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return;
int current = find_depth(p->left, p->val) + find_depth(p->right, p->val);
if (current > rmax)
rmax = current;
solution(p->left);
solution(p->right);
}
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) {
solution(root);
return rmax;
}
void printTree(TreeNode* p,int depth=0)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++)
cout << " ";
cout << p->val << endl;
printTree(p->left,depth+1);
printTree(p->right, depth+1);
}
int main()
{
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode* p = root->left;
p->left = new TreeNode(2);
p->right = new TreeNode(2);
p->left->left = new TreeNode(2);
//printTree(p);
p = root->right;
p->left = new TreeNode(2);
p->right = new TreeNode(2);
printTree(root);
cout << endl;
cout << longestUnivaluePath(root);
system("pause");
return 0;
}