流的特点
1. 只能遍历一次
我们可以把流想象成一条流水线,流水线的源头是我们的数据源(一个集合),数据源中的元素依次被输送到流水线上,我们可以在流水线上对元素进行各种操作。一旦元素走到了流水线的另一头,那么这些元素就被“消费掉了”,我们无法再对这个流进行操作。当然,我们可以从数据源那里再获得一个新的流重新遍历一遍。
2. 采用内部迭代方式
若要对集合进行处理,则需我们手写处理代码,这就叫做外部迭代。而要对流进行处理,我们只需告诉流我们需要什么结果,处理过程由流自行完成,这就称为内部迭代。
强大的 Stream API
位于包: java.util.stream .*
Stream 是 Java8 中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以指定你希望对集合进行的操作,可以执行非常复杂的查找、过滤和映射数据等操作。使用Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用 SQL 执行的数据库查询。也可以使用 Stream API 来并行执行操作。简而言之,Stream API 提供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式。
什么是 Stream
流 (Stream) 到底是什么呢 ?
是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。“集合讲的是数据,流讲的是计算! ”
注意:
①Stream 自己不会存储元素。
②Stream 不会改变源对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
③Stream 操作是延迟执行的。这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
Stream的操作三步骤
1、创建Stream
一个数据源(如:集合、数组),获取一个流
2、中间操作
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理
3、终止操作(终端操作)
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果
创建Stream
1.可以通过Collection 系列集合提供的stream()或parallelStream()方法
default Stream< E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
default Stream< E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
2.通过 Arrays 中的静态方法stream()获取数组流
static < T> Stream< T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流
重载形式,能够处理对应基本类型的数组:
public static IntStream stream(int[] array)
public static LongStream stream(long[] array)
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array)
3.通过Stream 类中的静态方法of(),通过显示值创建一个流。它可以接收任意数量的参数。
public static< T> Stream< T> of(T… values) : 返回一个流
4.创建无限流
可以使用静态方法 Stream.iterate() 和Stream.generate(), 创建无限流。
迭代
public static< T> Stream< T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator< T> f)
生成
public static< T> Stream< T> generate(Supplier< T> s)
//创建Stream
public void test1(){
//1.可以通过Collection 系列集合提供的stream()或parallelStream()
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream1 = list.stream();
//2.通过 Arrays 中的静态方法stream()获取数组流
Employee[] emps=new Employee[10];
Stream<Employee> stream2=Arrays.stream(emps);
//3.通过Stream 类中的静态方法of()
Stream<String> stream3=Stream.of("aa","bb","cc");
//4.创建无限流
//迭代
Stream<Integer> stream4=Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x+2);
stream4.limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
//生成
Stream.generate(() -> Math.random())
.limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
中间操作
多个中间操作可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理!而在终止操作时一次性处理,成为“惰性求值”。
createStream.java
public class SteamCreate {
public static void main(String[] a){
test1();
}
//创建Stream
private static void test1(){
//1.可以通过Collection 系列集合提供的stream()或parallelStream()
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("how");
list.add("are");
list.add("you");
Stream<String> stream1 = list.stream();
stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
//2.通过 Arrays 中的静态方法stream()获取数组流
Employee[] emps = new Employee[10];
Stream<Employee> stream2 = Arrays.stream(emps);
stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
//3.通过Stream 类中的静态方法of()
Stream<String> stream3 = Stream.of("aa","bb","cc");
stream3.forEach(System.out::println);
//4.创建无限流
//迭代
Stream<Integer> stream4 = Stream.iterate(0, x -> x+2);
stream4.limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
//stream4.limit(10).forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
//生成
Stream.generate(() -> Math.random())
.limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}stream操作streamAction.java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.DoubleSummaryStatistics;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import spark0910.Test1;
import spark0918_stream.Employee.Status;
public class StreamAction1 {
static List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(
new Employee("张三", 18, 9999.99, Status.FREE),
new Employee("李四", 58, 5555.55, Status.BUSY),
new Employee("王五", 26, 3333.33, Status.VOCATION),
new Employee("赵六", 36, 6666.66, Status.FREE),
new Employee("田七", 12, 8888.88, Status.BUSY)
);
public static void main(String[] args){
test4();
}
/*
* 查找与匹配
*/
public static void test1(){
boolean b1=employees.stream()//allMatch-检查是否匹配所有元素
.allMatch((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.BUSY));
System.out.println(b1);//false
boolean b2=employees.stream()//anyMatch-检查是否至少匹配一个元素
.anyMatch((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.BUSY));
System.out.println(b2);//true
boolean b3=employees.stream()//noneMatch-检查是否没有匹配所有元素
.noneMatch((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.BUSY));
System.out.println(b3);//false
Optional<Employee> op=employees.stream()//findFirst-返回第一个元素//Optional是Java8中避免空指针异常的容器类
.sorted((e1,e2)->Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary()))
.findFirst();
// op.forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println(op.get());//Employee [name=王五, age=26, salary=3333.33, Status=VOCATION]
Optional<Employee> op2=employees.parallelStream() //findAny-返回当前流中的任意元素
.filter((e)->e.getStatus().equals(Status.FREE))
.findAny();
System.out.println(op2.get());//Employee [name=赵六, age=36, salary=6666.66, Status=FREE]
Long count=employees.stream()//count-返回流中元素的总个数
.count();
System.out.println(count);//5
Optional<Employee> op3=employees.stream()//max-返回流中最大值
.max((e1,e2)->Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary()));
System.out.println(op3.get());//Employee [name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, Status=FREE]
Optional<Double> op4=employees.stream()//min-返回流中最小值
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.min(Double::compare);
System.out.println(op4.get());//3333.33
}
/*
* 归约
* reduce(T identity,BinaryOperator b) / reduce(BinaryOperator b)-可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。
*/
public static void test3(){
List<Integer> list=Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);
Integer sum=list.stream()//reduce(T identity,BinaryOperator b)
.reduce(0, (x,y)->x+y);//0为起始值
System.out.println(sum);//55
System.out.println("--------------------------");
Optional<Double> op=employees.stream()//reduce(BinaryOperator b)//没有起始值,map返回可能为空,所以返回Optional类型
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.reduce(Double::sum);
// .reduce((x1,x2)->Double.sum(x1, x2));
System.out.println(op.get());// 34444.41
}
/*
* 收集
* collect-将流转换为其他形式,接收一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法。
*/
public static void test4(){
List<String> list=employees.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
list.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------------------");
Set<String> set=employees.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
set.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------------------");
HashSet<String> hs=employees.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
hs.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------------------");
//总和
Long count=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(count);
Long count1=employees.stream()//value值为1
.collect(Collectors.reducing(0L, e -> 1L, Long::sum));
System.out.println(count1);
//平均值
Double avg=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(avg);
//总和
Double sum=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(sum);
//最大值
Optional<Employee> max=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy((e1,e2)->Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary())));
System.out.println(max.get());
//最小值
Optional<Double> min=employees.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.collect(Collectors.minBy(Double::compare));
System.out.println(min.get());
System.out.println("----------------------------");
//分组
Map<Status,List<Employee>> map=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getStatus));
System.out.println(map);//{FREE=[Employee [name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, Status=FREE], Employee [name=赵六, age=36, salary=6666.66, Status=FREE]], VOCATION=[Employee [name=王五, age=26, salary=3333.33, Status=VOCATION]], BUSY=[Employee [name=李四, age=58, salary=5555.55, Status=BUSY], Employee [name=田七, age=12, salary=8888.88, Status=BUSY]]}
//多级分组
Map<Status,Map<String,List<Employee>>> map2=employees.stream()
.collect( Collectors.groupingBy( Employee::getStatus,Collectors.groupingBy((e)->{
if(((Employee) e).getAge() <= 35){
return "青年";
}else if(((Employee) e).getAge() <= 50){
return "中年";
}else{
return "老年";
}
}) ) );
System.out.println(map2);//{FREE={青年=[Employee [name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, Status=FREE]], 中年=[Employee [name=赵六, age=36, salary=6666.66, Status=FREE]]}, VOCATION={青年=[Employee [name=王五, age=26, salary=3333.33, Status=VOCATION]]}, BUSY={青年=[Employee [name=田七, age=12, salary=8888.88, Status=BUSY]], 老年=[Employee [name=李四, age=58, salary=5555.55, Status=BUSY]]}}
//分区
Map<Boolean,List<Employee>> map3=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy((e)->e.getSalary()>8000));
System.out.println(map3);//{false=[Employee [name=李四, age=58, salary=5555.55, Status=BUSY], Employee [name=王五, age=26, salary=3333.33, Status=VOCATION], Employee [name=赵六, age=36, salary=6666.66, Status=FREE]], true=[Employee [name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, Status=FREE], Employee [name=田七, age=12, salary=8888.88, Status=BUSY]]}
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
DoubleSummaryStatistics dss=employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(dss.getSum());
System.out.println(dss.getAverage());
System.out.println(dss.getMax());
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
String strr=employees.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(strr);//张三李四王五赵六田七
}
}
1.筛选与切片
List<Employee> employees=Arrays.asList(
new Employee("张三",18,9999.99),
new Employee("李四",58,5555.55),
new Employee("王五",26,3333.33),
new Employee("赵六",36,6666.66),
new Employee("田七",12,8888.88),
new Employee("田七",12,8888.88)
);
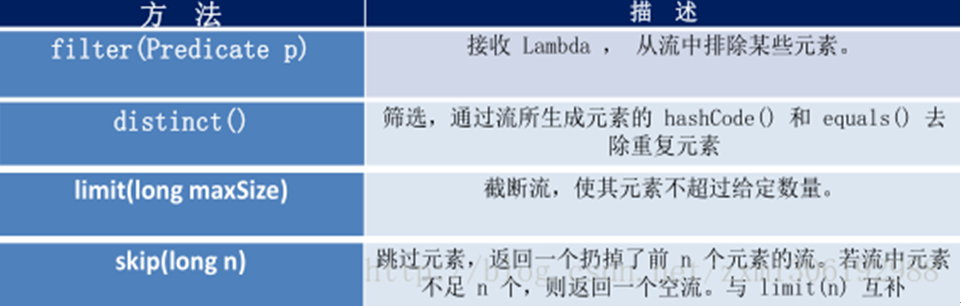
/* 筛选与切片
* filter--接收Lambda,从流中排除某些元素。
* limit--截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量。
* skip(n)--跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前n个元素的流。若流中元素不足n个,则返回一个空流。与limit(n) 互补
* distinct--筛选,通过流所生成元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去掉重复元素
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamConvert1 {
static List<Employee> employees=Arrays.asList(
new Employee("张三", 18, 9999.99),
new Employee("李四", 58, 5555.55),
new Employee("王五", 26, 3333.33),
new Employee("赵六", 36, 6666.66),
new Employee("田七", 12, 8888.88),
new Employee("田七", 12, 8888.88)
);
public static void main(String[] xxx){
test3();
}
/* 筛选与切片
* filter--接收Lambda,从流中排除某些元素。
* limit--截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量。
* skip(n)--跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前n个元素的流。若流中元素不足n个,则返回一个空流。与limit(n) 互补
* distinct--筛选,通过流所生成元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去掉重复元素
*/
//内部迭代:迭代操作由 Stream API 完成
private static void test1(){
//中间操作:不会执行任何操作
Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream().filter((e) -> e.getAge() > 35);
//终止操作:一次性执行全部内容,即 惰性求值
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
// 李四 null 58 5555.55 null
// 赵六 null 36 6666.66 null
}
//外部迭代
private static void test2(){
Iterator<Employee> it = employees.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
private static void test3(){//发现“短路”只输出了两次,说明只要找到 2 个 符合条件的就不再继续迭代
employees.stream()
.filter((e)->{
System.out.println("短路!");
return e.getSalary() > 5000;
})
.limit(2)//3,4
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
private static void test4(){
employees.stream()
.filter((e)->e.getSalary()>5000)
.skip(2)//跳过前两个 6,7
.distinct()//去重,注意:需要Employee重写hashCode 和 equals 方法
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//中间操作
/*
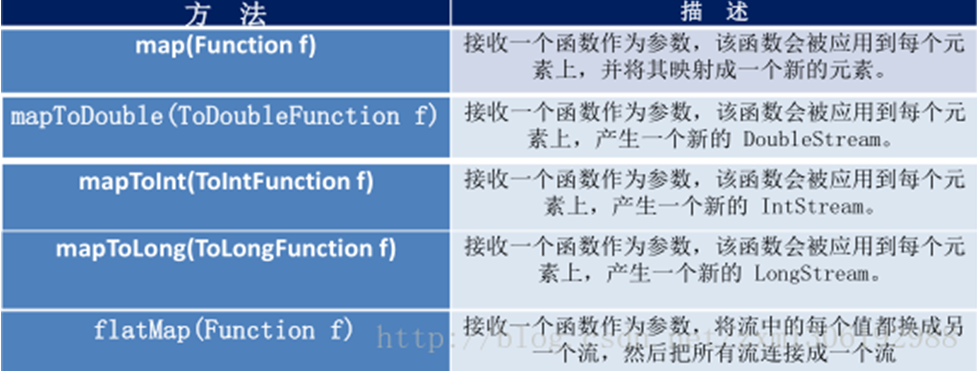
* 映射
* map--接收Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息。接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新元素。
* flatMap--接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流
*/
private static void test5(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
// list.stream()
// //.map((str)->str.toUpperCase())
// .map(String::toUpperCase)
// .forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println("------------------------");
//
// employees.stream()
// //.map(x -> x.getName())
// .map(Employee::getName)
// .forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println("------------------------");
// Stream<Stream<Character>> stream = list.stream().map(StreamConert2::filterChatacter);
// stream.forEach((sm)->{
// sm.forEach(System.out::println);
// //System.out.println();
// });
System.out.println("------------------------");
Stream<Character> sm=list.stream().flatMap(StreamConvert1::filterChatacter);
sm.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private static Stream<Character> filterChatacter(String str){
List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character ch : str.toCharArray()) {
list.add(ch);
}
return list.stream();
}
private static void test6(){//map和flatMap的关系 类似于 add(Object)和addAll(Collection coll)
List<String> list=Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
List list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(11);
list2.add(22);
list2.addAll(list);
System.out.println(list2);
}
//中间操作
/*
* 排序
* sorted()-自然排序(按照对象类实现Comparable接口的compareTo()方法 排序)
* sorted(Comparator com)-定制排序(Comparator)
*/
private static void test7(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("ccc","bbb","aaa");
list.stream()
.sorted((x1, x2) -> x2.compareTo(x1))
//.sorted(String::compareTo)
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------------");
employees.stream()
.sorted((e1,e2)->{
if(e1.getAge() == (e2.getAge())){
return e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName());
}else{
return e1.getAge() - e2.getAge();
}
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
2.映射
//中间操作
/*
* 映射
* map--接收Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息。接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新元素。
* flatMap--接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流
*/
import java.awt.print.Printable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamConert2 {
static List<Employee> employees=Arrays.asList(
new Employee("张三", 18, 9999.99),
new Employee("李四", 58, 5555.55),
new Employee("王五", 26, 3333.33),
new Employee("赵六", 36, 6666.66),
new Employee("田七", 12, 8888.88),
new Employee("田七", 12, 8888.88)
);
public static void main(String[] a){
test7();
}
//中间操作
/*
* 映射
* map--接收Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息。接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新元素。
* flatMap--接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流
*/
private static void test5(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
list.stream()
//.map((str)->str.toUpperCase())
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------------");
employees.stream()
//.map(x -> x.getName())
.map(Employee::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------------");
// Stream<Stream<Character>> stream = list.stream().map(StreamConert2::filterChatacter);
// stream.forEach((sm)->{
// sm.forEach(System.out::println);
// //System.out.println();
// });
//
// System.out.println("------------------------");
//
// Stream<Character> sm=list.stream().flatMap(x->filterChatacter(x));
// sm.forEach(System.out::println);
}
private static Stream<Character> filterChatacter(String str){
List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character ch : str.toCharArray()) {
list.add(ch);
}
return list.stream();
}
private static void test6(){//map和flatMap的关系 类似于 add(Object)和addAll(Collection coll)
List<String> list=Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
List list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(11);
list2.add(22);
list2.addAll(list);
System.out.println(list2);
}
//中间操作
/*
* 排序
* sorted()-自然排序(按照对象类实现Comparable接口的compareTo()方法 排序)
* sorted(Comparator com)-定制排序(Comparator)
*/
private static void test7(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("ccc","bbb","eee","aaa");
list.stream()
.sorted((x1, x2) -> x2.compareTo(x1))
//.sorted(String::compareTo)
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------------");
employees.stream()
.sorted((e1,e2)->{
if(e1.getAge() == (e2.getAge())){
return e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName());
}else{
// System.out.println(e1.getAge() - e2.getAge());
// System.out.println(e1.getName());
return e1.getAge() - e2.getAge();
}
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}