•反射的概念
•反射遍历成员
•用射调用类型成员
•属性概念(Attribute)
•属性的实例
•自定议属性
•三个属性
二次编辑一次运行
一次编译后
反射
反射是编程的读取与类型相关联的元数据的行为。通读取元数据,可以了解它是什么类型以及类型的成员。比如类中的属性,方法,事件等。
所属命名空间System.Reflection
反射-反射成员名称
类
class Demo_Class
{
public Demo_Class(int i)
{
Console.WriteLine("构造函数:" + i);
}
public void Method(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("A类参数为:" + s);
}
public int i;
public string S
{
get; set;
}
}
调用
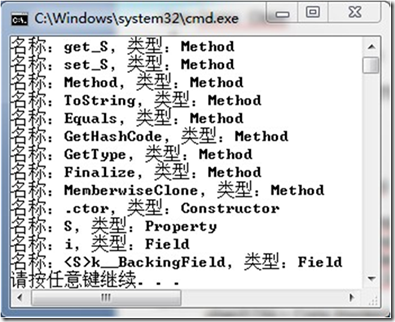
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type type = typeof(Demo_Class);
MemberInfo[] MI = type.GetMembers(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Public |BindingFlags .Instance );
foreach (MemberInfo mi in MI)
{
Console.WriteLine("名称:{0},类型:{1}",mi.Name,mi.MemberType .ToString ());
}
}
运行结果
反射-用反射调用无参构造类型成员
class Demo_Class
{
public void Method(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("A类参数为:" + s);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BindingFlags bf = BindingFlags.DeclaredOnly | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance;
Type t = typeof(Demo_Class);
ConstructorInfo Cons = t.GetConstructor(new Type[0]); //构造函数无参,所以构造函数无类型参数
object Obj = Cons.Invoke(null);//传入的构造参数为空,得到对象
object[] MethodPar = new object[] { “a” }; //方法的参数
MethodInfo mi = t.GetMethod(“Method”, bf);//得到方法
Console.WriteLine(mi.Invoke(Obj, MethodPar));
}
}
反射-用反射调用有参构造类型成员
class Demo_Class
{
public void Method(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("A类参数为:" + s);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BindingFlags bf = BindingFlags.DeclaredOnly | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance;
Type t = typeof(Demo_Class);
ConstructorInfo Cons = t.GetConstructor(new Type[]{typeof(int)}); //构造函数有参,类型为int
object Obj = Cons.Invoke(net object[]{123});//传入的构造参数, 得到对象
object[] MethodPar = new object[] { “a” }; //方法的参数
MethodInfo mi = t.GetMethod(“Method”, bf);//得到方法
Console.WriteLine(mi.Invoke(Obj, MethodPar));
}
}
属性-Attribute
Attribute非property(类的成员)
属性提供功能强大的方法以将声明信息与 C# 代码(类型、方法、属性等)相关联。
属性与程序实体关联后,即可在运行时使用名为“反射”的技术查询属性。
属性以两种形式出现:
1.一种是在公共语言运行库 (CLR) 中定义的属性。
2.另一种是可以创建的用于向代码中添加附加信息的自定义属性。此信息可在以后以编程方式检索。
属性具有以下特点:
1.属性可向程序中添加元数据。元数据是嵌入程序中的信息,如编译器指令或数据描述。
2.程序可以使用反射检查自己的元数据。
3.通常使用属性与 COM 交互。
一个例子:
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImportAttribute("user32.dll", EntryPoint = "MessageBoxW")]
public static extern int MessageBoxW([System.Runtime.InteropServices.InAttribute()] System.IntPtr hWnd, [System.Runtime.InteropServices.InAttribute()] [System.Runtime.InteropServices.MarshalAsAttribute(System.Runtime.InteropServices.UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string lpText, [System.Runtime.InteropServices.InAttribute()] [System.Runtime.InteropServices.MarshalAsAttribute(System.Runtime.InteropServices.UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string lpCaption, uint uType);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console .WriteLine ( MessageBoxW(IntPtr .Zero , "确定吗?", "提示",1));
}
自定义属性
通过定义一个属性类,可以创建您自己的自定义属性。该属性类直接或间接地从System. Attribute 派生,有助于方便快捷地在元数据中标识属性定义。假设您要用编写类或结构的程序员的名字标记类和结构。
[System.AttributeUsage(System.AttributeTargets.Class | System.AttributeTargets.Struct,AllowMultiple=true ,Inherited =true ) ] //Author属性只能用于类和结构,AllowMultiple是否允许多次用属性,Inherited是这个属性是滞延续到子类。
public class Author : System.Attribute
{
private string name;
public double version;
public Author(string name)
{
this.name = name; version = 1.0;
}
}
[Author(“张三”, version =2.0)]//张三是Author的构造函数的参数,version是字段
class SampleClass
{ }
三个特别的属性
1.AttributeUsage属性(上面的例子已经演示)
2.Conditional属性
3.Obsolete属性
三个特别的属性- Conditional
条件方法必须是类或结构声明中的方法,而且必须具有 void 返回类型。
#define TRACE_ON //这行标识代码决定着红色代码的执行与否。
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace R_A_Demo
{
public class Trace
{
[Conditional("TRACE_ON")]
public static void Msg(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
}
public class ProgramClass
{
static void Main()
{
Trace.Msg(“调试信息”);
Console.WriteLine(“代码正体");
}
}
}
另一种用法
#define TRACE_ON
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace R_A_Demo
{
public class Trace
{
#if TRACE_ON
public static void Msg(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
#endif
}
public class ProgramClass
{
static void Main()
{
Trace.Msg("Now in Main...");
Console.WriteLine("Done.");
}
}
}
三个特别的属性- Obsolete
[System.Obsolete("use class B")] //类会被在实例化时警告
class A
{
public void Method() { }
}
class B
{
[System.Obsolete("use NewMethod", false )] //方法调用时提示信息
public void OldMethod() { }
[System.Obsolete("use NewMethod", true)] //不可编译
public void NewMethod() { }
}
一句话总结:
反射:利用一次编译后的结果,反得到类型和类型成员。
属性(Attribute):额外给其他类型添加信息的类型。
0P5@($8SN6554F_thumb.jpg)