calcOpticalFlowFarneback
Computes a dense optical flow using the Gunnar Farneback’s algorithm.
- C++: void calcOpticalFlowFarneback(InputArray prev, InputArray next, InputOutputArray flow, double pyr_scale, int levels, int winsize, int iterations, int poly_n, double poly_sigma, int flags)
- C: void cvCalcOpticalFlowFarneback(const CvArr* prev, const CvArr* next, CvArr* flow, double pyr_scale, int levels, int winsize, int iterations, int poly_n, double poly_sigma, int flags)
- Python: cv2.calcOpticalFlowFarneback(prev, next, flow, pyr_scale, levels, winsize, iterations, poly_n, poly_sigma, flags) → flow
-
Parameters: - prev – first 8-bit single-channel input image.
- next – second input image of the same size and the same type as prev.
- flow – computed flow image that has the same size as prev and type CV_32FC2.
- pyr_scale – parameter, specifying the image scale (<1) to build pyramids for each image; pyr_scale=0.5 means a classical pyramid, where each next layer is twice smaller than the previous one.
- levels – number of pyramid layers including the initial image; levels=1 means that no extra layers are created and only the original images are used.
- winsize – averaging window size; larger values increase the algorithm robustness to image noise and give more chances for fast motion detection, but yield more blurred motion field.
- iterations – number of iterations the algorithm does at each pyramid level.
- poly_n – size of the pixel neighborhood used to find polynomial expansion in each pixel; larger values mean that the image will be approximated with smoother surfaces, yielding more robust algorithm and more blurred motion field, typically poly_n =5 or 7.
- poly_sigma – standard deviation of the Gaussian that is used to smooth derivatives used as a basis for the polynomial expansion; for poly_n=5, you can set poly_sigma=1.1, for poly_n=7, a good value would be poly_sigma=1.5.
- flags –
operation flags that can be a combination of the following:
- OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW uses the input flow as an initial flow approximation.
- OPTFLOW_FARNEBACK_GAUSSIAN uses the Gaussian
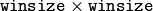 filter instead of a box filter of the same size for optical flow estimation; usually, this option gives z more accurate flow than with a box filter, at the cost of lower speed; normally, winsize for a Gaussian window should be set to a larger value to achieve the same level of robustness.
filter instead of a box filter of the same size for optical flow estimation; usually, this option gives z more accurate flow than with a box filter, at the cost of lower speed; normally, winsize for a Gaussian window should be set to a larger value to achieve the same level of robustness.
The function finds an optical flow for each prev pixel using the [Farneback2003] algorithm so that
![exttt{prev} (y,x) sim exttt{next} ( y + exttt{flow} (y,x)[1], x + exttt{flow} (y,x)[0])](http://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/_images/math/fbf93c97d884d92c45f13996a3698283840829cd.png)
Note
- An example using the optical flow algorithm described by Gunnar Farneback can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/fback.cpp
- (Python) An example using the optical flow algorithm described by Gunnar Farneback can be found at opencv_source_code/samples/python2/opt_flow.py