首先注意一点:mongoose所有的API都支持promise,例如find和findOne等等。接下来结合之前的mongoose操作案例,做个验证
凡是操作数据库,都是异步
之前的mongoose案例
/*1、引包*/ var mongoose = require('mongoose') var Schema = mongoose.Schema/*Schema译为架构、结构*/ /* 2、连接数据库 案例连接本地test数据库 注意:如果数据库不存在则会被创建,直到插入数据后便看见了 */ mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/20200203') /* 3、设计集合结构(通俗理解为设计表结构) 字段名称就是表结构中的属性名 值为属性值的类型 */ var userSchema = new Schema({ userName:{ type:String, required:true/*必须有,不能为空*/ }, password:{ type:String, required:true }, email:{ type:String } }) /*4、将设计的文档架构发布为模型*/ var User = mongoose.model('User',userSchema) /*5、增加*/ var admin = new User({ userName:'admin', password:'admin123456', email:'admin@qq.com' }) /*6、增加完后,需要进行持久化存储*/ // admin.save(function(error,result){ // if(error){ // console.log('存储失败') // }else{ // console.log('存储成功') // } // }) /*查询*/ // User.findOne(function(error,result){ // if(error){ // console.log('查询失败') // }else{ // console.log('查询成功') // console.log(result) // } // }) /*删除数据*/ // User.remove({ // userName:'张三' // },function(error,result){ // if(error){ // console.log('删除失败') // }else{ // console.log('删除成功') // console.log(result) // } // }) /*更新数据*/ User.findByIdAndUpdate('5e382e75331cd51830c10a1d',{ password:'666666' },function(error,result){ if(error){ console.log('更新失败') }else{ console.log(result) console.log('更新成功') } })
之前的方式:

现在将其改为promise方式

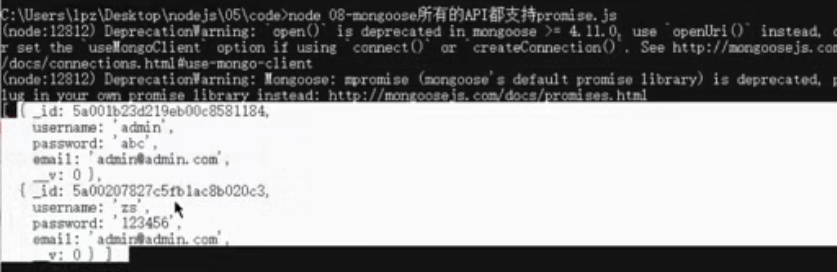
然后开启数据库服务,测试下查询操作,如下所示,可以正常查询获取
(1)场景举例

这里便涉及到异步操作
假设要注册一个已经存在的名字为admin的用户,此时可以正常查到
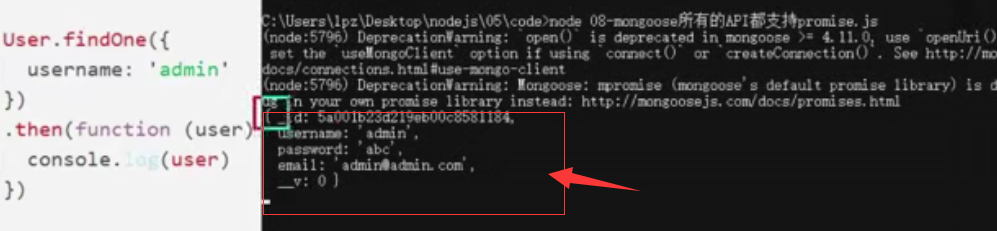
接下来判断用户是否存在,进行状况处理

之后可以查询数据库,可以看到数据已经存储。
只要出现异步回调嵌套,便可以使用promise方式解决
(2)老式嵌套方式

此时如果再有回调便容易成回调地狱

.