博客转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/21207-iHome/p/5235768.html
对于上一篇中的问题:X ∼ N(µ, σ^2 ) , Y = sin(X)要求随机变量Y的期望和方差。还有一种思路是对X进行采样,比如取500个采样点(这些采样点可以称为sigma点),然后求取这些采样点的期望和方差。当采样值足够大时,结果与理论值接近。这种思路的问题显而易见,当随机变量维数增大时采样点的数量会急剧增加,比如一维需要500个采样点,二维就需要500^=250,000个采样点,三维情况下需要500^3=125,000,000个采样点,显然这样会造成严重的计算负担。无迹卡尔曼滤法中采用一种方法来选取2n+1个sigma点,n为随机变量维数。

如上图所示,考虑正态分布曲线的对称性,选取3个sigma点来计算(sigma点的选取方法不唯一),其中一个是均值,另外两个sigma点关于均值对称分布。比如三个点可选为:
χ0 = μ; χ1 = μ + σ; χ2 = μ - σ;
然后选取合适的权值Wi满足如下关系:
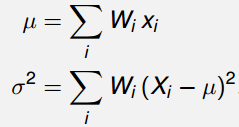
使用同样的公式近似计算Y=sin(X)分布的数字特征:

类比推广到多维随机变量X ∼ N(μ ,Σ),Σ为协方差矩阵,采用Cholesky分解计算出矩阵L(Σ = LLT) ,矩阵L可以类比一维情况下的标准差σ。则sigma点可以写成下面的形式:
χ0 = μ; χi = μ + cL; χn+i = μ - cL; c为一个正的常数
则对于非线性变换Y=g(X),可以计算出变换后的期望和方差:
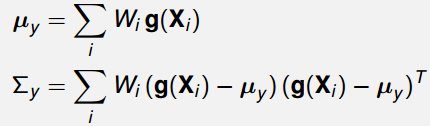
关键问题是如何选取sigma点和权值。常见的一种方法是第一个sigma点选为χ0=μ,n是随机变量X的维数,α,κ,λ均为常数,并有如下关系
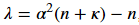
其余2n个sigma点的计算公式如下,其中下标i表示矩阵L的第i列
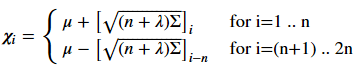
接下来要计算权值。对求期望来说,第一个sigma点的权值为:

对求方差来说,第一个sigma点的权值为如下,式子中的β也为一个常数

对于剩下的2n个sigma点来说求期望的权值和求方差的权值都相同:
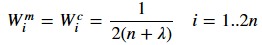
因此,一共有三个常数(α,β,κ)需要我们来设定。根据其它参考资料,选择参数的经验为:β=2 is a good choice for Gaussian problems, κ=3−n is a good choice for κ , and 0≤α≤1 is an appropriate choice for α.
α越大,第一个sigma点(平均值处)占的权重越大,并且其它sigma点越远离均值。如下图所示,对2维随机变量选取5个sigma点,点的大小代表权重,由感性认识可知sigma点离均值越远其权重应该越小。

根据上述计算步骤和公式我们可以编程实现sigma点的选择,权值的计算。在Python中我们可以采用现成的工具FilterPy安装pip工具后可以直接输入命令:pip install filterpy进行安装。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from filterpy.kalman import MerweScaledSigmaPoints as SigmaPoints mean = 0 # 均值 cov = 1 # 方差 points = SigmaPoints(n=1, alpha=0.1, beta=2.0, kappa=1.0) Wm, Wc = points.weights() sigmas = points.sigma_points(mean, cov) print Wm, Wc # 计算均值和方差的权值 print sigmas # sigma点的坐标
对于标准正态分,输出结果如下:

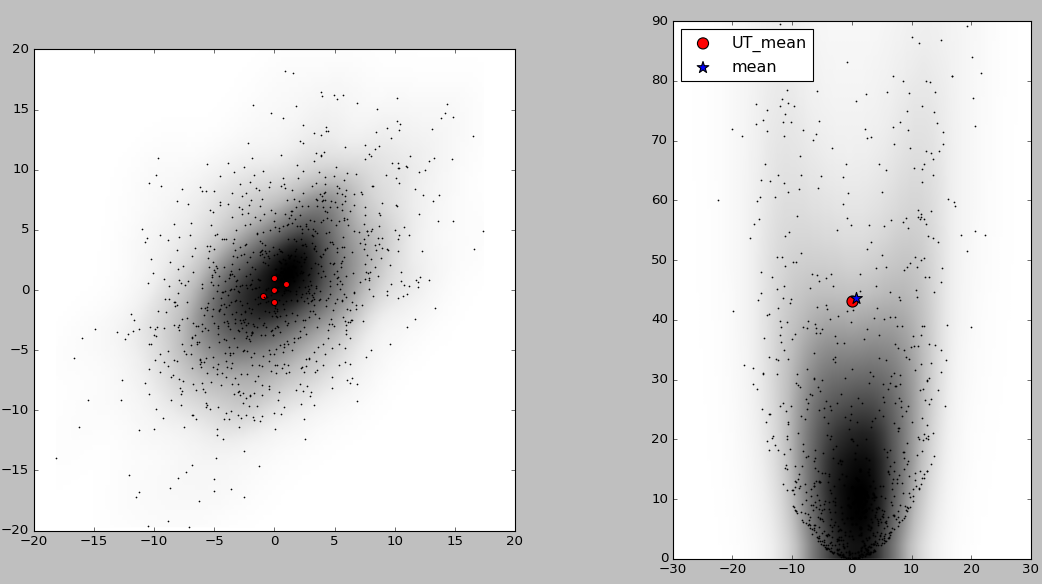
下面举一个2维正态分布的例子。从一个服从二维正态分布的随机变量中随机选取1000个点,该二维随机变量的期望和协方差矩阵为:
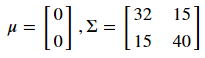
接下来将这1000个点进行如下非线性变换:
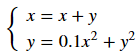
下面使用unscented transform方法近似计算非线性变换后随机变量的期望,并与直接从1000个点计算出的期望值对比
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from scipy import stats
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy.random import multivariate_normal
from filterpy.kalman import unscented_transform
from filterpy.kalman import MerweScaledSigmaPoints as SigmaPoints
# 非线性变换函数
def f_nonlinear_xy(x, y):
return np.array([x + y, 0.1*x**2 + y**2])
def plot1(xs, ys):
xs = np.asarray(xs)
ys = np.asarray(ys)
xmin = xs.min()
xmax = xs.max()
ymin = ys.min()
ymax = ys.max()
values = np.vstack([xs, ys])
kernel = stats.gaussian_kde(values)
X, Y = np.mgrid[xmin:xmax:100j, ymin:ymax:100j]
positions = np.vstack([X.ravel(), Y.ravel()])
Z = np.reshape(kernel.evaluate(positions).T, X.shape)
plt.imshow(np.rot90(Z),cmap=plt.cm.Greys,extent=[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax])
plt.plot(xs, ys, 'k.', markersize=2)
plt.xlim(-20, 20)
plt.ylim(-20, 20)
def plot2(xs, ys, f, mean_fx):
fxs, fys = f(xs, ys) # 将采样点进行非线性变换
computed_mean_x = np.average(fxs)
computed_mean_y = np.average(fys)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.grid(False)
plot1(xs, ys)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.grid(False)
plot1(fxs, fys)
plt.scatter(fxs, fys, marker='.', alpha=0.01, color='k')
plt.scatter(mean_fx[0], mean_fx[1], marker='o', s=100, c='r', label='UT_mean')
plt.scatter(computed_mean_x, computed_mean_y, marker='*',s=120, c='b', label='mean')
plt.ylim([-10, 200])
plt.xlim([-100, 100])
plt.legend(loc='best', scatterpoints=1)
print ('Difference in mean x={:.3f}, y={:.3f}'.format(
computed_mean_x-mean_fx[0], computed_mean_y-mean_fx[1]))
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
mean = [0, 0] # Mean of the N-dimensional distribution.
cov = [[32, 15], [15, 40]] # Covariance matrix of the distribution.
# create sigma points(2n+1个sigma点)
# uses 3 parameters to control how the sigma points are distributed and weighted
points = SigmaPoints(n=2, alpha=.1, beta=2., kappa=1.)
Wm, Wc = points.weights()
sigmas = points.sigma_points(mean, cov)
# pass through nonlinear function
sigmas_f = np.empty((5, 2))
for i in range(5):
sigmas_f[i] = f_nonlinear_xy(sigmas[i, 0], sigmas[i ,1])
# use unscented transform to get new mean and covariance
ukf_mean, ukf_cov = unscented_transform(sigmas_f, Wm, Wc)
# generate random points
xs, ys = multivariate_normal(mean, cov, size=1000).T # 从二维随机变量的正态分布中产生1000个数据点
plot2(xs, ys, f_nonlinear_xy, ukf_mean)
# 画sigma点
plt.xlim(-30, 30); plt.ylim(0, 90)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.scatter(sigmas[:,0], sigmas[:,1], c='r', s=30)
plt.show()
结果如下图所示,左图中黑点为1000个采样点,5个红色的点为sigma点,图中阴影表示概率密度的大小,颜色越深的地方概率密度越大。右图中的红点为用5个sigma点经UT变换计算出的近似期望,蓝色星号标记点为将1000个采样点非线性变换后直接计算出的期望。可以看出和直接产生1000个点经非线性变换计算期望相比,使用unscented transform的计算量要小的多,并且误差也不大。