Linux 下安装GTest
安装GTest
1、安装源代码
下载gtest,release-1.8.0
git clone https://github.com/google/googletest
gtest编译
cd googletest
生成Makefile文件(先安装cmake,brew install cmake),继续输入命令编译:
cmake CMakeLists.txt
执行make,生成两个静态库:libgtest.a libgtest_main.a
make
拷贝到系统目录,注意,如果下诉目录位置在不同版本位置有变动,用find . -name "libgtest*.a" 找到位置
sudo cp libgtest*.a /usr/lib
sudo cp –a include/gtest /usr/include
检查是否安装成功
可以写一个简单的测试代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#include<gtest/gtest.h>int add(int a,int b){ return a+b;}TEST(testCase,test0){ EXPECT_EQ(add(2,3),5);}int main(int argc,char **argv){ testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc,argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS();} |
在该文件的终端输入编译指令:
gqx@gqx-Lenovo-Product:~/workplace/aaaa$ g++ test.cc -lgtest -lpthread
gqx@gqx-Lenovo-Product:~/workplace/aaaa$ ./a.out
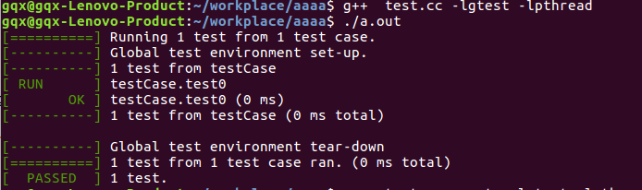
即得到如下显示结果:
GTest的一些基本概念
要测试一个类或函数,我们需要对其行为做出断言。当一个断言失败时,Google Test会在屏幕上输出该代码所在的源文件及其所在的位置行号,以及错误信息。也可以在编写断言时,提供一个自定义的错误信息,这个信息在失败时会被附加在Google Test的错误信息之后。
断言常常成对出现,它们都测试同一个类或者函数,但对当前功能有着不同的效果。ASSERT_*版本的断言失败时会产生致命失败,并结束当前函数。EXPECT_*版本的断言产生非致命失败,而不会中止当前函数。通常更推荐使用EXPECT_*断言,因为它们运行一个测试中可以有不止一个的错误被报告出来。但如果在编写断言如果失败,就没有必要继续往下执行的测试时,你应该使用ASSERT_*断言。 因为失败的ASSERT_*断言会立刻从当前的函数返回,可能会跳过其后的一些的清洁代码,这样也许会导致空间泄漏。
GTest的断言
1、布尔值检查
|
Fatal assertion |
Nonfatal assertion |
Verifies |
|
ASSERT_TRUE(condition); |
EXPECT_TRUE(condition); |
condition is true |
|
ASSERT_FALSE(condition); |
EXPECT_FALSE(condition); |
condition is false |
2、数值型数据检查
|
Fatal assertion |
Nonfatal assertion |
Verifies |
|
ASSERT_EQ(expected, actual); |
EXPECT_EQ(expected, actual); |
expected == actual |
|
ASSERT_NE(val1, val2); |
EXPECT_NE(val1, val2); |
val1 != val2 |
|
ASSERT_LT(val1, val2); |
EXPECT_LT(val1, val2); |
val1 < val2 |
|
ASSERT_LE(val1, val2); |
EXPECT_LE(val1, val2); |
val1 <= val2 |
|
ASSERT_GT(val1, val2); |
EXPECT_GT(val1, val2); |
val1 > val2 |
|
ASSERT_GE(val1, val2); |
EXPECT_GE(val1, val2); |
val1 >= val2 |
3、字符串比较
|
Fatal assertion |
Nonfatal assertion |
Verifies |
|
ASSERT_STREQ(expected_str, actual_str); |
EXPECT_STREQ(expected_str, actual_str); |
两个C字符串有相同的内容 |
|
ASSERT_STRNE(str1, str2); |
EXPECT_STRNE(str1, str2); |
两个C字符串有不同的内容 |
|
ASSERT_STRCASEEQ(expected_str, actual_str); |
EXPECT_STRCASEEQ(expected_str, actual_str); |
两个C字符串有相同的内容,忽略大小写 |
|
ASSERT_STRCASENE(str1, str2); |
EXPECT_STRCASENE(str1, str2); |
两个C字符串有不同的内容,忽略大小写 |
4、异常检查
|
Fatal assertion |
Nonfatal assertion |
Verifies |
|
ASSERT_THROW(statement, exception_type); |
EXPECT_THROW(statement, exception_type); |
statement throws an exception of the given type |
|
ASSERT_ANY_THROW(statement); |
EXPECT_ANY_THROW(statement); |
statement throws an exception of any type |
|
ASSERT_NO_THROW(statement); |
EXPECT_NO_THROW(statement); |
statement doesn't throw any exception |
5、浮点型检查
|
Fatal assertion |
Nonfatal assertion |
Verifies |
|
ASSERT_FLOAT_EQ(expected, actual); |
EXPECT_FLOAT_EQ(expected, actual); |
the two float values are almost equal |
|
ASSERT_DOUBLE_EQ(expected, actual); |
EXPECT_DOUBLE_EQ(expected, actual); |
the two double values are almost equal |
对相近的两个数比较:
|
Fatal assertion |
Nonfatal assertion |
Verifies |
|
ASSERT_NEAR(val1, val2, abs_error); |
EXPECT_NEAR(val1, val2, abs_error); |
the difference between val1and val2 doesn't exceed the given absolute error |
6、此外还有类型检查、谓词检查等
事件机制
全局事件
要实现全局事件,必须写一个类,继承testing::Environment类,实现里面的SetUp和TearDown方法。
1. SetUp()方法在所有案例执行前执行
2. TearDown()方法在所有案例执行后执行
还需要告诉gtest添加这个全局事件,我们需要在main函数中通过testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment方法将事件挂进来,也就是说,我们可以写很多个这样的类,然后将他们的事件都挂上去。
TestSuite事件
我们需要写一个类,继承testing::Test,然后实现两个静态方法
1. SetUpTestCase() 方法在第一个TestCase之前执行
2. TearDownTestCase() 方法在最后一个TestCase之后执行
在编写测试案例时,我们需要使用TEST_F这个宏,第一个参数必须是我们上面类的名字,代表一个TestSuite。
TestCase事件
TestCase事件是挂在每个案例执行前后的,实现方式和上面的几乎一样,不过需要实现的是SetUp方法和TearDown方法:
1. SetUp()方法在每个TestCase之前执行
2. TearDown()方法在每个TestCase之后执行
以下案例解决说明上述三个事件的使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
#include<gtest/gtest.h>#include<map>#include<iostream>using namespace std;class Student{public: Student(){ age=0; } Student(int a){ age=a; } void print(){ cout<<"*********** "<<age<<" **********"<<endl;; } private: int age;};class FooEnvironment : public testing::Environment{public: virtual void SetUp() { std::cout << "Foo FooEnvironment SetUP" << std::endl; } virtual void TearDown() { std::cout << "Foo FooEnvironment TearDown" << std::endl; }};static Student *s;//在第一个test之前,最后一个test之后调用SetUpTestCase()和TearDownTestCase()class TestMap:public testing::Test{public: static void SetUpTestCase() { cout<<"SetUpTestCase()"<<endl; s=new Student(23); } static void TearDownTestCase() { delete s; cout<<"TearDownTestCase()"<<endl; } void SetUp() { cout<<"SetUp() is running"<<endl; } void TearDown() { cout<<"TearDown()"<<endl; } };TEST_F(TestMap, Test1) { // you can refer to s here s->print();}int main(int argc, char** argv){ testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(new FooEnvironment); testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS();} |
相关结果和说明如下:

参数化
当考虑多次要为被测函数传入不同的值的情况时,可以按下面的方式去测试。必须添加一个类,继承testing::TestWithParam<T>。其中T就是你需要参数化的参数类型,如下面的案例是int型参数。(官方文档上的案例)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#include<gtest/gtest.h>// Returns true iff n is a prime number.bool IsPrime(int n){ // Trivial case 1: small numbers if (n <= 1) return false; // Trivial case 2: even numbers if (n % 2 == 0) return n == 2; // Now, we have that n is odd and n >= 3. // Try to divide n by every odd number i, starting from 3 for (int i = 3; ; i += 2) { // We only have to try i up to the squre root of n if (i > n/i) break; // Now, we have i <= n/i < n. // If n is divisible by i, n is not prime. if (n % i == 0) return false; } // n has no integer factor in the range (1, n), and thus is prime. return true;}class IsPrimeParamTest : public::testing::TestWithParam<int>{};TEST_P(IsPrimeParamTest, HandleTrueReturn){ int n = GetParam(); EXPECT_TRUE(IsPrime(n));}//被测函数须传入多个相关的值INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P(TrueReturn, IsPrimeParamTest, testing::Values(3, 5, 11, 23, 17));int main(int argc, char **argv){ testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS();} |
注:部分内容摘自网络(http://www.cnblogs.com/coderzh/archive/2009/04/06/1426755.html)