- tf
- tf.constant
- Variable
- reduce_sum()
- reduce_mean()
- tf.ones_like
- tf.multiply()
- tf.gradients
- tf.reshape
- path
- Setting the data type
- loss function
- Linear regression
- Batch training
- Dense layers
- Activation functions
- Multiclass classification problems
- Optimizers
- 随机初始化权重矩阵和bias
- 创建函数定义模型和损失函数
- Defining neural networks with Keras
- Defining a multiple input model
- Training and validation with Keras
- validation
- Overfitting detection
- Evaluate
- Training models with the Estimators API
- 完成证书
tf
tf.constant
创建一个常量
tf.constant(value,dtype=None,shape=None,name=’Const’)
创建一个常量tensor,按照给出value来赋值,可以用shape来指定其形状。value可以是一个数,也可以是一个list。
如果是一个数,那么这个常量中所有值的按该数来赋值。
如果是list,那么len(value)一定要小于等于shape展开后的长度。赋值时,先将value中的值逐个存入。不够的部分,则全部存入value的最后一个值。
Variable
创建变量
reduce_sum()
压缩求和,用于降维(可以指定按照行或者列)

按列求和
reduce_sum(wealth,1).numpy()
Out[4]: array([61, 9, 64, 3, 35], dtype=int32)
reduce_mean()
求平均
reduce_max()
求最大值
tf.ones_like
tf.ones_like(tensor,dype=None,name=None)
tf.zeros_like(tensor,dype=None,name=None)
新建一个与给定的tensor类型大小一致的tensor,其所有元素为1和0
tf.multiply()
算两个tensor的乘积,对应位置相乘
两个矩阵中对应元素各自相乘
格式: tf.multiply(x, y, name=None)
参数:
x: 一个类型为:half, float32, float64, uint8, int8, uint16, int16, int32, int64, complex64, complex128的张量。
y: 一个类型跟张量x相同的张量。
返回值: x * y element-wise.
注意:
(1)multiply这个函数实现的是元素级别的相乘,也就是两个相乘的数元素各自相乘,而不是矩阵乘法,注意和tf.matmul区别。
(2)两个相乘的数必须有相同的数据类型,不然就会报错。
2.tf.matmul()将矩阵a乘以矩阵b,生成a * b。
格式: tf.matmul(a, b, transpose_a=False, transpose_b=False, adjoint_a=False, adjoint_b=False, a_is_sparse=False, b_is_sparse=False, name=None)
参数:
a: 一个类型为 float16, float32, float64, int32, complex64, complex128 且张量秩 > 1 的张量。
b: 一个类型跟张量a相同的张量。
transpose_a: 如果为真, a则在进行乘法计算前进行转置。
transpose_b: 如果为真, b则在进行乘法计算前进行转置。
adjoint_a: 如果为真, a则在进行乘法计算前进行共轭和转置。
adjoint_b: 如果为真, b则在进行乘法计算前进行共轭和转置。
a_is_sparse: 如果为真, a会被处理为稀疏矩阵。
b_is_sparse: 如果为真, b会被处理为稀疏矩阵。
name: 操作的名字(可选参数)
返回值: 一个跟张量a和张量b类型一样的张量且最内部矩阵是a和b中的相应矩阵的乘积。
注意:
(1)输入必须是矩阵(或者是张量秩 >2的张量,表示成批的矩阵),并且其在转置之后有相匹配的矩阵尺寸。
(2)两个矩阵必须都是同样的类型,支持的类型如下:float16, float32, float64, int32, complex64, complex128。
引发错误:
ValueError: 如果transpose_a 和 adjoint_a, 或 transpose_b 和 adjoint_b 都被设置为真
In [1]: features = constant([[2, 24], [2, 26], [2, 57], [1, 37]])
... params = constant([[1000], [150]])
In [2]: billpred = matmul(features, params)
In [3]: billpred
Out[3]:
<tf.Tensor: shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[ 5600],
[ 5900],
[10550],
[ 6550]], dtype=int32)>
注意这个矩阵的形式:
features = constant([[2, 24], [2, 26], [2, 57], [1, 37]])
表现出来应该是这个,别把矩阵的形式搞混。
2 24
2 26
2 57
1 37
tf.gradients
用来进行梯度求解

def compute_gradient(x0):
# Define x as a variable with an initial value of x0
x = Variable(x0)
with GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(x)
# Define y using the multiply operation
y = multiply(x, x)
# Return the gradient of y with respect to x
return tape.gradient(y, x).numpy()
# Compute and print gradients at x = -1, 1, and 0
print(compute_gradient(-1.0))
print(compute_gradient(1.0))
print(compute_gradient(0.0))
<script.py> output:
-2.0
2.0
0.0
tf.reshape
重新指定张量的维度
# Reshape the grayscale image tensor into a vector
gray_vector = reshape(gray_tensor, (784, 1))
# Reshape model from a 1x3 to a 3x1 tensor
model = reshape(model, (3, 1))
# Multiply letter by model
output = matmul(letter, model)
# Sum over output and print prediction using the numpy method,这里的输出为啥要降维还没太懂
prediction = reduce_sum(output)
# 这里要记得把输出变成一个numpy数组,不然输出会报错
print(prediction.numpy())
path
路径单独写出来可以批量导入,或者导出,这是一个既定的规则
# Import pandas under the alias pd
import pandas as pd
# Assign the path to a string variable named data_path
data_path = 'kc_house_data.csv'
# Load the dataset as a dataframe named housing
housing = pd.read_csv(data_path)
# Print the price column of housing
print(housing['price'])
Setting the data type
tf.cast()
函数的作用是执行 tensorflow 中张量数据类型转换
tf.array()
# Import numpy and tensorflow with their standard aliases
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
# Use a numpy array to define price as a 32-bit float
price = np.array(housing['price'], np.float)
# Define waterfront as a Boolean using cast
waterfront = tf.cast(housing['waterfront'], tf.bool)
# Print price and waterfront
print(price)
print(waterfront)
<script.py> output:
[221900. 538000. 180000. ... 402101. 400000. 325000.]
tf.Tensor([False False False ... False False False], shape=(21613,), dtype=bool)
loss function
mse
均值误差
mae
平均绝对值误差
# Import the keras module from tensorflow
from tensorflow import keras
# Compute the mean absolute error (mae)
loss = keras.losses.mse(price, predictions)
loss = keras.losses.mae(price, predictions)
# Print the mean absolute error (mae)
print(loss.numpy())
<script.py> output:
141171604777.12717
<script.py> output:
268827.99302087986
# Initialize a variable named scalar
scalar = Variable(1.0, float32)
# Define the model
def model(scalar, features = features):
return scalar * features
# Define a loss function
def loss_function(scalar, features = features, targets = targets):
# Compute the predicted values
predictions = model(scalar, features)
# Return the mean absolute error loss
return keras.losses.mae(targets, predictions)
# Evaluate the loss function and print the loss
print(loss_function(scalar).numpy())
huber
Linear regression
线性回归
# Define a linear regression model
def linear_regression(intercept, slope, features = size_log):
return intercept + features*slope
# Set loss_function() to take the variables as arguments
def loss_function(intercept, slope, features = size_log, targets = price_log):
# Set the predicted values
predictions = linear_regression(intercept, slope, features)
# Return the mean squared error loss
return keras.losses.mse(targets, predictions)
# Compute the loss for different slope and intercept values
print(loss_function(0.1, 0.1).numpy())
print(loss_function(0.1, 0.5).numpy())
## 优化器优化,这个是梯度下降优化嘛,我还不太明白
# Initialize an adam optimizer
opt = keras.optimizers.Adam(0.5)
for j in range(100):
# Apply minimize, pass the loss function, and supply the variables
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(intercept, slope), var_list=[intercept, slope])
# Print every 10th value of the loss
if j % 10 == 0:
print(loss_function(intercept, slope).numpy())
# Plot data and regression line
plot_results(intercept, slope)
Multiple linear regression
其实目前很清晰,就是把数学公式复现,
# Define the linear regression model
def linear_regression(params, feature1 = size_log, feature2 = bedrooms):
return params[0] + feature1*params[1] + feature2*params[2]
# Define the loss function
def loss_function(params, targets = price_log, feature1 = size_log, feature2 = bedrooms):
# Set the predicted values
predictions = linear_regression(params, feature1, feature2)
# Use the mean absolute error loss
return keras.losses.mae(targets, predictions)
# Define the optimize operation
opt = keras.optimizers.Adam()
# Perform minimization and print trainable variables
for j in range(10):
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(params), var_list=[params])
print_results(params)
Batch training
(1)iteration:表示1次迭代(也叫training step),每次迭代更新1次网络结构的参数;
(2)batch-size:1次迭代所使用的样本量;
(3)epoch:1个epoch表示过了1遍训练集中的所有样本。诸葛村姑
chunksize
read_csv中有个参数chunksize,通过指定一个chunksize分块大小来读取文件,返回的是一个可迭代的对象TextFileReader
分块读取大文件,这里分成100块
# Initialize adam optimizer
opt = keras.optimizers.Adam()
# Load data in batches
for batch in pd.read_csv('kc_house_data.csv', chunksize=100):
size_batch = np.array(batch['sqft_lot'], np.float32)
# Extract the price values for the current batch
price_batch = np.array(batch['price'], np.float32)
# Complete the loss, fill in the variable list, and minimize
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(intercept, slope, price_batch, size_batch), var_list=[intercept, slope])
# Print trained parameters
print(intercept.numpy(), slope.numpy())
Dense layers
yi'zhi

一直没太搞明白dense层到底是哪个层。。
这个图的话给了很好的解释,就是hiden layer
这样简单定义一个网络结构就比较清晰了
# From previous step
bias1 = Variable(1.0)
weights1 = Variable(ones((3, 2)))
product1 = matmul(borrower_features, weights1)
dense1 = keras.activations.sigmoid(product1 + bias1)
# Initialize bias2 and weights2
bias2 = Variable(1.0)
weights2 = Variable(ones((2, 1)))
# Perform matrix multiplication of dense1 and weights2
product2 = matmul(dense1 ,weights2)
# Apply activation to product2 + bias2 and print the prediction
prediction = keras.activations.sigmoid(product2 + bias2)
print('
prediction: {}'.format(prediction.numpy()[0,0]))
print('
actual: 1')
神经网络是一个看上去很阔怕,但是很底层原理很简答的东西,就是很多线性运算和矩阵相乘
比如这个栗子
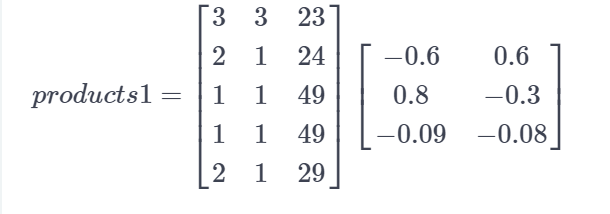
# Compute the product of borrower_features and weights1
products1 = matmul(borrower_features, weights1)
# Apply a sigmoid activation function to products1 + bias1
dense1 = keras.activations.sigmoid(products1 + bias1)
# Print the shapes of borrower_features, weights1, bias1, and dense1
print('
shape of borrower_features: ', borrower_features.shape)
print('
shape of weights1: ', weights1.shape)
print('
shape of bias1: ', bias1.shape)
print('
shape of dense1: ', dense1.shape)
<script.py> output:
shape of borrower_features: (5, 3)
shape of weights1: (3, 2)
shape of bias1: (1,)
shape of dense1: (5, 2)
自定义dense层
keras.layers.Dense(units,
activation=None,
use_bias=True,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
bias_initializer='zeros',
kernel_regularizer=None,
bias_regularizer=None,
activity_regularizer=None,
kernel_constraint=None,
bias_constraint=None)
# 参数说明
units:
该层有几个神经元
activation:
该层使用的激活函数
use_bias:
是否添加偏置项
kernel_initializer:
权重初始化方法
bias_initializer:
偏置值初始化方法
kernel_regularizer:
权重规范化函数
bias_regularizer:
偏置值规范化方法
activity_regularizer:
输出的规范化方法
kernel_constraint:
权重变化限制函数
bias_constraint:
偏置值变化限制函数
这个栗子里面的话就是有2个hiden layer
# Define the first dense layer
dense1 = keras.layers.Dense(7, activation='sigmoid')(borrower_features)
# Define a dense layer with 3 output nodes
dense2 = keras.layers.Dense(3, activation='sigmoid')(dense1)
# Define a dense layer with 1 output node
predictions = keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(dense2)
# Print the shapes of dense1, dense2, and predictions
print('
shape of dense1: ', dense1.shape)
print('
shape of dense2: ', dense2.shape)
print('
shape of predictions: ', predictions.shape)
<script.py> output:
shape of dense1: (100, 7)
shape of dense2: (100, 3)
shape of predictions: (100, 1)
Activation functions
Define inputs as a 32-bit floating point constant tensor using bill_amounts.
Set dense1 to be a dense layer with 3 output nodes and a relu activation function.
Set dense2 to be a dense layer with 2 output nodes and a relu activation function.
Set the output layer to be a dense layer with a single output node and a sigmoid activation function.
# 目前觉得这样的写法很清晰,似乎可以得到每一层想要的东西,比keras的另一种写法要好很多
# Construct input layer from features
inputs = constant(bill_amounts, float32)
# dense层的第一个参数指定输出结点数
# Define first dense layer
dense1 = keras.layers.Dense(3, activation='relu')(inputs)
# Define second dense layer
dense2 = keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='relu')(dense1)
# Define output layer
outputs = keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(dense2)
# Print error for first five examples
error = default[:5] - outputs.numpy()[:5]
print(error)
<script.py> output:
[[ 1. ]
[ 1. ]
[ 0. ]
[ 0. ]
[-0.5]]
Multiclass classification problems
多分类问题
其实就是output层的units变成>1的数
# Construct input layer from borrower features
inputs = constant(borrower_features, float32)
# Define first dense layer
dense1 = keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='sigmoid')(inputs)
# Define second dense layer
dense2 = keras.layers.Dense(8, activation='relu')(dense1)
# Define output layer
outputs = keras.layers.Dense(6, activation='softmax')(dense2)
# Print first five predictions
print(outputs.numpy()[:5])
<script.py> output:
[[0.11626432 0.1127151 0.25804487 0.24624525 0.15216675 0.11456368]
[0.22433662 0.0683961 0.28301975 0.260067 0.07099433 0.09318623]
[0.17588586 0.12475339 0.13749284 0.2883481 0.11527162 0.15824823]
[0.09378582 0.14427742 0.20788462 0.21056697 0.2047638 0.13872144]
[0.14584291 0.11100206 0.27645484 0.21310686 0.13811046 0.1154829 ]]
Optimizers
优化器
一般会把model定义为一个函数
把loss function定义为一个函数
# Initialize x_1 and x_2
x_1 = Variable(6.0,float32)
x_2 = Variable(0.3,float32)
# Define the optimization operation
opt = keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
for j in range(100):
# Perform minimization using the loss function and x_1
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(x_1), var_list=[x_1])
# Perform minimization using the loss function and x_2
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(x_2), var_list=[x_2])
# Print x_1 and x_2 as numpy arrays
print(x_1.numpy(), x_2.numpy())
换个损失函数
# Initialize x_1 and x_2
x_1 = Variable(0.05,float32)
x_2 = Variable(0.05,float32)
# Define the optimization operation for opt_1 and opt_2
opt_1 = keras.optimizers.RMSprop(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.99)
opt_2 = keras.optimizers.RMSprop(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.00)
## 这里就是迭代100次的损失函数
for j in range(100):
opt_1.minimize(lambda: loss_function(x_1), var_list=[x_1])
# Define the minimization operation for opt_2
opt_2.minimize(lambda: loss_function(x_2), var_list=[x_2])
# Print x_1 and x_2 as numpy arrays
print(x_1.numpy(), x_2.numpy())
随机初始化权重矩阵和bias
# Define the layer 1 weights
w1 = Variable(random.normal([23, 7]))
# Initialize the layer 1 bias
b1 = Variable(ones([7]))
# Define the layer 2 weights
w2 = Variable(random.normal([7, 1]))
# Define the layer 2 bias
b2 = Variable(0.0)
创建函数定义模型和损失函数
# Define the model
def model(w1, b1, w2, b2, features = borrower_features):
# Apply relu activation functions to layer 1
layer1 = keras.activations.relu(matmul(features, w1) + b1)
# Apply dropout
dropout = keras.layers.Dropout(0.25)(layer1)
return keras.activations.sigmoid(matmul(dropout, w2) + b2)
# Define the loss function
def loss_function(w1, b1, w2, b2, features = borrower_features, targets = default):
predictions = model(w1, b1, w2, b2)
# Pass targets and predictions to the cross entropy loss
return keras.losses.binary_crossentropy(targets, predictions)
梯度下降进行优化
# Train the model
# 迭代100次
for j in range(100):
# Complete the optimizer
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(w1, b1, w2, b2),
var_list=[w1, b1, w2, b2])
# Make predictions with model
model_predictions = model(w1, b1, w2, b2,test_features)
# Construct the confusion matrix,看来混淆矩阵可以输出
confusion_matrix(test_targets, model_predictions)
Defining neural networks with Keras
其实就是序列化的输入方式
sequence
其实这里想想真的很方便,定义
输入层input
隐藏层hiden layer (可以以一层,可以多层,按照顺序拼接就好)
输出层output
然后按照顺序拼接起来
使用keras是有两种方式的,一种是直接定义好一个sequential,然后一直add层就好了
# Define a Keras sequential model
model = keras.Sequential()
# Define the first dense layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
# Define the second dense layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(8, activation='relu'))
# Define the output layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax'))
# Print the model architecture
print(model.summary())
<script.py> output:
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 16) 12560
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 8) 136
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 4) 36
=================================================================
Total params: 12,732
Trainable params: 12,732
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
None
定义好一个sequence之后编译complie
compile
# Define the first dense layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='sigmoid', input_shape=(784,)))
# Apply dropout to the first layer's output
model.add(keras.layers.Dropout(0.25))
# Define the output layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax'))
# Compile the model
model.compile('adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy')
# Print a model summary
print(model.summary())
<script.py> output:
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 16) 12560
_________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 16) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 4) 68
=================================================================
Total params: 12,628
Trainable params: 12,628
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
None
Defining a multiple input model
定义一个多输入的网络模型
多输入和多输出
# For model 1, pass the input layer to layer 1 and layer 1 to layer 2
m1_layer1 = keras.layers.Dense(12, activation='sigmoid')(m1_inputs)
m1_layer2 = keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax')(m1_layer1)
# For model 2, pass the input layer to layer 1 and layer 1 to layer 2
m2_layer1 = keras.layers.Dense(12, activation='relu')(m2_inputs)
m2_layer2 = keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax')(m2_layer1)
# Merge model outputs and define a functional model
merged = keras.layers.add([m1_layer2, m2_layer2])
model = keras.Model(inputs=[m1_inputs, m2_inputs], outputs=merged)
# Print a model summary
print(model.summary())
<script.py> output:
Model: "model"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 784)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
input_2 (InputLayer) [(None, 784)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 12) 9420 input_1[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 12) 9420 input_2[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 4) 52 dense[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 4) 52 dense_2[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
add (Add) (None, 4) 0 dense_1[0][0]
dense_3[0][0]
==================================================================================================
Total params: 18,944
Trainable params: 18,944
Non-trainable params: 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
None
Training and validation with Keras
# Define a sequential model
model = keras.Sequential()
# Define a hidden layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
# Define the output layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax'))
# Compile the model
model.compile('SGD', loss='categorical_crossentropy')
# Complete the fitting operation
model.fit(sign_language_features, sign_language_labels, epochs=5)
<script.py> output:
Train on 2000 samples
Epoch 1/5
32/2000 [..............................] - ETA: 30s - loss: 1.5861
640/2000 [========>.....................] - ETA: 1s - loss: 1.3109
1280/2000 [==================>...........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.2190
1920/2000 [===========================>..] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.1552
2000/2000 [==============================] - 1s 328us/sample - loss: 1.1465
Epoch 2/5
32/2000 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.9728
672/2000 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.9270
1312/2000 [==================>...........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.8795
1952/2000 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.8326
2000/2000 [==============================] - 0s 81us/sample - loss: 0.8299
Epoch 3/5
32/2000 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5687
672/2000 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6832
1312/2000 [==================>...........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6657
1952/2000 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6453
2000/2000 [==============================] - 0s 81us/sample - loss: 0.6441
Epoch 4/5
32/2000 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5858
672/2000 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5500
1312/2000 [==================>...........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5479
1952/2000 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5322
2000/2000 [==============================] - 0s 80us/sample - loss: 0.5300
Epoch 5/5
32/2000 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.3786
672/2000 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.4668
1312/2000 [==================>...........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.4582
1952/2000 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.4504
2000/2000 [==============================] - 0s 80us/sample - loss: 0.4510
validation
# Define sequential model
model = keras.Sequential()
# Define the first layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='sigmoid', input_shape=(784,)))
# Add activation function to classifier
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax'))
# Set the optimizer, loss function, and metrics
model.compile(optimizer='RMSprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Add the number of epochs and the validation split
model.fit(sign_language_features, sign_language_labels, epochs=10, validation_split=0.1)
<script.py> output:
Train on 1799 samples, validate on 200 samples
Epoch 1/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 43s - loss: 1.4871 - accuracy: 0.2188
608/1799 [=========>....................] - ETA: 1s - loss: 1.2876 - accuracy: 0.4309
1216/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.1833 - accuracy: 0.5255
1792/1799 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.1138 - accuracy: 0.5725
1799/1799 [==============================] - 1s 619us/sample - loss: 1.1135 - accuracy: 0.5725 - val_loss: 0.9707 - val_accuracy: 0.5600
Epoch 2/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.9954 - accuracy: 0.6250
608/1799 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.8494 - accuracy: 0.7796
1216/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.8153 - accuracy: 0.7796
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 101us/sample - loss: 0.7811 - accuracy: 0.7916 - val_loss: 0.6716 - val_accuracy: 0.9200
Epoch 3/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6939 - accuracy: 0.8750
640/1799 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6641 - accuracy: 0.8422
1248/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6311 - accuracy: 0.8534
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 100us/sample - loss: 0.5984 - accuracy: 0.8694 - val_loss: 0.5287 - val_accuracy: 0.9400
Epoch 4/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5383 - accuracy: 0.8750
640/1799 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.5119 - accuracy: 0.9031
1248/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.4884 - accuracy: 0.9087
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 100us/sample - loss: 0.4621 - accuracy: 0.9133 - val_loss: 0.4863 - val_accuracy: 0.8450
Epoch 5/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.4294 - accuracy: 0.8438
640/1799 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.3951 - accuracy: 0.9375
1248/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.3847 - accuracy: 0.9431
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 100us/sample - loss: 0.3686 - accuracy: 0.9489 - val_loss: 0.4299 - val_accuracy: 0.9250
Epoch 6/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.3646 - accuracy: 0.9375
640/1799 [=========>....................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.3231 - accuracy: 0.9547
1216/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.3070 - accuracy: 0.9646
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 106us/sample - loss: 0.2930 - accuracy: 0.9672 - val_loss: 0.3686 - val_accuracy: 0.7850
Epoch 7/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2952 - accuracy: 0.8438
352/1799 [====>.........................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2509 - accuracy: 0.9659
704/1799 [==========>...................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2546 - accuracy: 0.9659
1056/1799 [================>.............] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2447 - accuracy: 0.9697
1312/1799 [====================>.........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2396 - accuracy: 0.9733
1728/1799 [===========================>..] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2398 - accuracy: 0.9722
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 173us/sample - loss: 0.2415 - accuracy: 0.9711 - val_loss: 0.2143 - val_accuracy: 0.9850
Epoch 8/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2202 - accuracy: 1.0000
448/1799 [======>.......................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2020 - accuracy: 0.9754
800/1799 [============>.................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2098 - accuracy: 0.9712
1216/1799 [===================>..........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1987 - accuracy: 0.9753
1664/1799 [==========================>...] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1941 - accuracy: 0.9766
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 150us/sample - loss: 0.1921 - accuracy: 0.9778 - val_loss: 0.2852 - val_accuracy: 0.8650
Epoch 9/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2495 - accuracy: 0.8438
480/1799 [=======>......................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1926 - accuracy: 0.9625
992/1799 [===============>..............] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1783 - accuracy: 0.9798
1504/1799 [========================>.....] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1654 - accuracy: 0.9827
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 121us/sample - loss: 0.1583 - accuracy: 0.9850 - val_loss: 0.2024 - val_accuracy: 0.9500
Epoch 10/10
32/1799 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2180 - accuracy: 0.9375
480/1799 [=======>......................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1492 - accuracy: 0.9729
992/1799 [===============>..............] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1467 - accuracy: 0.9758
1536/1799 [========================>.....] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1389 - accuracy: 0.9798
1799/1799 [==============================] - 0s 131us/sample - loss: 0.1360 - accuracy: 0.9822 - val_loss: 0.1397 - val_accuracy: 0.9650
Overfitting detection
过拟合检测
# Define sequential model
model = keras.Sequential()
# Define the first layer
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(1024, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
# Add activation function to classifier
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(4, activation='softmax'))
# Finish the model compilation
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01),
loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Complete the model fit operation
model.fit(sign_language_features, sign_language_labels, epochs=200, validation_split=0.5)
Evaluate
# Evaluate the small model using the train data
small_train = small_model.evaluate(train_features, train_labels)
# Evaluate the small model using the test data
small_test = small_model.evaluate(test_features, test_labels)
# Evaluate the large model using the train data
large_train = large_model.evaluate(train_features, train_labels)
# Evaluate the large model using the test data
large_test = large_model.evaluate(test_features, test_labels)
# Print losses
print('
Small - Train: {}, Test: {}'.format(small_train, small_test))
print('Large - Train: {}, Test: {}'.format(large_train, large_test))
Training models with the Estimators API
定义特征变量
# Define feature columns for bedrooms and bathrooms
bedrooms = feature_column.numeric_column("bedrooms")
bathrooms = feature_column.numeric_column("bathrooms")
# Define the list of feature columns
feature_list = [bedrooms, bathrooms]
def input_fn():
# Define the labels
labels = np.array(housing['price'])
# Define the features
features = {'bedrooms':np.array(housing['bedrooms']),
'bathrooms':np.array(housing['bathrooms'])}
return features, labels
完成证书
