小白月赛33题解(全)
A.字符统计
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/A
直接读入字符串进行遍历即可。用getline()读一行字符串,注意:cin读入后的回车会留在输入缓冲区,getline()的不会,所以在使用cin后,getline()之前需要清空输入缓冲区
注意行开头空格和空行的特殊处理。
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string s;
int r, dc, zf;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
getline(cin, s);
while(t--)
{
r = dc = zf = 0;
while(getline(cin, s) && s != "=====")
{
r++;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if(s[i] == ' ' && i) dc++;
zf++;
}
if(s.size())dc++;
}
cout << r << ' ' << dc << ' ' << zf << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B.连分数
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/B
对一般的(p/q),(p / q = a + 1 / m, 其中m = q / (p \% q)),然后令分子 = q, 分母 = p % q,继续上述操作,直到$ p % q == 0$时结束操作。
细节处理:
- 没输出一个a,如果p、q更新后可以进行操作,则输出“+1/{”,并且记录输出的’{‘的数量
- 如果p、q更新后不可进行操作,即(p \% q == 0),则说明到最后一个数了,不用输出大括号,并且下一轮会结束循环
- 最后输出等量的’}‘。
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int t, p, q;
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &p, &q);
printf("%d/%d = ", p, q);
int kh = 0;
while(q)
{
printf("%d", p / q);
int t = p % q;
p = q, q = t;
if(q)
{
if(p % q != 0)
{
printf("+1/{");
kh++;
}
else printf("+1/");
}
}
while(kh--) printf("}");
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
C.挪酒瓶
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/C
参考题解:https://www.nowcoder.com/discuss/643079、https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/efd1e10b345a42e1ae0231fc4ae9e7b4
对于一个有 n 个元素的置换群p,从最后一个 a往前开始换,则费用为 ((w_a+w_b)+(w_a+w_c)+...=(n−2)w_a+sum_{iin p}w_i)
最优的策略则是选择较小的 (w_a) 开始换。
对于多个置换群而言,单独内部交换并不是最优解,可以把目前最轻的酒瓶拿进来替换,最后再换回去。令置换群 p 内最轻重量为 (m_p=min_{iin p}wi),令全部的酒里面最轻重量为 (m_{all})。这个策略的花费为 (2(m_{all}+m_p)+(n−2)m_{all}+sum_{iin p}w_i - m_p + m_{all})(交换两次最小值花费:(2(m_{all}+m_p)),交换后的所有费用和为:(sum_{iin p}w_i - m_p + m_{all}))
最后对于每一个置换群,考虑两个 Case 如下,都选择最优即可:
- ((n−2)w_p+sum_{iin p}w_i)
- (2(m_{all}+m_p)+(n−2)m_{all}+∑_{iεp}w_i - m_p + m_{all}) = ((n + 1)*m_{all} + m_p + sum_{iin p}w_i)
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int a[N], w[N];
bool st[N];
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
int n, ans = 0, min_all = 1e9;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &w[i]);
//找出全局最小值
min_all = min(min_all, w[i]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(!st[i])
{
int cnt = 0, minv = 1e9;
//求一个置换群
for(int j = i; !st[j]; j = a[j])
{
cnt++;
ans += w[j];
minv = min(minv, w[j]);
st[j] = true;
}
//最优解更新
ans += min((cnt - 2) * minv, (cnt + 1) * min_all + minv);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D.购物
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/D
将物品名称映射到数字,用数组记录每一个物品的数量,然后遍历每个人,将其没有的物品的数量-1,最后遍历计算物品数量大于0的个数。
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int t, s, n;
int a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
unordered_map<string, int> goods;
string str;
int x, idx = 0;
scanf("%d%d", &s, &n);
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++)
{
cin >> str >> x;
goods.insert({str, idx++});
a[goods[str]] = x;
}
//for(int i = 0; i < idx; i++) cout << a[i] << ' ';
//puts("");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
bool has[N];
memset(has, false, sizeof has);
cin >> x;
for(int j = 0; j < x; j++)
{
cin >> str;
has[goods[str]] = true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < idx; i++)
if(!has[i]) a[i]--;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < idx; i++)
if(a[i] > 0) ans++;
if(ans) cout << ans << endl;
else puts("Need to be lucky");
}
return 0;
}
E.喝可乐
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/E
直接枚举每种可乐买多少瓶的所有情况,对每种情况计算能喝到的瓶数,记录最大值即可。
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int t, n, a, b;
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
int ans = 0;
cin >> n >> a >> b;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
int Max = n, an = i, bn = n - i;
while(an >= a || bn >= b)
{
if(an >= a)
{
Max += an / a;
bn += an / a;
an = an % a;
}
if(bn >= b)
{
Max += bn / b;
an += bn / b;
bn = bn % b;
}
}
ans = max(Max, ans);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
F.天旋地转
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/F
模拟,把坐标系的四种不同情况下的移动偏移量存下来,然后按步骤一步一步操作即可。
注意在计算逆时针旋转时,标记坐标轴方向的数字fx需要变为非负数
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second;
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int t, n;
PII Move[4][4] = {{{0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}},
{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}},
{{0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}},
{{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}}};
unordered_map<char, int> f {{'w', 0}, {'a', 1}, {'d', 2}, {'s', 3}};
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
LL xx = 0, yy = 0, fx = 0, k;
cin >> n;
while(n--)
{
char c;
cin >> c >> k;
if(c == 'r') fx = (fx + k) % 4;
else if(c == 'l') fx = ((fx - k) % 4 + 4) % 4;
else xx += k * Move[fx][f[c]].x, yy += k * Move[fx][f[c]].y;
//cout << fx << ' ' << xx << ',' << yy << endl;
}
cout << xx << ' ' << yy << endl;
}
return 0;
}
G.切圈圈
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/G
首先预处理出前缀和数组。可以知道性质:前缀和数组中相等的两点,之间的区间和一定是0。题目已经给出整个数组的和为0,那么只要确定数组中的一段和为0的区间,则另外一段(包含首尾的那一段)也就一定区间和为0了。所以可以直接在一维线性结构上进行求解。
当已经确定了一个区间和为0的区间时,这区间的端点前缀和数组的值一定相等。如果该区间内可以再分,由性质可得,区间内的切分点的前缀和数组值一定和两个端点的值相等。(环的另外一段也是如此)
由此可以进一步推出:最后分割出来的区间,所有端点的前缀和数组值一定相等。
所以,只要求出前缀和数组值相等的最大数量,即为答案。
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int t, n;
int a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> n;
int ans = 0;
map<int, int> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
//预处理前缀和数组
a[i] += a[i - 1];
//记录值为a[i]的点有多少个
m[a[i]]++;
ans = max(ans, m[a[i]]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
H.货物运输
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/H
根据题目建有向图,然后直接套最短路模板即可。
关于建图,难点在处理好边权:
边权:w[i] = c * min(f, d) + max(0, f - d) * cc
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110;
int t, n, m, s, ee, f;
int a, b, c, d, cc;
int h[N], e[N * N], ne[N * N], idx;
LL w[N * N], dist[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, LL c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void dij(int u)
{
dist[u] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int k = -1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(!st[j] && (k == -1 || dist[k] > dist[j]))
k = j;
for(int j = h[k]; j != -1; j = ne[j])
{
dist[e[j]] = min(dist[e[j]], dist[k] + w[j]);
}
st[k] = true;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
idx = 0;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(st, false, sizeof st);
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &ee, &f);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d, &cc);
//注意d、f的大小
add(a, b, (LL)c * min(d, f) + (LL)max(0, f - d) * cc);
}
dij(s);
//for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// cout << i << ':' << dist[i] << endl;
printf("%lld
", dist[ee]);
}
return 0;
}
I.三角尼姆
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/I
首先手动模拟发现:N = 1时Alice必赢,此时一共有1个空位;N = 2时Alice必赢,此时一共有3个空位;N = 3时Bob必赢,此时一共有6个空位;N = 4时Bob必赢,此时一共有10个空位。。。。。。
大胆猜测出:当空位总数为偶数个是,先手必赢,否则先手必输
经代码检验猜测正确。
证明:最后输的条件一定是只剩1个空位,往前推一下就是倒数第二次放棋子一定是3个空位,即最后面对的必输局面是剩下奇数个空位。
由:奇数 - 奇数 = 偶数,偶数 - 奇数 = 奇数,且每次减少空位一定是1或者3(奇数)
可得:剩余空位数一定是以“奇偶奇偶...”或者“偶奇偶奇...”的顺序出现的
进一步可得:如果玩家第一次面对的是偶数个空位,则一直是面对偶数个空位,则一定不会碰到奇数的情况,就一定不会输
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int t, n;
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
cin >> n;
n = (1 + n) * n / 2;
if(n & 1) puts("Alice");
else puts("Bob");
}
return 0;
}
J.线段的交
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11210/J
分两步:判断线段是否相交、求面积。
解法一:利用向量叉积判断线段相交及求四边形面积。
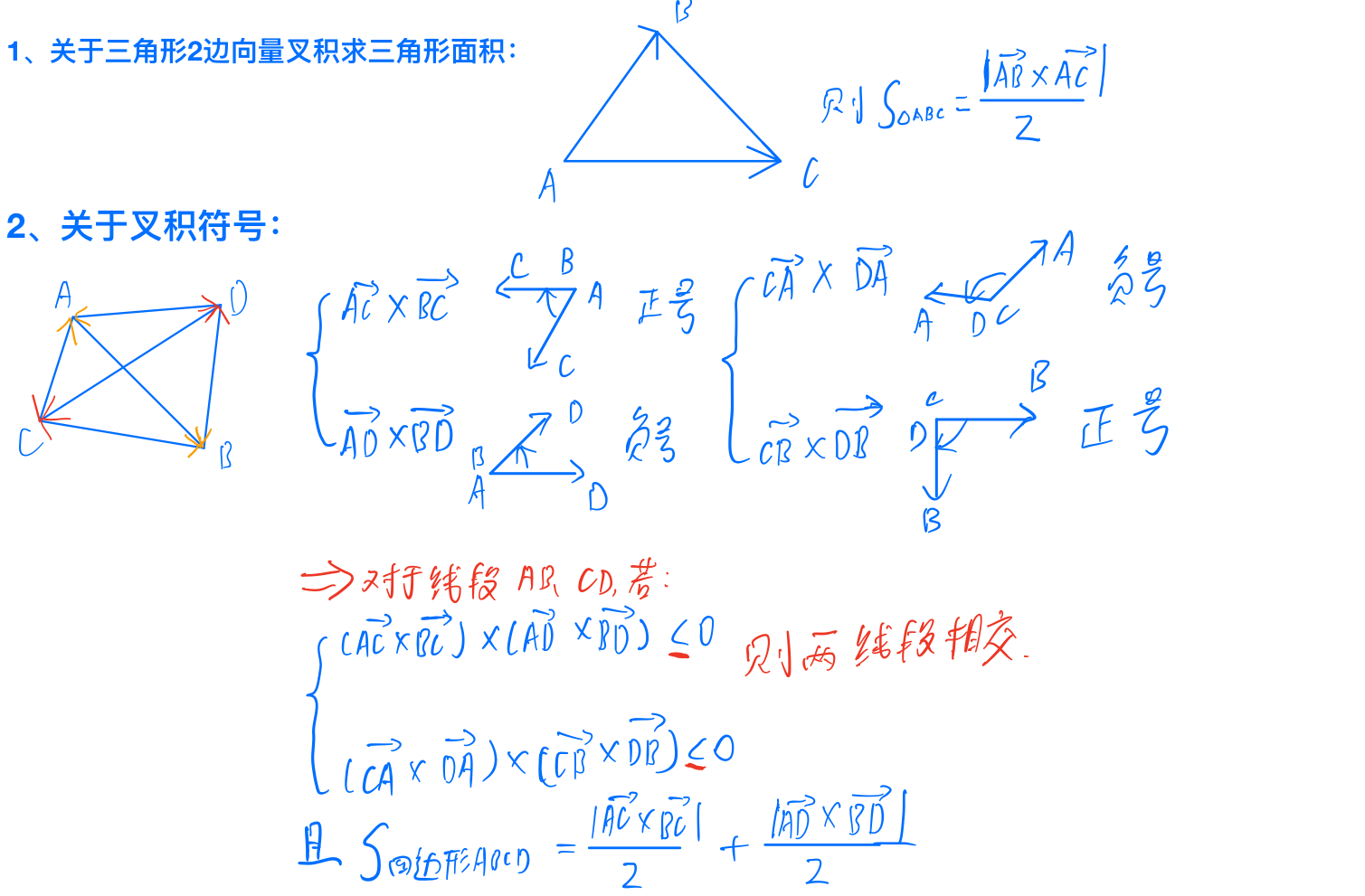
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
double x1, yy1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4;
struct Point
{
double x, y;
}p1, p2, q1, q2;
double cj(Point p, Point q)
{
return p.x * q.y - q.x * p.y;
}
double area(Point p1, Point p2, Point q1)
{
Point xl1 = {p2.x - p1.x, p2.y - p1.y};
Point xl2 = {q1.x - p1.x, q1.y - p1.y};
return cj(xl1, xl2);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &x1, &yy1, &x2, &y2, &x3, &y3, &x4, &y4);
p1 = {x1, yy1}, p2 = {x2, y2}, q1 = {x3, y3}, q2 = {x4, y4};
double s1 = area(p1, p2, q1);
double s2 = area(p1, p2, q2);
double s3 = area(q1, q2, p1);
double s4 = area(q1, q2, p2);
if(s1 * s2 <= 0 && s3 * s4 <= 0) printf("%.8f
", (fabs(s1) + fabs(s2)) / 2);
else cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
解法二:利用快速排斥实验和跨立实验判断直线相交,在用向量叉积求四边形面积
WA代码(case通过率92%,bug未知):
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
double x1, yy1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4;
struct Point
{
double x, y;
}p1, p2, q1, q2;
//快速排斥实验
bool kspc(Point p1, Point p2, Point q1, Point q2)
{
double minRx = min(p1.x, p2.x), minRy = min(p1.y, p1.y);
double maxRx = max(p1.x, p2.x), maxRy = max(p1.y, p2.y);
double minTx = min(q1.x, q2.x), minTy = min(q1.y, q2.y);
double maxTx = max(q1.x, q2.x), maxTy = max(q1.y, q2.y);
double minFx = max(minRx, minTx), minFy = max(minRy, minTy);
double maxFx = min(maxRx, maxTx), maxFy = min(maxRy, maxTy);
return (minFx <= maxFx && minFy <= maxFy);
}
//求向量叉积
double cj(Point p, Point q)
{
return p.x * q.y - q.x * p.y;
}
//跨立实验
bool kl(Point p1, Point p2, Point q1, Point q2)
{
Point xl1 = {p1.x - q1.x, p1.y - q1.y}, xl2 = {q2.x - q1.x, q2.y - q1.y}, xl3 = {p2.x - q1.x, p2.y - q1.y};
Point xl4 = {q1.x - p1.x, q1.y - p1.y}, xl5 = {p2.x - p1.x, p2.y - p1.y}, xl6 = {q2.x - p1.x, q2.y - p1.y};
return (cj(xl1, xl2) * cj(xl2, xl3) >= 0 && cj(xl4, xl5) * cj(xl5, xl6) >= 0);
}
//求面积
void area()
{
/*
double s1 = fabs(p1.x * p2.y - p2.x * p1.y + p2.x * q1.y - q1.x * p2.y + q1.x * p1.y - p1.x * q1.y) / 2;
double s2 = fabs(p1.x * p2.y - p2.x * p1.y + p2.x * q2.y - q2.x * p2.y + q2.x * p1.y - p1.x * q2.y) / 2;
*/
Point xl1 = {p2.x - p1.x, p2.y - p1.y};
Point xl2 = {q1.x - p1.x, q1.y - p1.y};
Point xl3 = {q2.x - p1.x, q2.y - p1.y};
printf("%.8lf
", (fabs(cj(xl1, xl2)) + fabs(cj(xl1, xl3))) / 2);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &x1, &yy1, &x2, &y2, &x3, &y3, &x4, &y4);
p1 = {x1, yy1}, p2 = {x2, y2}, q1 = {x3, y3}, q2 = {x4, y4};
if(kspc(p1, p2, q1, q2) && kl(p1, p2, q1, q2)) area();
else cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}