Fork-Join
介绍
演示代码:gitee仓库地址
在JDK1.7版本中提供了Fork-Join并行执行任务框架,它的主要作用是把大任务分割成若干个小任务,再对每个小任务得到的结果进行汇总,此种开发方法也叫分治编程,分治编程可以极大地利用CPU资源,提高任务执行的效率,也是目前与多线程有关的前沿技术。
不使用Fork-Join 使用线程池
任务规模分的可能不够小
package com.itcode._06Fork_join;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @author 夏天
* @date 2020年11月01日 14:21
* 递归开启线程求和 会有问题:线程数不够会导致一直在等待()
*/
public class SumRecursiveMT {
public static class RecursiveSumTask implements Callable<Long>{
public static final int SEQUENTIAL_CUTOFF=1;
int lo;
int hi;
int []arr;
ExecutorService executorService;
public RecursiveSumTask( ExecutorService executorService,int[] arr,int lo, int hi) {
this.lo = lo;
this.hi = hi;
this.arr = arr;
this.executorService = executorService;
}
@Override
public Long call() throws Exception {
System.out.format("%s range [%d-%d] begin to compute %n",
Thread.currentThread().getName(),lo, hi);
long result=0;
if(hi-lo<=SEQUENTIAL_CUTOFF){
for (int i=lo;i<hi;i++){
result+=arr[i];
}
}else {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
RecursiveSumTask left=new RecursiveSumTask(executorService,arr,lo,mid);
RecursiveSumTask right=new RecursiveSumTask(executorService,arr,mid,hi);
final Future<Long> lr = executorService.submit(left);
final Future<Long> rr = executorService.submit(right);
result =lr.get()+rr.get();
System.out.format( "%s range [%d-%d] finished to compute %n",
Thread .currentThread().getName(),lo, hi);
}
return result;
}
}
public static long sum(int[] arr)throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService=null;
try {
//cpu核数
int nofProcessors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nofProcessors);
RecursiveSumTask task = new RecursiveSumTask(executorService, arr, 0, arr.length);
return executorService.submit(task).get();
} finally {
assert executorService != null;
executorService.shutdown();
//100-200
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final int[] arr = Utils.buildRandomIntArray(10);
final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("数组长度:%d
",arr.length);
final long result = sum(arr);
System.out.printf("结果是:%d
",result);
System.out.printf("耗时:%d毫秒",System.currentTimeMillis()-start);
}
}
Fork-Join使用
基本思想:把一个规模大的问题划分为规模较小的子问题,然后分而治之,最后合并子问题的解得到原问题的解。
步骤:
分割原问题:
求解子问题:
合并子问题的解为原问题的解。
在分治法中,子问题一般是相互独立的,因此,经常通过递归调用算法来求解子问题。
示例代码:
package com.itcode._06Fork_join.ForkJoin;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
/**
* The class first sums an array sequentially then sums the array using the F/J framework.
* This proves that for < 100 computational steps, sequential is better.
* <p>
* To prove that for > 100 computational steps, F/J is better, change boolean: extraWork = true;
*/
class LongSum extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
static final int SEQUENTIAL_THRESHOLD = 1;
static final long NPS = (1000L * 1000 * 1000);
static final boolean extraWork = true; // change to add more than just a sum
int low;
int high;
int[] array;
LongSum(int[] arr, int lo, int hi) {
array = arr;
low = lo;
high = hi;
}
@Override
protected Long compute() {
System.out.printf("%s [%d]-[%d]
",Thread.currentThread().getName(),low,high);
if (high - low <= SEQUENTIAL_THRESHOLD) {
long sum = 0;
for (int i = low; i < high; ++i) {
sum += array[i];
// for non-trivial work
// if (extraWork)
//Utils.doCpuIntensiveCalculation();
}
return sum;
} else {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
LongSum left = new LongSum(array, low, mid);
LongSum right = new LongSum(array, mid, high);
//添加到任务队列中
left.fork();
//right.fork();
//以本线程继续执行compute
long rightAns = right.compute();
//join使用线程
long leftAns = left.join();
return leftAns + rightAns;
}
}
}
创建线程的示意图
当前线程进行细分的同时当前线程也会继续执行,不会像使用Exectors时等待线程结束导致无限等待
1 Fork-Join分治编程与类结构
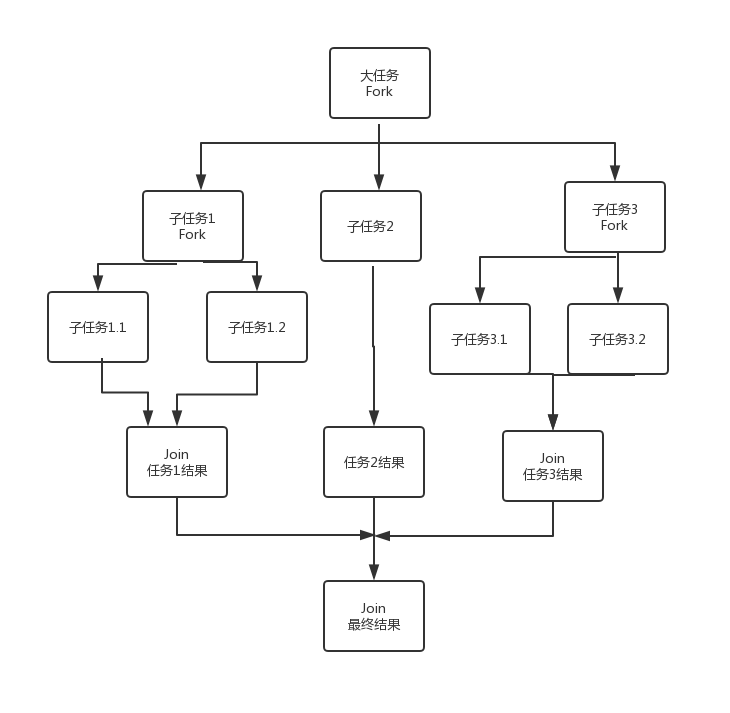
在JDK中并行执行框架Fork-Join使用了“工作窃取”算法,它是指某个线程从其他队列里窃取任务来执行,那这样做有什么好处呢?
比如要完成一个比较大的任务,完全可以把这个大的任务分割为若干个互不依赖的子任务/小任务,为了更加方便地管理这些任务,于是把这些子任务分别放到不同的队列里,这时就会出现有的线程会先把自己队列里的任务快速执行完毕,而其他线程对应的队列里还有任务等待处理,完成任务的线程与其等着,不如去帮助其他线程分担要执行的任务,于是它就去其他线程的队列里窃取一个任务来执行,这就是所谓的“工作窃取”算法。
在JKD1.7中实现分治编程需要使用ForkJoinPool类,此类的主要任务是创建一个任务池,类信息如下:
public class ForkJoinPool extends AbstractExecutorService{
该类也是从AbstractExecutorService类继承下来的
类ForkJoinPool所提供的功能是一个任务池,而执行具体任务却不是ForkJoinPool,而是ForkJoinTask类。
所以需要该类的3个子类CountedCompleter,RecursiveAction,RecursiveTask来实现具体功能。
2 使用RecursiveAction让任务跑起来
使用类RecursiveAction执行的任务是具有无返回值的,仅执行一次任务。
public class MyRecursiveAction extends RecursiveAction{
@Override
protected void compute() {
System.out.println("跑起来了");
}
}
..................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.submit(new MyRecursiveAction());
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
跑起来了
3 使用RecursiveAction分解任务
前面的实例仅是让任务运行起来,并打印一个字符串信息,任务并没有得到fork分解,也就是并没有体现分治编程的运行效果。在调用ForkJoinTask.java类中的fork()方法时需要注意一下效率的问题,因为每一次调用fork都会分离任务,增加系统运行负担,所以在ForkJoinTask.java类中提供了public static void invokeAll(ForkJoinTask<?>t1,ForkJoinTask<?>t2)方法来优化执行效率。
public class MyRecursiveAction extends RecursiveAction{
private int beginValue;
private int endValue;
public MyRecursiveAction(int beginValue,int endValue) {
super();
this.beginValue = beginValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
protected void compute() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"------------");
if(endValue -beginValue>2) {
int middelNum = (beginValue+endValue)/2;
MyRecursiveAction leftAction = new MyRecursiveAction(beginValue,middelNum);
MyRecursiveAction rightAction = new MyRecursiveAction(middelNum+1,endValue);
this.invokeAll(leftAction,rightAction);
}else {
System.out.println("打印组合:"+beginValue+"-"+endValue);
}
}
.........................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.submit(new MyRecursiveAction(1,10));
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3------------
打印组合:1-3
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3------------
打印组合:4-5
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1------------
打印组合:9-10
打印组合:6-8
4 使用RecursiveTask取得返回值与join()和get()方法的区别
使用get()获得返回值
public class MyRecursiveTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
System.out.println("compute time ="+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 100;
}
}
.............................
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
MyRecursiveTask task1 = new MyRecursiveTask();
System.out.println(task1.hashCode());
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask task2 = pool.submit(task1);
System.out.println(task2.hashCode()+" "+task2.get());
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
666641942
compute time =1556522593926
666641942 100
使用join()获得返回值
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRecursiveTask task1 = new MyRecursiveTask();
System.out.println(task1.hashCode());
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Integer> task2 = pool.submit(task1);
System.out.println(task2.hashCode()+"-"+task2.join());
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
666641942
compute time =1556523044041
666641942-100
方法join()与get()虽然都能取得计算后的结果值,但它们之间还是在出现异常时有处理上的区别。
使用get()方法执行任务时,当子任务出现异常时可以在main主线程中进行捕获。方法join()遇到异常直接抛出。
5 使用RecursiveTask执行多个任务并打印返回值
public class MyRecursiveTaskA extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"begin A"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"end A"+System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100;
}
}
.......................................
public class MyRecursiveTaskB extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"begin B"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"end B"+System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100;
}
}
......................................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Integer> runTaskA = pool.submit(new MyRecursiveTaskA());
ForkJoinTask<Integer> runTaskB = pool.submit(new MyRecursiveTaskB());
System.out.println("准备打印"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(runTaskA.join()+"A:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(runTaskB.join()+"B:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
pool.submit(new MyRecursiveAction(1,10));
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
准备打印1556524413868
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5begin B1556524413868
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3begin A1556524413869
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3end A1556524416869
100A:1556524416869
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5end B1556524418868
100B:1556524418868
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5------------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7------------
打印组合:9-10
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3------------
打印组合:1-3
打印组合:6-8
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7------------
打印组合:4-5
每个任务返回值为100,并且任务之间的运行方式是异步的,但join()方法是同步的。
6 使用RecursiveTask实现字符串累加
public class MyRecursiveTask extends RecursiveTask<String>{
private int beginValue;
private int endValue;
public MyRecursiveTask(int beginValue,int endValue) {
this.beginValue = beginValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
protected String compute() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-----------");
if(endValue -beginValue>2) {
int middelValue = (beginValue+endValue)/2;
MyRecursiveTask leftTask = new MyRecursiveTask(beginValue,middelValue);
MyRecursiveTask rightTask = new MyRecursiveTask(middelValue+1,endValue);
this.invokeAll(leftTask,rightTask);
return leftTask.join()+rightTask.join();
}else {
String returnString = "";
for(int i = beginValue;i<=endValue;i++) {
returnString = returnString+(i);
}
System.out.println("else 返回"+returnString+" "+beginValue+" "+endValue);
return returnString;
}
}
}
..................................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
MyRecursiveTask taskA = new MyRecursiveTask(1,20);
ForkJoinTask<String> runTaskA = pool.submit(taskA);
System.out.println(runTaskA.join());
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
else 返回123 1 3
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7-----------
else 返回678 6 8
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7-----------
else 返回910 9 10
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7-----------
else 返回45 4 5
else 返回161718 16 18
else 返回111213 11 13
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
else 返回1920 19 20
else 返回1415 14 15
7 使用Fork-Join实现求和
public class MyRecursiveTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
private int beginPosition;
private int endPosition;
public MyRecursiveTask(int beginValue,int endValue) {
this.beginPosition = beginValue;
this.endPosition = endValue;
System.out.println("#"+beginValue+" "+endValue);
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-----------");
Integer sumValue =0 ;
System.out.println("compute"+beginPosition+" "+endPosition);
if(endPosition -beginPosition>2) {
int middelValue = (beginPosition+endPosition)/2;
MyRecursiveTask leftTask = new MyRecursiveTask(beginPosition,middelValue);
MyRecursiveTask rightTask = new MyRecursiveTask(middelValue+1,endPosition);
this.invokeAll(leftTask,rightTask);
return leftTask.join()+rightTask.join();
}else {
int count = 0;
for(int i = beginPosition;i<=endPosition;i++) {
count = count + i;
}
return count;
}
}
}
..................................................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
MyRecursiveTask taskA = new MyRecursiveTask(1,10);
ForkJoinTask<Integer> runTaskA = pool.submit(taskA);
System.out.println("结果值:"+runTaskA.join());
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
#1 10
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
compute1 10
#1 5
#6 10
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
compute1 5
#1 3
#4 5
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5-----------
compute6 10
#6 8
#9 10
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
compute1 3
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5-----------
compute6 8
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3-----------
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5-----------
compute4 5
compute9 10
结果值:55
ForkJoinPool核心方法的实验
8 方法public void execute(ForkJoinTask<?>task)的使用
public class MyRecursiveAction2 extends RecursiveAction {
@Override
protected void compute() {
System.out.println("ThreadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
.............................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.execute(new MyRecursiveAction2());
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
ThreadName=ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3
9 方法public void execute(ForkJoinTask<?>task>如何处理返回值
public class MyRecursiveTask2 extends RecursiveTask<String>{
@Override
protected String compute() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "我是返回值";
}
}
...............................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRecursiveTask2 task = new MyRecursiveTask2();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.execute(task);
//execute方法无返回值
//想去的返回值得通过RecursiveTask对象
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
System.out.println(task.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
1556527570550
我是返回值
1556527575551
虽然public void execute(ForkJoinTask<?>task)方法无返回值,但还是可以通过RecursiveTask对象处理返回值。
10 方法public ForkJoinTasksubmit(ForkJoinTasktask)的使用
方法execute()无返回值,submit()有返回值。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRecursiveTask2 task = new MyRecursiveTask2();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<String> returnTask = pool.submit(task);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
System.out.println(returnTask.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
运行结果:
1556528067791
我是返回值2
1556528072792
11 方法public ForkJoinTasksubmit(Runnable task)的使用
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
System.out.println("begin"+System.currentTimeMillis());
ForkJoinTask task = pool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("ThreadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
try {
System.out.println(task.get());
System.out.println("end"+System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
begin1556528380463
ThreadName=ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3
null
end1556528385466
任务成功被运行,传入Runnable接口虽然没有返回值,但调用get()方法呈阻塞状态。
9.12 方法public ForkJoinTasksubmit(Callable task)的使用
如上
9.13 方法public ForkJoinTasksubmit(Callable task,T result)的使用
public class Userinfo {
private String username;
public Userinfo() {
super();
}
public Userinfo(String username) {
super();
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
}
.....................................................
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private Userinfo userinfo;
public MyRunnable(Userinfo userinfo) {
super();
this.userinfo = userinfo;
}
@Override
public void run() {
userinfo.setUsername("设置的值");
System.out.println("已经设置完结!");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
.........................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable(userinfo);
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.submit(runnable,userinfo);
//取不到值
System.out.println("username="+userinfo.getUsername());
}
}
运行结果:
username=null
已经设置完结!
运行结果是未取到值,因为是异步运行的,所以要加一个延时功能。
如果用Thread.sleep(time);//结果仍具有不确定性。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Userinfo userinfo = new Userinfo();
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable(userinfo);
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
Future<Userinfo> future = pool.submit(runnable,userinfo);
//建议使用此种方式future.get()
//因为get()方法呈阻塞性
System.out.println("username="+future.get().getUsername());
}
}
运行结果:
已经设置完结!
username=设置的值
9.14 方法public List<Future> invokeAll(Collection<?extends Callable> task)的使用
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
private long sleepValue;
public MyCallable(long sleepValue) {
super();
this.sleepValue = sleepValue;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"sleep"+sleepValue+"nowTime:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return "我是返回值";
}
}
............................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new MyCallable(5000));
list.add(new MyCallable(4000));
list.add(new MyCallable(3000));
list.add(new MyCallable(2000));
list.add(new MyCallable(1000));
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
List<Future<String>> listFuture = pool.invokeAll(list);
for(int i = 0;i<listFuture.size();i++) {
System.out.println(listFuture.get(i)+"nowTime:"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
.......................................................................
运行结果:
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5sleep4000nowTime:1556530245418
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1sleep2000nowTime:1556530245419
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3sleep5000nowTime:1556530245418
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-5sleep1000nowTime:1556530245419
ForkJoinPool-1-worker-7sleep3000nowTime:1556530245418
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask$AdaptedCallable@133314b[Wrapped task = cn.yu.forkjoin.MyCallable@b1bc7ed]nowTime:1556530245419
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask$AdaptedCallable@7cd84586[Wrapped task = cn.yu.forkjoin.MyCallable@30dae81]nowTime:1556530245419
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask$AdaptedCallable@1b2c6ec2[Wrapped task = cn.yu.forkjoin.MyCallable@4edde6e5]nowTime:1556530245419
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask$AdaptedCallable@70177ecd[Wrapped task = cn.yu.forkjoin.MyCallable@1e80bfe8]nowTime:1556530245419
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask$AdaptedCallable@66a29884[Wrapped task = cn.yu.forkjoin.MyCallable@4769b07b]nowTime:1556530245420
9.15 方法public void shutdown()的使用
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.submit(myRunnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
pool.shutdown();
System.out.println("main end");
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
1234567
任务正常运行,正常结束
2.
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.submit(myRunnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
pool.shutdown();
pool.submit(myRunnable);
System.out.println("main end");
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
12345678
上述代码运行后程序立马被销毁,说明对ForkJoinPool对象调用shutdown()方法后再执行任务时出现异常,进程也就马上销毁了,而正在运行的线程任务也被销毁了。
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.submit(myRunnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
pool.shutdown();
if(pool.isShutdown()==false){
pool.submit(myRunnable);
}
System.out.println("main end");
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
12345678910
9.16 方法public List shutdownNow()的使用
shotdown:
1.每个任务正常运行直到结束
2.池关闭后不再运行有新任务被执行并抛出RejectExecutionException异常
shutdownNow结合isInterrupted() == true判断
1.立即停止当前正在执行的任务
2.池关闭后不再运行有新任务被执行并抛出RejectExecutionException()异常
shutdownNow未结合isInterrupted() == true判断
1.每个任务正常运行直到结束
2.池关闭后不再运行有新任务被执行并抛出RejectExecutionException异常
9.17 方法isTerminating()和isTerminated()的使用
1.使用shutdown()方法关闭pool池之前,isTerminating()方法的返回值一直是false.
2.先调用shutdown()再调用get()方法不出现异常,而先调用shutdownNow()再调用get()方法出现异常CancellationException,说明方法shutdown()与shutdownNow()在对get()方法的处理行为上是不一样的。
9.18 方法 public boolean awaitTermination(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)的使用
方法awaitTermination(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)的作用是等待池被销毁的最长时间,具有阻塞特性。
9.19 方法publicT invoke(ForkJoinTask)的使用
方法execute(task)、submit(task)、invoke(task)都可以在异步队列中执行任务,需要注意的是,方法invoke()是阻塞的,而他们在使用上的区别其实很简单,execute(task)只执行任务,没有返回值,而submit(task)方法具有返回值,返回值类型是ForkJoinTask,想取得返回值时,需要使用ForkJoinTask对象的get()方法,而invoke(task)和submit(task)方法一样都具有返回值的功能,区别就是invoke(task)方法直接将返回值进行返回,而不是通过ForkJoinTask对象的get()方法。
9.20 监视pool池的状态
方法getParallelism():获得并行的数量,与CPU的内核数有关。
方法getPoolSize():获得任务池的大小
方法getQueuedSubmissionCount():取得已经提交但尚未被执行的任务数量
方法hasQueuedSubmissions():判断队列中是否有未执行的任务。
方法getActiveThreadCount():获得活动的线程个数
方法getQueuedTaskCount()获得任务的总个数
方法getStealCount():获得偷窃的任务个数
方法getRunningThreadCount():获得正在运行并且不再阻塞状态下的线程个数。
方法isQuiescent():判断任务池是否是静止未执行任务的状态
9.21 方法isTerminating()和isTerminated()的使用
public class MyRecursiveTask2 extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
Integer.parseInt("A");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
}
return 100;
}
}
....................................................
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
MyRecursiveTask2 action = new MyRecursiveTask2();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask task = pool.submit(action);
System.out.println(task.isCompletedAbnormally()+"-"+task.isCompletedNormally());
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(task.isCompletedAbnormally()+"-"+task.isCompletedNormally());
System.out.println(task.getException());
}
}
...................................................
运行结果:
false-false
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "A"
at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:68)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:658)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:776)
at Test/cn.yu.forkjoin.MyRecursiveTask2.compute(MyRecursiveTask2.java:11)
at Test/cn.yu.forkjoin.MyRecursiveTask2.compute(MyRecursiveTask2.java:1)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask.exec(RecursiveTask.java:94)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:290)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.topLevelExec(ForkJoinPool.java:1020)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.scan(ForkJoinPool.java:1656)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1594)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:177)
true-false
java.lang.NumberFormatException
本章总结:
虽然分治编程可以有效地利用CPU资源,但不要为了分治编程而分治,应该结合具体的业务场景来进行使用。


