ITERATOR 迭代器
template<class InputIterator,class T>
InputIterator find(InputIterator first,InputIterator last,const T& value)
{
while(first != last && *first != value)
++first;
return first;
}
代码示例
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <list> 4 #include <deque> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <iostream> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 11 { 12 const int arraySize = 7; 13 int ia[arraySize] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6}; 14 15 vector<int> ivect(ia,ia+arraySize); 16 list<int> ilist(ia,ia+arraySize); 17 deque<int> ideque(ia,ia+arraySize); 18 19 vector<int>::iterator it1 = find(ivect.begin(),ivect.end(),4); 20 if(it1 == ivect.end()) 21 cout << "4 not found." << endl; 22 else 23 cout << "4 found. " << * it1 << endl; 24 25 list<int>::iterator it2 = find(ilist.begin(),ilist.end(),6); 26 if(it2 == ilist.end()) 27 cout << "6 not found. " << endl; 28 else 29 cout << "6 found. " << *it2 << endl; 30 31 deque<int>::iterator it3 = find(ideque.begin(),ideque.end(),8); 32 if(it3 == ideque.end()) 33 cout << "8 not found. " << endl; 34 else 35 cout << "8 find " << *it3 << endl; 36 37 38 return 0; 39 }
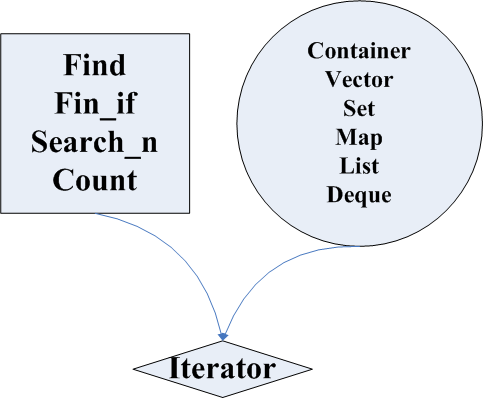
stl中容器有vectorsetlist等等等等
算法有findcount等
两者独立 而他们之间的联系便是由iterator进行连接 将两者粘合起来
iterator类似智能指针
智能指针auto_ptr 除了拥有平常指针概念的功能 还具有引用计数功能
通过对该指针指向的元素的引用计数 自动释放元素内存资源 而不必手动调用delete
(auto_ptr 在c++11之后已经被智能指针shared_ptr unique_ptr取代)
示例代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class auto_ptr{
public:
explicit auto_ptr(T* p = 0):pointer(p){}
template<typename U>
auto_ptr(auto_ptr<U>& rhs):pointer(rhs.release()){}
~auto_ptr(){ cout << "enter delete status
";delete pointer;}
template<class U>
auto_ptr<T>& operator=(auto_ptr<U>& rhs){
if(this != &rhs) reset(rhs.release());
return *this;
}
T& operator*()const{return *pointer;}
T* operator->()const{return pointer;}
T* get()const{return pointer;}
private:
T* pointer;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
auto_ptr<string> ps(new string("test"));
cout << *ps << endl;
cout << ps->size() << endl;
return 0;
}
要使用iterator这个智能指针 就需要识别指向的元素的相关信息,比如类别、引用等
代码使用了trait技巧将元素信息提取出来
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
struct INT{
typedef int value_type;
typedef int difference_type;
typedef int* pointer;
typedef int& reference;
};
struct FLOAT{
typedef float value_type;
typedef float difference_type;
typedef float* pointer;
typedef float& reference;
};
template<class I>
struct Iterator_Traits{
//typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename I::value_type value_type;
typedef typename I::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename I::pointer pointer;
typedef typename I::reference reference;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << typeid(Iterator_Traits<INT>::reference).name() << std::endl;
std::cout << typeid(Iterator_Traits<FLOAT>::reference).name() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
至此 除了
//typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
还没解决 其他都解决完毕
iterator_category是什么东西呢?
iterator迭代器也是有类型区分的

那么在实际代码中是如何进行识别呢?
在代码执行时才识别区分 效率太低

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
//申请五个作为迭代器iterator类别的结构
struct input_iterator_tag_{};
struct output_iterator_tag_{};
struct forward_iterator_tag_:public input_iterator_tag_{};
struct bidirectional_iterator_tag_:public forward_iterator_tag_{};
struct random_access_iterator_tag_:public bidirectional_iterator_tag_{};
struct INT{
typedef input_iterator_tag_ iterator_category;
typedef int value_type;
typedef int difference_type;
typedef int* pointer;
typedef int& reference;
};
struct FLOAT{
typedef output_iterator_tag_ iterator_category;
typedef float value_type;
typedef float difference_type;
typedef float* pointer;
typedef float& reference;
};
template<class I>
struct MyIterator_Traits{
typedef typename I::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename I::value_type value_type;
typedef typename I::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename I::pointer pointer;
typedef typename I::reference reference;
};
template<typename T,typename Distance>
void test(T t,Distance n){
typename MyIterator_Traits<T>::iterator_category SELECT_TYPE;
test_(t,n,SELECT_TYPE);
}
template<typename InputIterator,typename Distance>
void test_(InputIterator i,Distance j,input_iterator_tag_){
cout << "input_iterator_tag_" << endl;
}
template<typename InputIterator,typename Distance>
void test_(InputIterator i,Distance j,output_iterator_tag_){
cout << "output_iterator_tag_" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
INT i;
FLOAT f;
char c;
test(i,c);
test(f,c);
return 0;
}
我们对不同的迭代器 指定不同的tag 这样就会进入到不同的函数中去了

