There are n integers b1, b2, ..., bn written in a row. For all i from 1 to n, values ai are defined by the crows performing the following procedure:
- The crow sets ai initially 0.
- The crow then adds bi to ai, subtracts bi + 1, adds the bi + 2 number, and so on until the n'th number. Thus, ai = bi - bi + 1 + bi + 2 - bi + 3....
Memory gives you the values a1, a2, ..., an, and he now wants you to find the initial numbers b1, b2, ..., bn written in the row? Can you do it?
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of integers written in the row.
The next line contains n, the i'th of which is ai ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the value of the i'th number.
Print n integers corresponding to the sequence b1, b2, ..., bn. It's guaranteed that the answer is unique and fits in 32-bit integer type.
5
6 -4 8 -2 3
2 4 6 1 3
5
3 -2 -1 5 6
1 -3 4 11 6
In the first sample test, the crows report the numbers 6, - 4, 8, - 2, and 3 when he starts at indices 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. It is easy to check that the sequence 2 4 6 1 3 satisfies the reports. For example, 6 = 2 - 4 + 6 - 1 + 3, and - 4 = 4 - 6 + 1 - 3.
In the second sample test, the sequence 1, - 3, 4, 11, 6 satisfies the reports. For example, 5 = 11 - 6 and 6 = 6.
思路:a[i]+a[i+1];
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=1e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=1e9+10,mod=1e9+7; const ll INF=1e18+10; ll a[N]; int main() { int x; scanf("%d",&x); for(int i=1;i<=x;i++) scanf("%lld",&a[i]); for(int i=1;i<=x;i++) printf("%lld ",a[i]+a[i+1]); return 0; }
Memory is performing a walk on the two-dimensional plane, starting at the origin. He is given a string s with his directions for motion:
- An 'L' indicates he should move one unit left.
- An 'R' indicates he should move one unit right.
- A 'U' indicates he should move one unit up.
- A 'D' indicates he should move one unit down.
But now Memory wants to end at the origin. To do this, he has a special trident. This trident can replace any character in s with any of 'L', 'R', 'U', or 'D'. However, because he doesn't want to wear out the trident, he wants to make the minimum number of edits possible. Please tell Memory what is the minimum number of changes he needs to make to produce a string that, when walked, will end at the origin, or if there is no such string.
The first and only line contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100 000) — the instructions Memory is given.
If there is a string satisfying the conditions, output a single integer — the minimum number of edits required. In case it's not possible to change the sequence in such a way that it will bring Memory to to the origin, output -1.
RRU
-1
UDUR
1
RUUR
2
In the first sample test, Memory is told to walk right, then right, then up. It is easy to see that it is impossible to edit these instructions to form a valid walk.
In the second sample test, Memory is told to walk up, then down, then up, then right. One possible solution is to change s to "LDUR". This string uses 1 edit, which is the minimum possible. It also ends at the origin.
题意:上下左右的走,问最少变几步可以回到原点;
思路:奇数步,显然不能回到,ans=(abs(l-r)+abs(u-d))/ 2;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=1e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=1e9+10,mod=1e9+7; const ll INF=1e18+10; char a[N]; int flag[10]; int main() { int x; scanf("%s",a); x=strlen(a); if(x&1) { printf("-1 "); return 0; } for(int i=0;i<x;i++) { if(a[i]=='U') flag[1]++; if(a[i]=='D') flag[2]++; if(a[i]=='L') flag[3]++; if(a[i]=='R') flag[4]++; } printf("%d ",(abs(flag[1]-flag[2])+abs(flag[3]-flag[4]))/2); return 0; }
Memory is now interested in the de-evolution of objects, specifically triangles. He starts with an equilateral triangle of side length x, and he wishes to perform operations to obtain an equilateral triangle of side length y.
In a single second, he can modify the length of a single side of the current triangle such that it remains a non-degenerate triangle (triangle of positive area). At any moment of time, the length of each side should be integer.
What is the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y?
The first and only line contains two integers x and y (3 ≤ y < x ≤ 100 000) — the starting and ending equilateral triangle side lengths respectively.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y if he starts with the equilateral triangle of side length x.
6 3
4
8 5
3
22 4
6
In the first sample test, Memory starts with an equilateral triangle of side length 6 and wants one of side length 3. Denote a triangle with sides a, b, and c as (a, b, c). Then, Memory can do 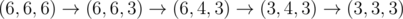 .
.
In the second sample test, Memory can do 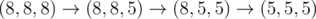 .
.
In the third sample test, Memory can do: 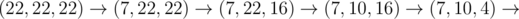
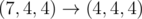 .
.
题意:给你一个边长为x的等边三角形,可以改变一条边使其成为另一个三角形,求最少改变的次数,得到边长为y的等边三角形;
思路:贪心,从y往上最大的改变;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=1e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=1e9+10,mod=1e9+7; const ll INF=1e18+10; int a[10]; int main() { int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)a[i]=y; int ans=0; while(1) { if(a[1]==x&&a[2]==x&&a[3]==x) break; sort(a+1,a+4); a[1]=min(x,a[2]+a[3]-1); ans++; } cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }