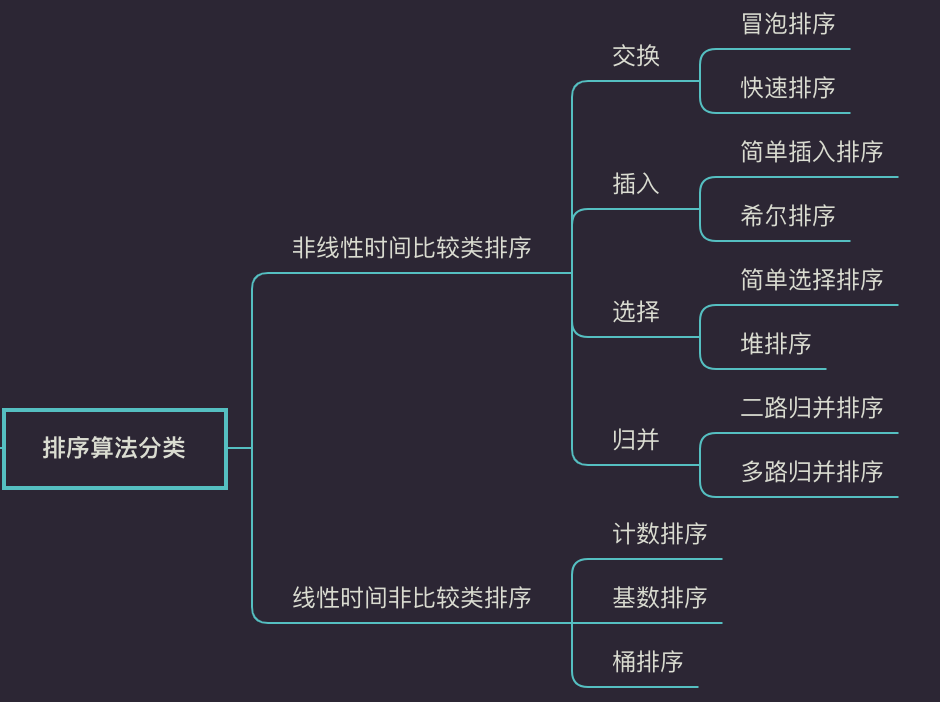
算法分类
十种常见排序算法可以分为两大类:
非线性时间比较类排序:通过比较来决定元素间的相对次序,由于其时间复杂度不能突破O(nlogn),因此称为非线性时间比较类排序。
线性时间非比较类排序:不通过比较来决定元素间的相对次序,它可以突破基于比较排序的时间下界,以线性时间运行,因此称为线性时间非比较类排序。
详情如下:
算法评估
排序算法的性能依赖于以下三个标准:
稳定性:如果a原本在b前面,而a=b,排序之后a仍然在b的前面,则稳定;如果a原本在b的前面,而a=b,排序之后 a 可能会出现在 b 的后面,则不稳定。
时间复杂度:对排序数据的总的操作次数。反映当n变化时,操作次数呈现什么规律。
空间复杂度:是指算法在计算机内执行时所需存储空间的度量,它也是数据规模n的函数。
排序算法综合评估如下:

1、冒泡排序
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地走访过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果它们的顺序错误就把它们交换过来。走访数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。这个算法的名字由来是因为越小的元素会经由交换慢慢“浮”到数列的顶端。
1.1 算法描述
- 比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换它们两个;
- 对每一对相邻元素作同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对,这样在最后的元素应该会是最大的数;
- 针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个;
- 重复步骤1~3,直到排序完成。
1.2 动图演示

1.3 代码实现
private static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); int count = 0, len = arr.length; for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { // 相邻元素两两对比 int temp = arr[j + 1]; // 元素交换 arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; count++; } } } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("bubbleSort 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); }
2、快速排序
快速排序的基本思想:通过一趟排序将待排记录分隔成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分的关键字小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序。
2.1 算法描述
快速排序使用分治法来把一个串(list)分为两个子串(sub-lists)。具体算法描述如下:
- 从数列中挑出一个元素,称为 “基准”(pivot);
- 重新排序数列,所有元素比基准值小的摆放在基准前面,所有元素比基准值大的摆在基准的后面(相同的数可以到任一边)。在这个分区退出之后,该基准就处于数列的中间位置。这个称为分区(partition)操作;
- 递归地(recursive)把小于基准值元素的子数列和大于基准值元素的子数列排序。
2.2 动图演示
2.3 代码实现
/** * 使用分治法来把一个串(list)分为两个子串(sub-lists),通过一趟排序将待排记录分隔成独立的两部分 * 其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分的关键字小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序。 * * @param arr */ private static void quickSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 使用单链表进行排序 int count = spilt(arr.clone(), 0, arr.length - 1, 0); long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("使用单链表进行排序花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); printArray(arr); System.out.println("quickSort(使用单链表进行排序) 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); current = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 使用双链表进行排序 count = partition(arr.clone(), 0, arr.length - 1, 0); cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("使用双链表进行排序花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); printArray(arr); System.out.println("quickSort(使用双链表进行排序) 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); } private static int spilt(int[] arr, int low, int high, int count) { if (low >= high) { return count; //未发生比较,比较计数器不变 } int len = arr.length; int temp, i = low; for (int j = low + 1; j < len; j++) { if (arr[low] > arr[j]) { temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[i + 1]; arr[i + 1] = temp; i++; count++; } } if (i > low) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[low]; arr[low] = temp; count++; } count = spilt(arr, low, i - 1, count); count = spilt(arr, i + 1, high, count); return count; } public static int partition(int a[], int low, int high, int count) { if (low < high) { //划分数组并获取比较元素的位置 int x = a[low], temp; //将该数组第一个元素设置为比较元素 int i = low; int j = high; while (i < j) { while (i < j && a[j] >= x) j--; //从右至左找到第一个小于比较元素的数 while (i < j && a[i] <= x) i++; //从左至右找到第一个大于比较元素的数 /*需要注意的是,这里的j--与i++的顺序不可以调换! *如果调换了顺序,i会走过头,以至于将后面较大的元素交换到数组开头*/ //将大数与小数交换 if (i != j) { temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; count++; } } //将比较元素交换到期望位置 temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[low]; a[low] = temp; count++; count = partition(a, low, i - 1, count); //对比较元素左边进行排序 count = partition(a, i + 1, high, count); //对比较元素右边进行排序 } return count; } private static void printArray(int[] arr) { System.out.print(" "); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); }
3、简单插入排序(Insertion Sort)
插入排序(Insertion-Sort)的算法描述是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是通过构建有序序列,对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。
3.1 算法描述
一般来说,插入排序都采用in-place在数组上实现。具体算法描述如下:
- 从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序;
- 取出下一个元素,在已经排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描;
- 如果该元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素移到下一位置;
- 重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置;
- 将新元素插入到该位置后;
- 重复步骤2~5。
3.2 动图演示
3.3 代码实现
private static void insertionSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); int len = arr.length; int preIndex, temp, count = 0; for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { preIndex = i - 1; temp = arr[i]; while (preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > temp) { arr[preIndex + 1] = arr[preIndex]; count++; preIndex--; } arr[preIndex + 1] = temp; count++; } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("insertionSort 发生了 " + count + " 次移动。"); }
3.4 算法分析
插入排序在实现上,通常采用in-place排序(即只需用到O(1)的额外空间的排序),因而在从后向前扫描过程中,需要反复把已排序元素逐步向后挪位,为最新元素提供插入空间。
4、希尔排序
希尔排序是简单插入排序的改进版。它与插入排序的不同之处在于,它会优先比较距离较远的元素。希尔排序又叫缩小增量排序。
4.1 算法描述
先将整个待排序的记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序,具体算法描述:
- 选择一个增量序列t1,t2,…,tk,其中ti>tj,tk=1;
- 按增量序列个数k,对序列进行k 趟排序;
- 每趟排序,根据对应的增量ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排序。仅增量因子为1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为整个序列的长度。
4.2 动图演示
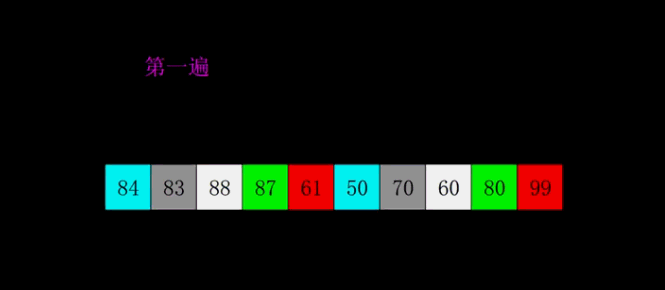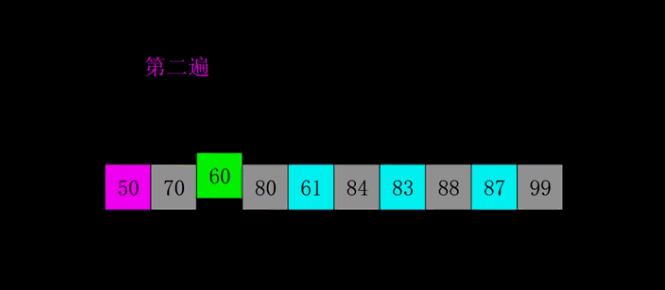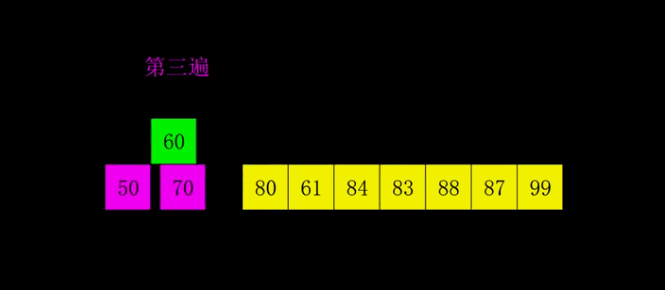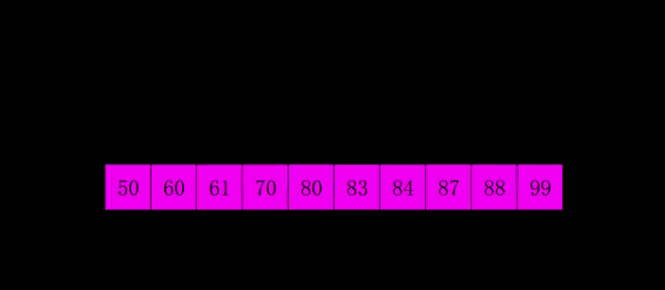
4.3 代码实现
/** * shell Sort using exchange method(希尔排序内部用了交换的方式) * * @param arr */ private static void shellSortUsingBubble(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); int count = 0, len = arr.length; //间隔变化 for (int gap = len / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) { //对固定间隔的排序 for (int i = gap; i < len; i++) { for (int j = i; j > gap - 1; j -= gap) { if (arr[j] < arr[j - gap]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j - gap]; arr[j - gap] = temp; count++; } } } } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("shellSortUsingBubble 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); } /** * shell Sort using insert Method: Knuth序列 * h = 1 * h = 3*h + 1 * 一个很长的数组,我们要用能对这个数组采用最大的间隔。最大间隔不能超过数组长度的1/3,当h>1/3时 3h+1 就大于整个数组的长度了,所以就不适合了。 */ public static void shellSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); int temp, h = 1, count = 0; while (h < arr.length / 3) { h = h * 3 + 1; } for (int gap = h; gap > 0; gap = (gap - 1) / 3) { for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++) { temp = arr[i]; int preIndex = i - gap; while (preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > temp) { arr[preIndex + gap] = arr[preIndex]; count++; preIndex -= gap; } arr[preIndex + gap] = temp; count++; } } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("shellSort 发生了 " + count + " 次移动。"); }
4.4 算法分析
希尔排序的核心在于间隔序列的设定。既可以提前设定好间隔序列,也可以动态的定义间隔序列。动态定义间隔序列的算法是《算法(第4版)》的合著者Robert Sedgewick提出的。
5、选择排序
选择排序(Selection-sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理:首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,然后,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾。以此类推,直到所有元素均排序完毕。
5.1 算法描述
n个记录的直接选择排序可经过n-1趟直接选择排序得到有序结果。具体算法描述如下:
- 初始状态:无序区为R[1..n],有序区为空;
- 第i趟排序(i=1,2,3…n-1)开始时,当前有序区和无序区分别为R[1..i-1]和R(i..n)。该趟排序从当前无序区中-选出关键字最小的记录 R[k],将它与无序区的第1个记录R交换,使R[1..i]和R[i+1..n)分别变为记录个数增加1个的新有序区和记录个数减少1个的新无序区;
- n-1趟结束,数组有序化了。
5.2 动图演示
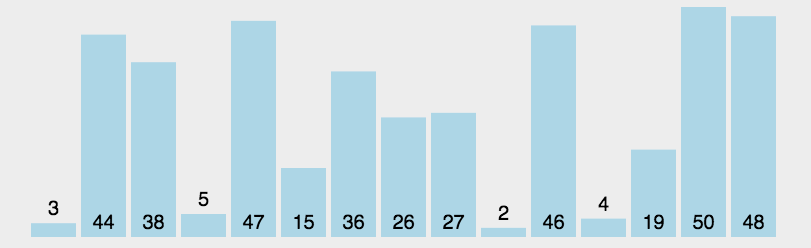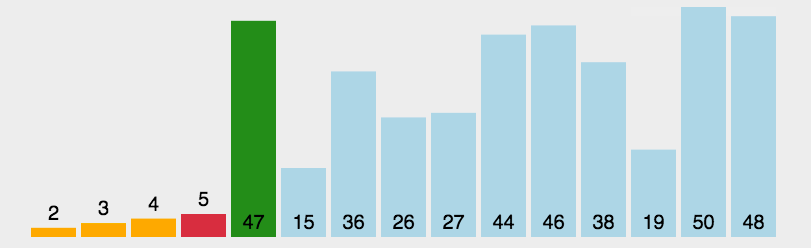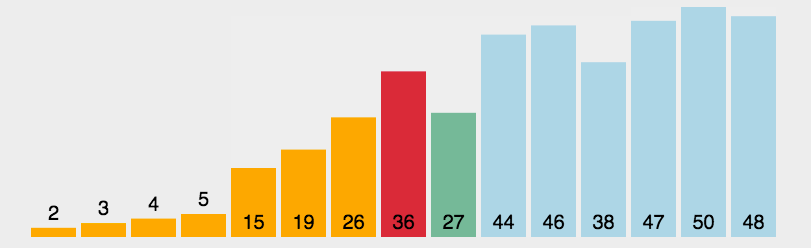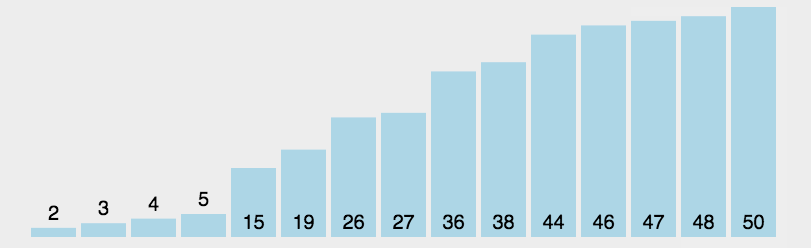
5.3 代码实现
private static void selectionSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); int len = arr.length; int minIndex, temp, count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { minIndex = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { // 寻找最小的数 minIndex = j; // 将最小数的索引保存 } } temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[minIndex]; arr[minIndex] = temp; count++; } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("selectionSort 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); }
5.4 算法分析
表现最稳定的排序算法之一,因为无论什么数据进去都是O(n2)的时间复杂度,所以用到它的时候,数据规模越小越好。唯一的好处可能就是不占用额外的内存空间了吧。
6、堆排序
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。堆积是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆积的性质:即子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点。
6.1 算法描述
- 将初始待排序关键字序列(R1,R2….Rn)构建成大顶堆,此堆为初始的无序区;
- 将堆顶元素R[1]与最后一个元素R[n]交换,此时得到新的无序区(R1,R2,……Rn-1)和新的有序区(Rn),且满足R[1,2…n-1]<=R[n];
- 由于交换后新的堆顶R[1]可能违反堆的性质,因此需要对当前无序区(R1,R2,……Rn-1)调整为新堆,然后再次将R[1]与无序区最后一个元素交换,得到新的无序区(R1,R2….Rn-2)和新的有序区(Rn-1,Rn)。不断重复此过程直到有序区的元素个数为n-1,则整个排序过程完成。
6.2 动图演示
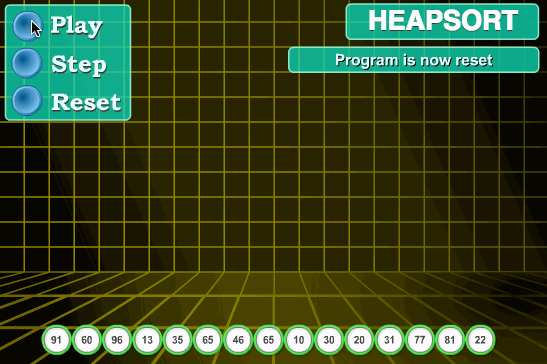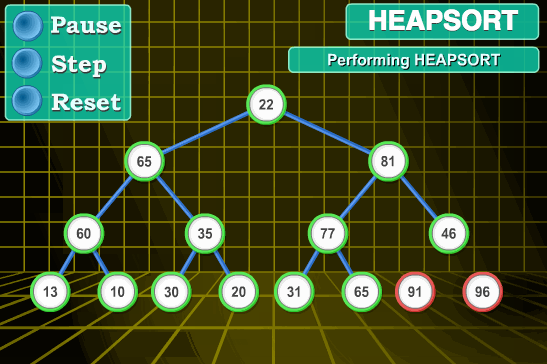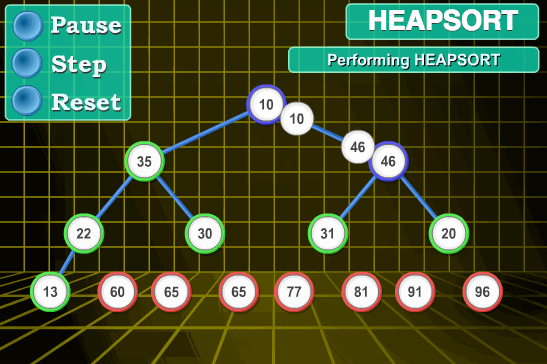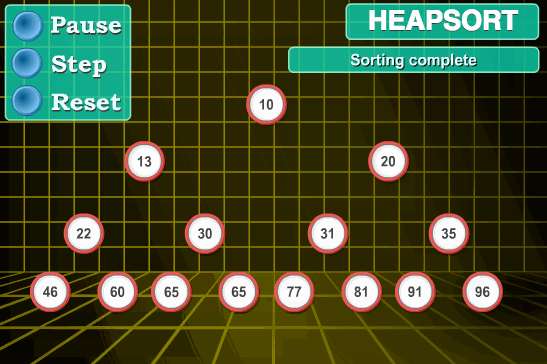
6.3 代码实现
private static void heapSort(int[] arr, int heapSize) { int temp; if (heapSize > 0) { for (int i = heapSize; i > 0; i--) { if (arr[(i - 1) / 2] < arr[i]) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[(i - 1) / 2]; arr[(i - 1) / 2] = temp; } } temp = arr[0]; arr[0] = arr[heapSize]; arr[heapSize] = temp; heapSort(arr, --heapSize); } }
7、归并排序
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为2-路归并。
7.1 算法描述
- 把长度为n的输入序列分成两个长度为n/2的子序列;
- 对这两个子序列分别采用归并排序;
- 将两个排序好的子序列合并成一个最终的排序序列。
7.2 动图演示
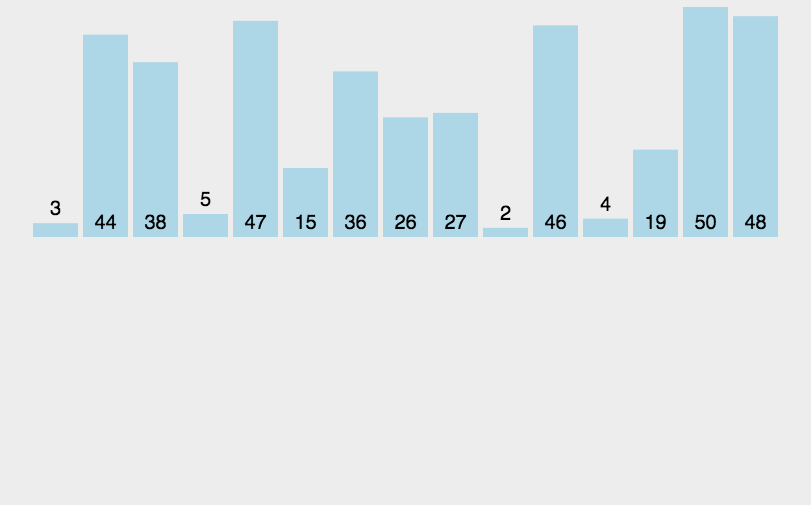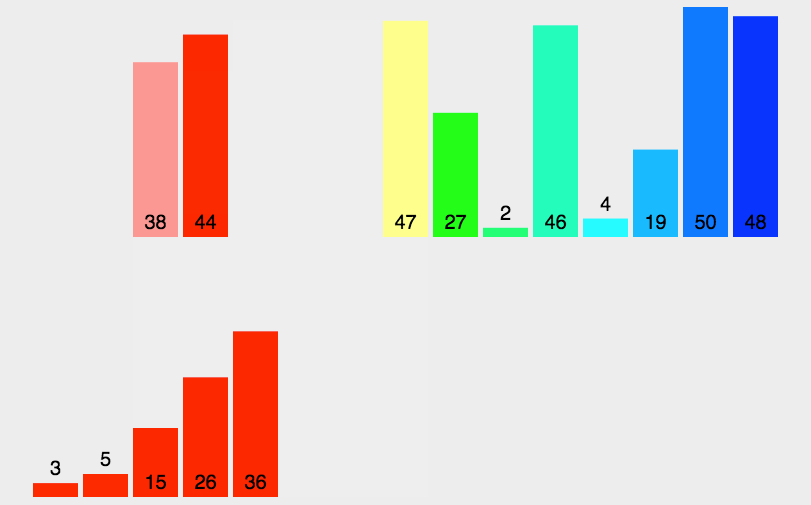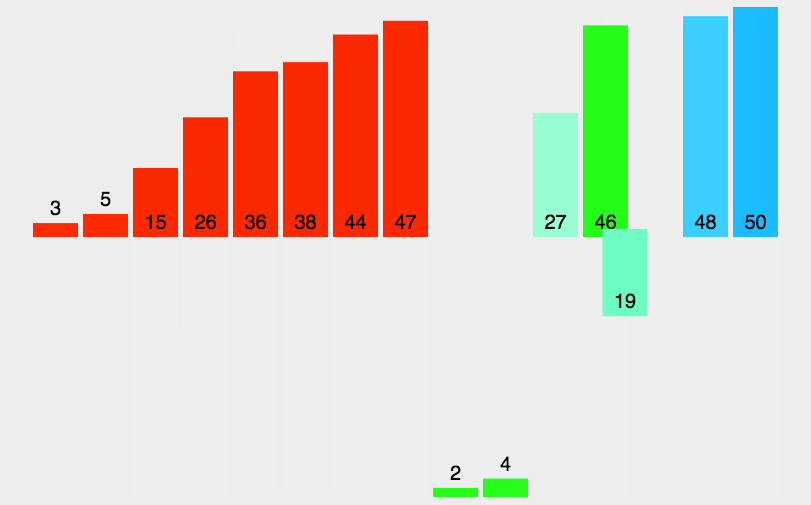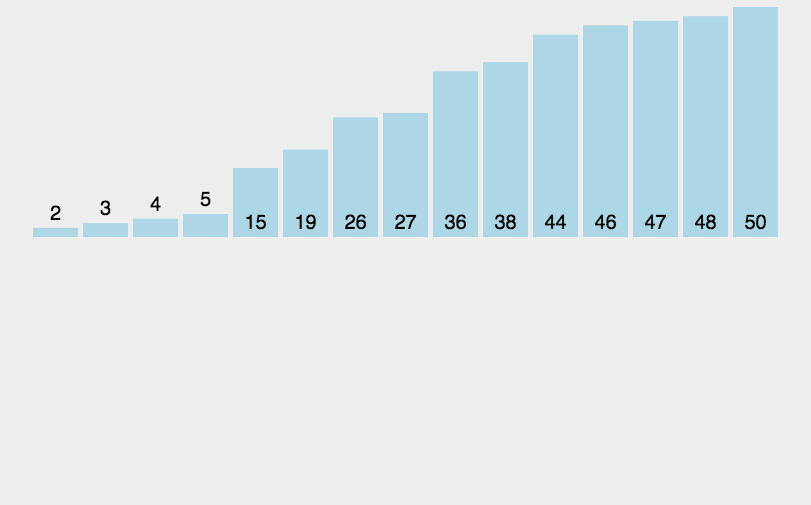
7.3 代码实现
private static void mergeSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); int[] temp = new int[arr.length]; divide(0, arr.length - 1, arr, temp); long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); } private static void divide(int low, int high, int[] arr, int[] temp) { if (high <= low) { return; } int mid = (low + high) / 2; divide(low, mid, arr, temp); divide(mid + 1, high, arr, temp); for (int i = low; i <= high; i++) { temp[i] = arr[i]; } int i = low, j = mid + 1; for (int index = low; index <= high; ++index) { // 如果低位数组用完 则 将高位数组依次复制 if (i > mid) { arr[index] = temp[j++]; } // 如果高位数组用完 则 将低位数组依次复制 else if (j > high) { arr[index] = temp[i++]; } // 如果高位数组最左侧元素 小于 低位数组最左侧元素 则 将高位数组最左侧元素复制 else if (temp[j] < temp[i]) { arr[index] = temp[j++]; } // 如果低位数组最左侧元素 小于或等于 高位数组最左侧元素 则 将低位数组最左侧元素复制 else { arr[index] = temp[i++]; } } if (low == 0 && high == arr.length - 1) { System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); printArray(arr); } }
7.4 算法分析
归并排序是一种稳定的排序方法。和选择排序一样,归并排序的性能不受输入数据的影响,但表现比选择排序好的多,因为始终都是O(nlogn)的时间复杂度。代价是需要额外的内存空间。
8、计数排序
计数排序不是基于比较的排序算法,其核心在于将输入的数据值转化为键存储在额外开辟的数组空间中。 作为一种线性时间复杂度的排序,计数排序要求输入的数据必须是有确定范围的整数。
8.1 算法描述
- 找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素;
- 统计数组中每个值为i的元素出现的次数,存入数组C的第i项;
- 对所有的计数累加(从C中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加);
- 反向填充目标数组:将每个元素i放在新数组的第C(i)项,每放一个元素就将C(i)减去1。
8.2 动图演示
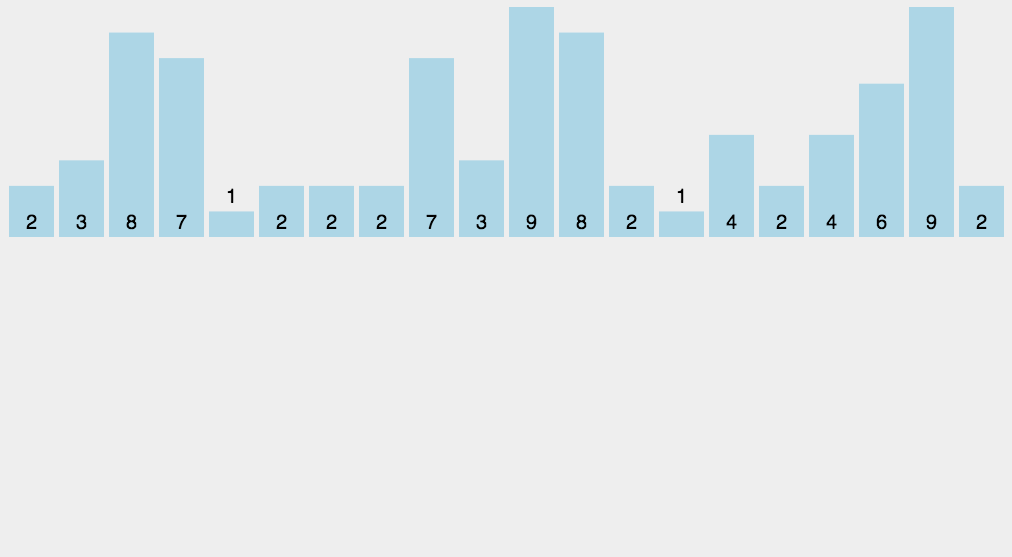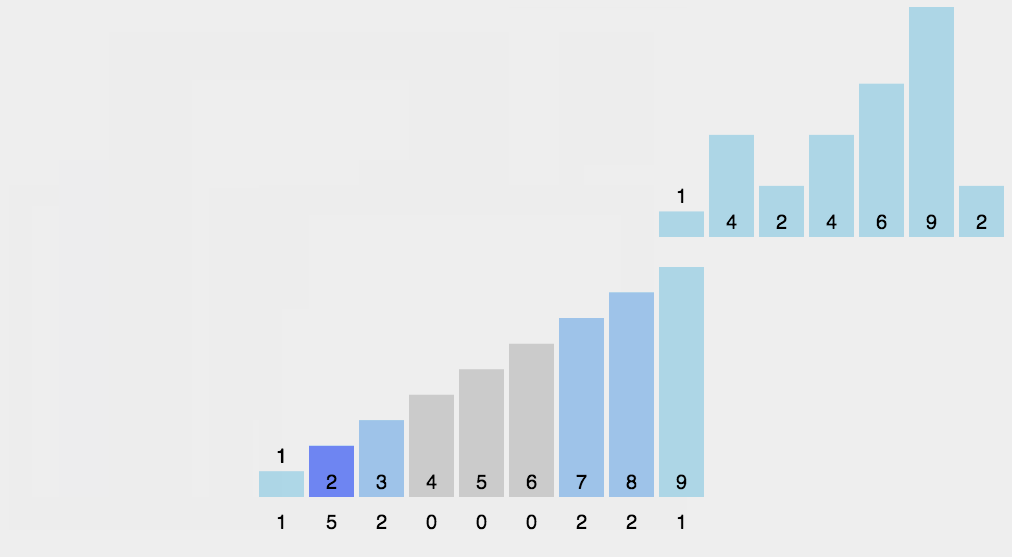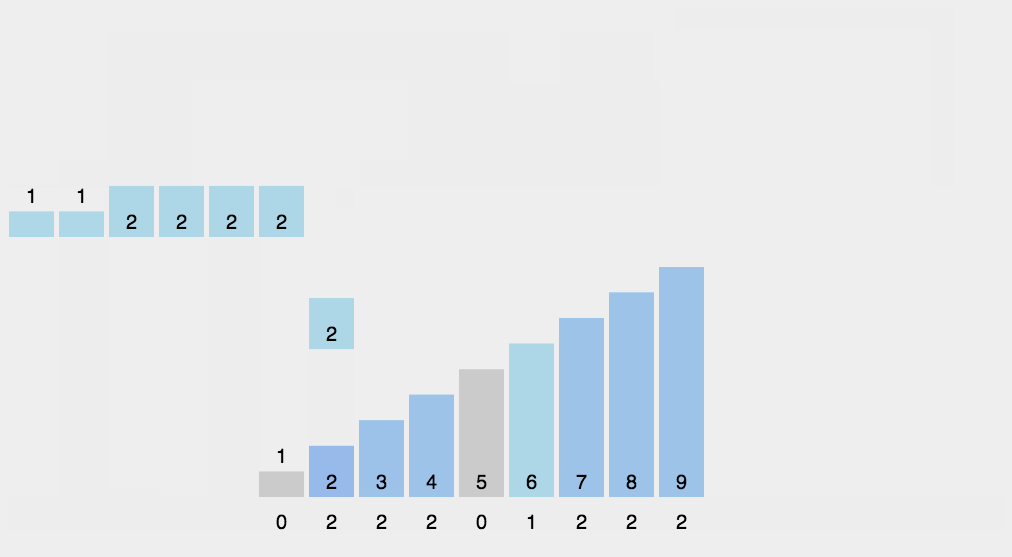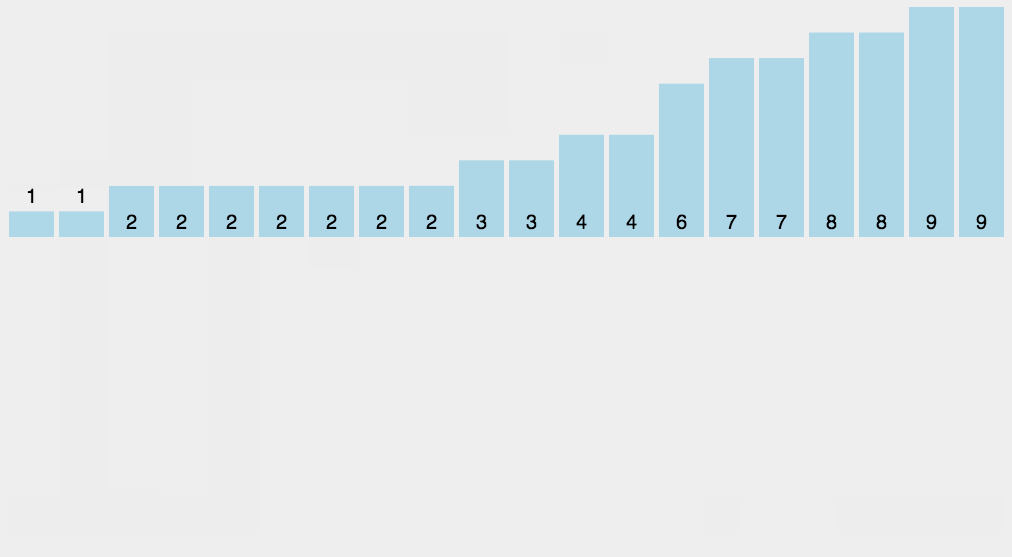
8.3 代码实现
private static void countingSort(int[] arr,int range) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //假设数值范围为0-100 int[] count = new int[range+1]; int len = arr.length; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { count[arr[i]]++; } int countLen = count.length; int data = 0; for (int j = 0; j < countLen; j++) { for (int k = 0; k < count[j]; k++) { arr[data++] = j; } } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); }
8.4 算法分析
计数排序是一个稳定的排序算法。当输入的元素是 n 个 0到 k 之间的整数时,时间复杂度是O(n+k),空间复杂度也是O(n+k),其排序速度快于任何比较排序算法。当k不是很大并且序列比较集中时,计数排序是一个很有效的排序算法。
9、基数排序
基数排序是按照低位先排序,然后收集;再按照高位排序,然后再收集;依次类推,直到最高位。有时候有些属性是有优先级顺序的,先按低优先级排序,再按高优先级排序。最后的次序就是高优先级高的在前,高优先级相同的低优先级高的在前。
9.1 算法描述
- 取得数组中的最大数,并取得位数;
- arr为原始数组,从最低位开始取每个位组成radix数组;
- 对radix进行计数排序(利用计数排序适用于小范围数的特点);
9.2 动图演示
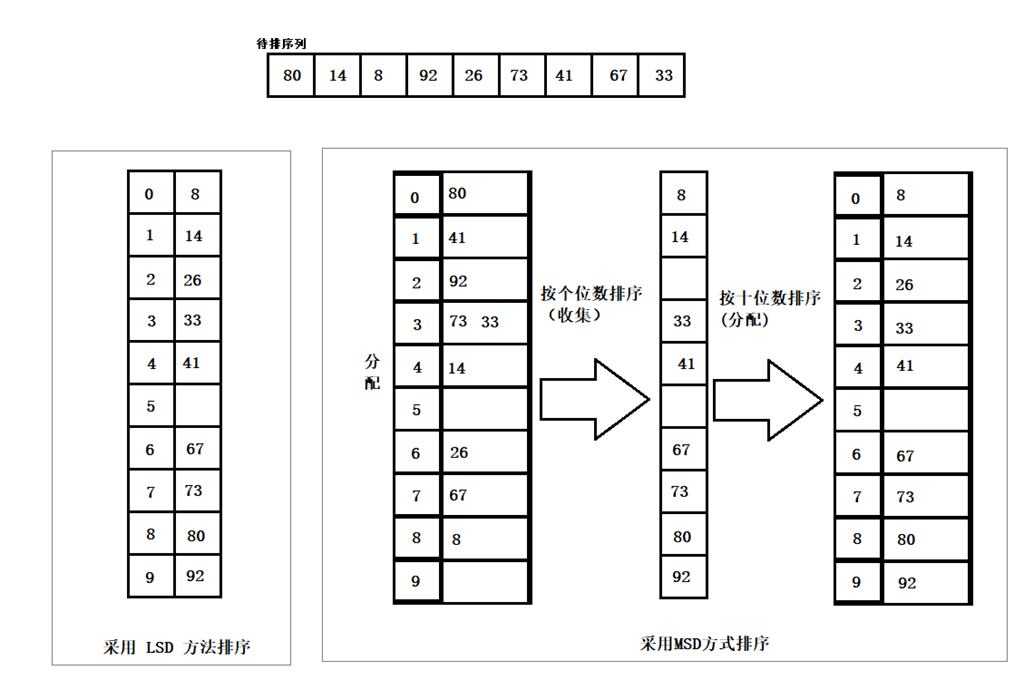

9.3 代码实现
/** * 高位优先法 * * @param arr 待排序列,必须为自然数 */ private static void radixSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //待排序列最大值 int max = arr[0]; int exp;//指数 //计算最大值 for (int anArr : arr) { if (anArr > max) { max = anArr; } } //从个位开始,对数组进行排序 for (exp = 1; max / exp > 0; exp *= 10) { //存储待排元素的临时数组 int[] temp = new int[arr.length]; //分桶个数 int[] buckets = new int[10]; //将数据出现的次数存储在buckets中 for (int value : arr) { //(value / exp) % 10 :value的最底位(个位) buckets[(value / exp) % 10]++; } //更改buckets[i], for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { buckets[i] += buckets[i - 1]; } //将数据存储到临时数组temp中 for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { temp[buckets[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i]; buckets[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--; } //将有序元素temp赋给arr System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, 0, arr.length); } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); }
9.4 算法分析
基数排序基于分别排序,分别收集,所以是稳定的。但基数排序的性能比桶排序要略差,每一次关键字的桶分配都需要O(n)的时间复杂度,而且分配之后得到新的关键字序列又需要O(n)的时间复杂度。假如待排数据可以分为d个关键字,则基数排序的时间复杂度将是O(d*2n) ,当然d要远远小于n,因此基本上还是线性级别的。
基数排序的空间复杂度为O(n+k),其中k为桶的数量。一般来说n>>k,因此额外空间需要大概n个左右。
10、桶排序
桶排序是计数排序的升级版。它利用了函数的映射关系,高效与否的关键就在于这个映射函数的确定。桶排序 (Bucket sort)的工作的原理:假设输入数据服从均匀分布,将数据分到有限数量的桶里,每个桶再分别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序进行排)。
10.1 算法描述
- 设置一个定量的数组当作空桶;
- 遍历输入数据,并且把数据一个一个放到对应的桶里去;
- 对每个不是空的桶进行排序;
- 从不是空的桶里把排好序的数据拼接起来。
10.2 图片演示

10.3 代码实现
public static void bucketSort(int[] arr) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { return; } int len = arr.length; // 根据原始序列的长度,设置桶的数量。这里假设每个桶放平均放4个元素 int bucketCount = len / 4; // 遍历原始序列,找出最大值和最小值 int min = 0, max = 0; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { if (arr[i] > max) { max = arr[i]; } else if (arr[i] < min) { min = arr[i]; } } // 每个桶的数值范围 int range = (max - min + 1) / bucketCount; int[][] buckets = new int[bucketCount][]; // 遍历原始序列 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { int val = arr[i]; // 计算当前值属于哪个桶 int bucketIndex = (int) Math.floor((val - min) / range); // 向桶中添加元素 buckets[bucketIndex] = appendItem(buckets[bucketIndex], val); } // 最后合并所有的桶 int k = 0; for (int[] b : buckets) { if (b != null) { for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { arr[k++] = b[i]; } } } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); printArray(arr); } private static int[] appendItem(int[] bucketArr, int val) { if (bucketArr == null || bucketArr.length == 0) { return new int[]{val}; } // 拷贝一下原来桶的序列,并增加一位 int[] arr = Arrays.copyOf(bucketArr, bucketArr.length + 1); // 这里使用插入排序,将新的值val插入到序列中 int i; for (i = arr.length - 2; i >= 0 && arr[i] > val; i--) { // 从新序列arr的倒数第二位开始向前遍历(倒数第一位是新增加的空位,还没有值) // 如果当前序列值大于val,那么向后移位 arr[i + 1] = arr[i]; } arr[i + 1] = val; return arr; }
10.4 算法分析
桶排序的时间复杂度为O(n + c), 其中n为待排序数据量,c = n * (logn - logm), m为桶的个数。极端情况下,当桶的个数与数据量相等时,桶排序时间复杂度为O(n)。
看一些博客里写道桶排序是稳定排序,另一些博客则说是非稳定排序。实际上,桶排序的稳定性取决于桶内排序所使用的算法,若使用插入排序,则是稳定排序,若使用快排,则是非稳定排序。
所有排序算法实现以及测试代码如下:

1 public class SortMethod { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 int[] array = {1, 34, 45, 13, 6, 68, 47, 22, 49, 33, 7, 16, 50}; 6 // int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13}; 7 // int[] array = {13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; 8 9 System.out.println("排序前数组为:"); 10 printArray(array); 11 System.out.println("----------------------------------交 换 排 序----------------------------------"); 12 bubbleSort(array.clone()); 13 shellSortUsingBubble(array.clone()); 14 quickSort(array.clone()); 15 System.out.println("----------------------------------插 入 排 序----------------------------------"); 16 insertionSort(array.clone()); 17 shellSort(array.clone()); 18 System.out.println("----------------------------------选 择 排 序----------------------------------"); 19 selectionSort(array.clone()); 20 heapSort(array.clone(), array.length - 1, 0); 21 System.out.println("----------------------------------归 并 排 序----------------------------------"); 22 mergeSort(array.clone()); 23 System.out.println("----------------------------------计 数 排 序----------------------------------"); 24 countingSort(array.clone(),100); 25 System.out.println("----------------------------------基 数 排 序----------------------------------"); 26 radixSort(array.clone()); 27 System.out.println("------------------------------------桶 排 序----------------------------------"); 28 bucketSort(array.clone()); 29 System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); 30 31 } 32 33 private static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) { 34 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 35 int count = 0, len = arr.length; 36 for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { 37 for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) { 38 if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { // 相邻元素两两对比 39 int temp = arr[j + 1]; // 元素交换 40 arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; 41 arr[j] = temp; 42 count++; 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 47 48 // System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 49 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 50 // printArray(arr); 51 System.out.println("bubbleSort 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); 52 } 53 54 55 /** 56 * 使用分治法来把一个串(list)分为两个子串(sub-lists),通过一趟排序将待排记录分隔成独立的两部分 57 * 其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分的关键字小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序。 58 * 59 * @param arr 60 */ 61 private static void quickSort(int[] arr) { 62 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 63 // 使用单链表进行排序 64 int count = spilt(arr.clone(), 0, arr.length - 1, 0); 65 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 66 67 // System.out.println("使用单链表进行排序花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 68 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 69 // printArray(arr); 70 System.out.println("quickSort(使用单链表进行排序) 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); 71 72 73 // current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 74 // // 使用双链表进行排序 75 count = partition(arr.clone(), 0, arr.length - 1, 0); 76 // cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 77 // System.out.println("使用双链表进行排序花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 78 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 79 // printArray(arr); 80 System.out.println("quickSort(使用双链表进行排序) 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); 81 } 82 83 private static int spilt(int[] arr, int low, int high, int count) { 84 if (low >= high) { 85 return count; //未发生比较,比较计数器不变 86 } 87 int len = arr.length; 88 int temp, i = low; 89 for (int j = low + 1; j < len; j++) { 90 if (arr[low] > arr[j]) { 91 temp = arr[j]; 92 arr[j] = arr[i + 1]; 93 arr[i + 1] = temp; 94 i++; 95 count++; 96 } 97 } 98 if (i > low) { 99 temp = arr[i]; 100 arr[i] = arr[low]; 101 arr[low] = temp; 102 count++; 103 } 104 count = spilt(arr, low, i - 1, count); 105 count = spilt(arr, i + 1, high, count); 106 return count; 107 } 108 109 public static int partition(int a[], int low, int high, int count) { 110 if (low < high) { 111 //划分数组并获取比较元素的位置 112 int x = a[low], temp; //将该数组第一个元素设置为比较元素 113 int i = low; 114 int j = high; 115 while (i < j) { 116 while (i < j && a[j] >= x) 117 j--; //从右至左找到第一个小于比较元素的数 118 while (i < j && a[i] <= x) 119 i++; //从左至右找到第一个大于比较元素的数 120 /*需要注意的是,这里的j--与i++的顺序不可以调换! 121 *如果调换了顺序,i会走过头,以至于将后面较大的元素交换到数组开头*/ 122 123 //将大数与小数交换 124 if (i != j) { 125 temp = a[i]; 126 a[i] = a[j]; 127 a[j] = temp; 128 count++; 129 } 130 131 } 132 //将比较元素交换到期望位置 133 temp = a[i]; 134 a[i] = a[low]; 135 a[low] = temp; 136 count++; 137 count = partition(a, low, i - 1, count); //对比较元素左边进行排序 138 count = partition(a, i + 1, high, count); //对比较元素右边进行排序 139 } 140 return count; 141 } 142 143 // private static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high, int count) { 144 // if (low >= high) { 145 // return count; //未发生比较,比较计数器不变 146 // } 147 // 148 // int temp; 149 // int i = low + 1, j = high; 150 // if (high == low + 1 && arr[high] < arr[low]) { 151 // temp = arr[low]; 152 // arr[low] = arr[high]; 153 // arr[high] = temp; 154 // count++; 155 // return count; 156 // } 157 // while (i < j) { 158 // while (arr[i] <= arr[low] && j > i) { 159 // i++; 160 // } 161 // while (arr[j] >= arr[low] && j > i) { 162 // j--; 163 // } 164 // if (i < j) { 165 // temp = arr[j]; 166 // arr[j] = arr[i]; 167 // arr[i] = temp; 168 // count++; 169 // } 170 // } 171 // if (i > low + 1) { 172 // temp = arr[i - 1]; 173 // arr[i - 1] = arr[low]; 174 // arr[low] = temp; 175 // count++; 176 // } 177 // count = partition(arr, low, i - 2, count); 178 // count = partition(arr, i, high, count); 179 // return count; 180 // } 181 182 /** 183 * 插入排序 184 * 185 * @param arr 186 */ 187 private static void insertionSort(int[] arr) { 188 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 189 int len = arr.length; 190 int preIndex, temp, count = 0; 191 for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { 192 preIndex = i - 1; 193 temp = arr[i]; 194 while (preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > temp) { 195 arr[preIndex + 1] = arr[preIndex]; 196 count++; 197 preIndex--; 198 } 199 arr[preIndex + 1] = temp; 200 count++; 201 } 202 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 203 204 // System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 205 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 206 // printArray(arr); 207 System.out.println("insertionSort 发生了 " + count + " 次移动。"); 208 } 209 210 /** 211 * shell Sort using exchange method(希尔排序内部用了交换的方式) 212 * 213 * @param arr 214 */ 215 private static void shellSortUsingBubble(int[] arr) { 216 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 217 int count = 0, len = arr.length; 218 //间隔变化 219 for (int gap = len / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) { 220 //对固定间隔的排序 221 for (int i = gap; i < len; i++) { 222 for (int j = i; j > gap - 1; j -= gap) { 223 if (arr[j] < arr[j - gap]) { 224 int temp = arr[j]; 225 arr[j] = arr[j - gap]; 226 arr[j - gap] = temp; 227 count++; 228 } 229 } 230 } 231 } 232 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 233 234 // System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 235 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 236 // printArray(arr); 237 System.out.println("shellSortUsingBubble 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); 238 } 239 240 /** 241 * shell Sort using insert Method: Knuth序列 242 * h = 1 243 * h = 3*h + 1 244 * 一个很长的数组,我们要用能对这个数组采用最大的间隔。最大间隔不能超过数组长度的1/3,当h>1/3时 3h+1 就大于整个数组的长度了,所以就不适合了。 245 */ 246 public static void shellSort(int[] arr) { 247 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 248 int temp, h = 1, count = 0; 249 while (h < arr.length / 3) { 250 h = h * 3 + 1; 251 } 252 253 for (int gap = h; gap > 0; gap = (gap - 1) / 3) { 254 255 for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++) { 256 temp = arr[i]; 257 int preIndex = i - gap; 258 while (preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > temp) { 259 arr[preIndex + gap] = arr[preIndex]; 260 count++; 261 preIndex -= gap; 262 } 263 arr[preIndex + gap] = temp; 264 count++; 265 } 266 } 267 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 268 269 // System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 270 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 271 // printArray(arr); 272 System.out.println("shellSort 发生了 " + count + " 次移动。"); 273 } 274 275 private static void selectionSort(int[] arr) { 276 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 277 int len = arr.length; 278 int minIndex, temp, count = 0; 279 for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { 280 minIndex = i; 281 for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) { 282 if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { // 寻找最小的数 283 minIndex = j; // 将最小数的索引保存 284 } 285 } 286 temp = arr[i]; 287 arr[i] = arr[minIndex]; 288 arr[minIndex] = temp; 289 count++; 290 } 291 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 292 293 // System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 294 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 295 // printArray(arr); 296 System.out.println("selectionSort 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); 297 } 298 299 private static int heapSort(int[] arr, int heapSize, int count) { 300 int temp; 301 if (heapSize > 0) { 302 for (int i = heapSize; i > 0; i--) { 303 if (arr[(i - 1) / 2] < arr[i]) { 304 temp = arr[i]; 305 arr[i] = arr[(i - 1) / 2]; 306 arr[(i - 1) / 2] = temp; 307 count++; 308 } 309 } 310 temp = arr[0]; 311 arr[0] = arr[heapSize]; 312 arr[heapSize] = temp; 313 count++; 314 count = heapSort(arr, --heapSize, count); 315 } else { 316 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 317 // printArray(arr); 318 System.out.println("selectionSort 发生了 " + count + " 次交换, 相当于 " + count * 3 + " 次移动。"); 319 } 320 return count; 321 } 322 323 private static void mergeSort(int[] arr) { 324 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 325 int[] temp = new int[arr.length]; 326 divide(0, arr.length - 1, arr, temp); 327 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 328 System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 329 } 330 331 private static void divide(int low, int high, int[] arr, int[] temp) { 332 if (high <= low) { 333 return; 334 } 335 int mid = (low + high) / 2; 336 divide(low, mid, arr, temp); 337 divide(mid + 1, high, arr, temp); 338 339 for (int i = low; i <= high; i++) { 340 temp[i] = arr[i]; 341 } 342 343 int i = low, j = mid + 1; 344 for (int index = low; index <= high; ++index) { 345 // 如果低位数组用完 则 将高位数组依次复制 346 if (i > mid) { 347 arr[index] = temp[j++]; 348 } 349 // 如果高位数组用完 则 将低位数组依次复制 350 else if (j > high) { 351 arr[index] = temp[i++]; 352 } 353 // 如果高位数组最左侧元素 小于 低位数组最左侧元素 则 将高位数组最左侧元素复制 354 else if (temp[j] < temp[i]) { 355 arr[index] = temp[j++]; 356 } 357 // 如果低位数组最左侧元素 小于或等于 高位数组最左侧元素 则 将低位数组最左侧元素复制 358 else { 359 arr[index] = temp[i++]; 360 } 361 } 362 363 if (low == 0 && high == arr.length - 1) { 364 System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 365 printArray(arr); 366 } 367 } 368 369 private static void countingSort(int[] arr,int range) { 370 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 371 372 //假设数值范围为0-100 373 int[] count = new int[range+1]; 374 int len = arr.length; 375 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { 376 count[arr[i]]++; 377 } 378 int countLen = count.length; 379 int data = 0; 380 for (int j = 0; j < countLen; j++) { 381 for (int k = 0; k < count[j]; k++) { 382 arr[data++] = j; 383 } 384 } 385 386 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 387 // System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 388 // System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 389 printArray(arr); 390 391 } 392 393 /** 394 * 高位优先法 395 * 396 * @param arr 待排序列,必须为自然数 397 */ 398 private static void radixSort(int[] arr) { 399 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 400 //待排序列最大值 401 int max = arr[0]; 402 int exp;//指数 403 404 //计算最大值 405 for (int anArr : arr) { 406 if (anArr > max) { 407 max = anArr; 408 } 409 } 410 411 //从个位开始,对数组进行排序 412 for (exp = 1; max / exp > 0; exp *= 10) { 413 //存储待排元素的临时数组 414 int[] temp = new int[arr.length]; 415 //分桶个数 416 int[] buckets = new int[10]; 417 418 //将数据出现的次数存储在buckets中 419 for (int value : arr) { 420 //(value / exp) % 10 :value的最底位(个位) 421 buckets[(value / exp) % 10]++; 422 } 423 424 //更改buckets[i], 425 for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { 426 buckets[i] += buckets[i - 1]; 427 } 428 429 //将数据存储到临时数组temp中 430 for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 431 temp[buckets[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i]; 432 buckets[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--; 433 } 434 435 //将有序元素temp赋给arr 436 System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, 0, arr.length); 437 } 438 439 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 440 System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 441 System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 442 printArray(arr); 443 444 } 445 446 public static void bucketSort(int[] arr) { 447 long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 448 if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { 449 return; 450 } 451 int len = arr.length; 452 // 根据原始序列的长度,设置桶的数量。这里假设每个桶放平均放4个元素 453 int bucketCount = len / 4; 454 // 遍历原始序列,找出最大值和最小值 455 int min = 0, max = 0; 456 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { 457 if (arr[i] > max) { 458 max = arr[i]; 459 } else if (arr[i] < min) { 460 min = arr[i]; 461 } 462 } 463 // 每个桶的数值范围 464 int range = (max - min + 1) / bucketCount; 465 int[][] buckets = new int[bucketCount][]; 466 // 遍历原始序列 467 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { 468 int val = arr[i]; 469 // 计算当前值属于哪个桶 470 int bucketIndex = (int) Math.floor((val - min) / range); 471 // 向桶中添加元素 472 buckets[bucketIndex] = appendItem(buckets[bucketIndex], val); 473 } 474 // 最后合并所有的桶 475 int k = 0; 476 for (int[] b : buckets) { 477 if (b != null) { 478 for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { 479 arr[k++] = b[i]; 480 } 481 } 482 } 483 long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - current; 484 System.out.println("当前排序算法花费时间为:" + cost + " ms。"); 485 System.out.println("排序后结果为:"); 486 printArray(arr); 487 } 488 489 private static int[] appendItem(int[] bucketArr, int val) { 490 if (bucketArr == null || bucketArr.length == 0) { 491 return new int[]{val}; 492 } 493 // 拷贝一下原来桶的序列,并增加一位 494 int[] arr = Arrays.copyOf(bucketArr, bucketArr.length + 1); 495 // 这里使用插入排序,将新的值val插入到序列中 496 int i; 497 for (i = arr.length - 2; i >= 0 && arr[i] > val; i--) { 498 // 从新序列arr的倒数第二位开始向前遍历(倒数第一位是新增加的空位,还没有值) 499 // 如果当前序列值大于val,那么向后移位 500 arr[i + 1] = arr[i]; 501 } 502 arr[i + 1] = val; 503 return arr; 504 } 505 506 507 private static void printArray(int[] arr) { 508 System.out.print(" "); 509 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 510 System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); 511 } 512 System.out.println(); 513 } 514 515 }
