Building bridges
Problem Description
Hululu and Cululu are two pacific ocean countries made up of many islands. These two country has so many years of friendship so they decide to build bridges to connect their islands. Now they want to build the first bridge to connect an island of Hululu and an island of Culuu .
Their world can be considered as a matrix made up of three letters 'H','C' and 'O'.Every 'H' stands for an island of Hululu, every 'C' stands for an island of Cululu, and 'O' stands for the ocean. Here is a example:
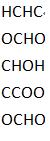
The coordinate of the up-left corner is (0,0), and the down-right corner is (4, 3). The x-direction is horizontal, and the y-direction is vertical.
There may be too many options of selecting two islands. To simplify the problem , they come up with some rules below:
1. The distance between the two islands must be as short as possible. If the two islands' coordinates are (x1,y1) and (x2,y2), the distance is |x1-x2|+|y1-y2|.
2. If there are more than one pair of islands satisfied the rule 1, choose the pair in which the Hululu island has the smallest x coordinate. If there are still more than one options, choose the Hululu island which has the smallest y coordinate.
3.After the Hululu island is decided, if there are multiple options for the Cululu island, also make the choice by rule 2.
Please help their people to build the bridge.
Their world can be considered as a matrix made up of three letters 'H','C' and 'O'.Every 'H' stands for an island of Hululu, every 'C' stands for an island of Cululu, and 'O' stands for the ocean. Here is a example:
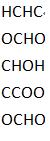
The coordinate of the up-left corner is (0,0), and the down-right corner is (4, 3). The x-direction is horizontal, and the y-direction is vertical.
There may be too many options of selecting two islands. To simplify the problem , they come up with some rules below:
1. The distance between the two islands must be as short as possible. If the two islands' coordinates are (x1,y1) and (x2,y2), the distance is |x1-x2|+|y1-y2|.
2. If there are more than one pair of islands satisfied the rule 1, choose the pair in which the Hululu island has the smallest x coordinate. If there are still more than one options, choose the Hululu island which has the smallest y coordinate.
3.After the Hululu island is decided, if there are multiple options for the Cululu island, also make the choice by rule 2.
Please help their people to build the bridge.
Input
There are multiple test cases.
In each test case, the first line contains two integers M and N, meaning that the matrix is M×N ( 2<=M,N <= 40).
Next M lines stand for the matrix. Each line has N letters.
The input ends with M = 0 and N = 0.
It's guaranteed that there is a solution.
In each test case, the first line contains two integers M and N, meaning that the matrix is M×N ( 2<=M,N <= 40).
Next M lines stand for the matrix. Each line has N letters.
The input ends with M = 0 and N = 0.
It's guaranteed that there is a solution.
Output
For each test case, choose two islands, then print their coordinates in a line in following format:
x1 y1 x2 y2
x1,y1 is the coordinate of Hululu island, x2 ,y2 is the coordinate of Cululu island.
x1 y1 x2 y2
x1,y1 is the coordinate of Hululu island, x2 ,y2 is the coordinate of Cululu island.
Sample Input
4 4
CHCH
HCHC
CCCO
COHO
5 4
OHCH
HCHC
CCCO
COHO
HCHC
0 0
Sample Output
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 2
Source
我想说的话:
这种模拟题吧,正规现场赛经常会有,如果1A的话往往就可以赶上铜奖末班车。这种题还是要思路清晰,不要怕代码长,要对STL熟悉一点,对写代码有很大的帮助的。
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> #include <set> #include <limits.h> #define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b)) #define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b)) using namespace std ; const int size=48 ; struct Me{ int N ,M ; char str[48][48] ; Me(){} Me(int n ,int m):N(n),M(m){} struct Point{ int x ; int y ; Point(){} Point(int i,int j):x(i),y(j){} }; struct Ans{ int H_x ,H_y ; int C_x ,C_y ; Ans(){} Ans(int h_x ,int h_y ,int c_x,int c_y):H_x(h_x),H_y(h_y),C_x(c_x),C_y(c_y){} friend bool operator <(const Ans A ,const Ans B){ if(A.H_x!=B.H_x) return A.H_x<B.H_x ; else{ if(A.H_y!=B.H_y) return A.H_y<B.H_y ; else{ if(A.C_x!=B.C_x) return A.C_x<B.C_x ; else return A.C_y<B.C_y ; } } } }; vector<Point>H ; vector<Point>C ; vector<Ans>dist[100] ; void read(){ for(int i=0;i<N;i++) scanf("%s",str[i]) ; } int Abs(int x){ return x>0?x:-x ; } void get_H_C(){ H.clear() ; C.clear() ; for(int i=0;i<N;i++) for(int j=0;j<M;j++){ if(str[i][j]=='H') H.push_back(Point(i,j)) ; else if(str[i][j]=='C') C.push_back(Point(i,j)) ; } } int find_min_dist(){ read() ; get_H_C() ; for(int i=0;i<100;i++) dist[i].clear() ; for(int i=0;i<H.size();i++) for(int j=0;j<C.size();j++){ dist[Abs(H[i].x-C[j].x)+Abs(H[i].y-C[j].y)].push_back(Ans(H[i].x,H[i].y,C[j].x,C[j].y)) ; } for(int i=1;i<100;i++){ if(dist[i].size()>0) return i ; } } void gao_qi(){ int d=find_min_dist() ; Ans ans[40*40] ; int i ; for(i=0;i<dist[d].size();i++){ ans[i].H_x=dist[d][i].H_x ; ans[i].H_y=dist[d][i].H_y ; ans[i].C_x=dist[d][i].C_x ; ans[i].C_y=dist[d][i].C_y ; } printf("%d %d %d %d ",ans[0].H_x,ans[0].H_y,ans[0].C_x,ans[0].C_y) ; } }; int main(){ int n ,m ; while(cin>>n>>m){ if(n==0&&m==0) break ; Me me(n,m) ; me.gao_qi() ; } return 0 ; }