题目描述
The queen wishes to build a patio paved with of a circular center stone surrounded by circular rings of circular stones. All the stones in a ring will be the same size with the same number of stones in each ring. The stones in the innermost ring will be placed touching (tangent to) the adjacent stones in the
ring and the central stone. The stones in the other rings will touch the two adjacent stones in the next inner ring and their neighbors in the same ring. The fi gures below depict a patio with one ring of three stones and a patio with 5 rings of 11 stones. The patio is to be surrounded by a fence that goes around the outermost stones and straight between them (the heavier line in the fi gures).
 The queen does not yet know how many stones there will be in each circle nor how many circles of stones there will be. To be prepared for whatever she decides, write a program to calculate the sizes of the stones in each circle and the length of the surrounding fence. The radius of the central stone is to be one queenly foot.
The queen does not yet know how many stones there will be in each circle nor how many circles of stones there will be. To be prepared for whatever she decides, write a program to calculate the sizes of the stones in each circle and the length of the surrounding fence. The radius of the central stone is to be one queenly foot.
ring and the central stone. The stones in the other rings will touch the two adjacent stones in the next inner ring and their neighbors in the same ring. The fi gures below depict a patio with one ring of three stones and a patio with 5 rings of 11 stones. The patio is to be surrounded by a fence that goes around the outermost stones and straight between them (the heavier line in the fi gures).

输入
The first line of input contains a single integer P, (1 ≤ P ≤ 1000), which is the number of data sets that follow. Each data set should be processed identically and independently.
Each data set consists of a single line of input. It contains the data set number, K, the number, N (3 ≤ N ≤ 20), of stones in each circle and the number, M (1 ≤ M ≤ 15), of circles of stones around the central stone.
Each data set consists of a single line of input. It contains the data set number, K, the number, N (3 ≤ N ≤ 20), of stones in each circle and the number, M (1 ≤ M ≤ 15), of circles of stones around the central stone.
输出
For each data set there is a single line of output. It contains the data set number, K, followed by a single space which is then followed by the radius (in queenly feet) of the stones in the outermost ring (to 3 decimal places) which is followed by a single space which is then followed by the length (in queenly feet) of the fence (to 3 decimal places).
样例输入
3
1 3 1
2 7 3
3 11 5
样例输出
1 6.464 79.400
2 3.834 77.760
3 2.916 82.481
思路:逐层递推r(勾股定理)。
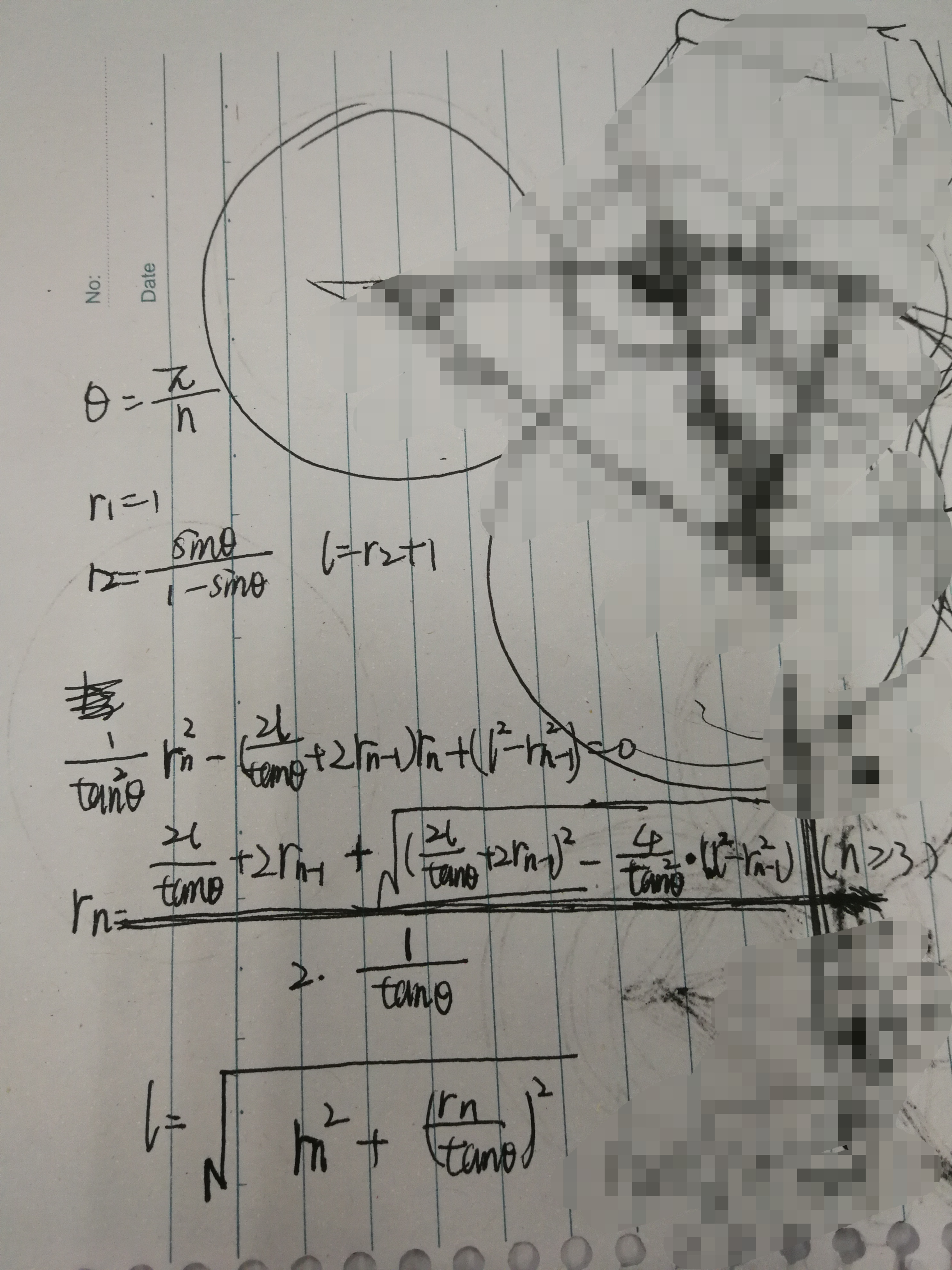
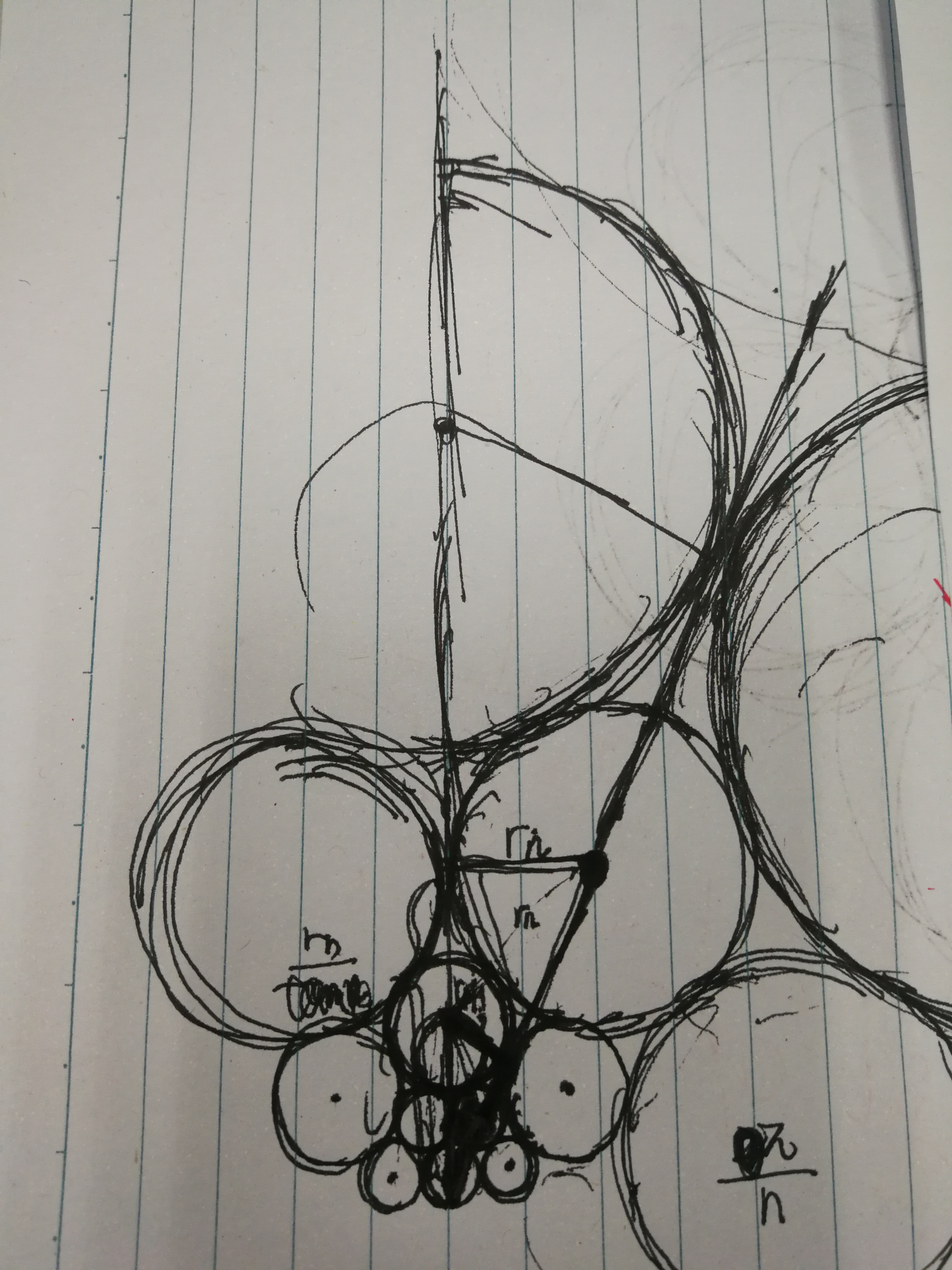
AC代码:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const double PI=acos(-1.0); double r[25]; int main() { int p;scanf("%d",&p); while(p--){ int k,n,m;scanf("%d%d%d",&k,&n,&m); double x=PI*1.0/n; r[1]=1.0; r[2]=sin(x)*1.0/(1.0-sin(x)); double l=r[2]+1.0; for(int i=3;i<=m+1;i++){ double a=1.0/tan(x)/tan(x); double b=-2.0*l/tan(x)-2.0*r[i-1]; double c=l*l-r[i-1]*r[i-1]; double delta=b*b-4.0*a*c; r[i]=(-1.0*b+sqrt(delta))/(2.0*a); l=sqrt(1.0+1.0/tan(x)/tan(x))*r[i]; } double ans=(n+PI)*2.0*r[m+1]; printf("%d %.3f %.3f ",k,r[m+1],ans); } return 0; }
