——1、对话框 Dialog
java.awt.Dialog
和Window一样可以独立存在的一个窗体
但是注意:
1、Dialog对象一定需要一个依附的父级窗口
2、两种模式(模式和非模式),模式打开后总是位于父级窗口的上面,且没关闭对话框是无法获得的父级窗口的焦点
案例:
package cn.dzz; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建窗体 Frame frame = new Frame(); // 创建两个对话框,一个模式的,一个非模式的 Dialog modalDialog = new Dialog(frame, "modal-dialog", true); Dialog nonModalDialog = new Dialog(frame, "non-modal-dialog", false); // 通过setBounds来实现出现在界面上的位置 modalDialog.setBounds(20,30,300,200); nonModalDialog.setBounds(20,30,300,200); // 通过按钮触发弹出 Button mdBtn = new Button("modal-dialog-button"); Button nmdBtn = new Button("non-modal-dialog-button"); mdBtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { modalDialog.setVisible(true); } }); nmdBtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { nonModalDialog.setVisible(true); } }); Box verticalBox = Box.createVerticalBox(); verticalBox.add(mdBtn); verticalBox.add(nmdBtn); frame.add(verticalBox, BorderLayout.CENTER); // 可见 与 自适应 frame.setVisible(true); frame.pack(); } }
案例2:在dialog对象基础上,再向里面添加组件
package cn.dzz; import javafx.scene.layout.Border; import javafx.scene.layout.Pane; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame("GUI-LESSON"); Box verticalBox = Box.createVerticalBox(); Button button = new Button("dialog-demo"); verticalBox.add(button); frame.add(verticalBox, BorderLayout.CENTER); // dialog嵌入 Dialog dialog = new Dialog(frame, "dialog", true); Box verticalBox1 = Box.createVerticalBox(); verticalBox1.add(new TextField(20)); verticalBox1.add(new Button("OK")); dialog.add(verticalBox1, BorderLayout.CENTER); button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { dialog.setVisible(true); } }); frame.pack(); dialog.pack(); // 不要忘记dialog对象也是一个窗体,也需要进行pack自适应 frame.setVisible(true); } }
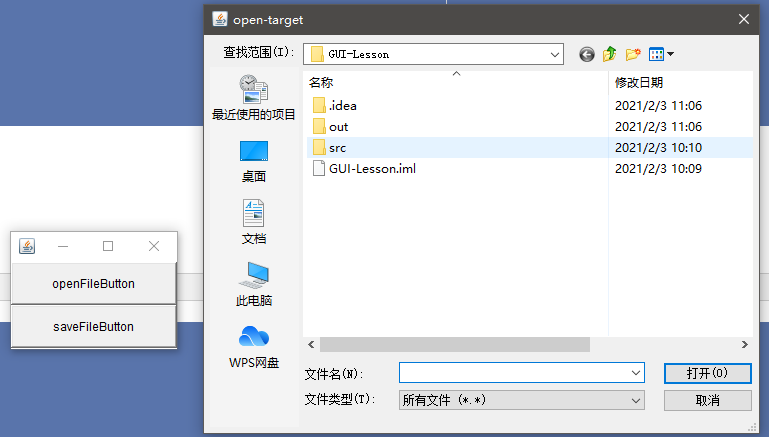
——2、FileDialog文件对话框
java.awt.FileDialog
表示文件对话框,无法选择模式,由底层操作系统的状态决定
几个方法:
String getDirectory(); 获取打开或者保存的文件路径(绝对路径)
String getFile(); 获取打开或者保存的文件名称(仅名称)
案例:
package cn.dzz; import javafx.scene.layout.Border; import javafx.scene.layout.Pane; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame("GUI-LESSON"); // 先来设置打开文件对话框的按钮 Box verticalBox = Box.createVerticalBox(); Button openFileButton = new Button("openFileButton"); Button saveFileButton = new Button("saveFileButton"); verticalBox.add(openFileButton); verticalBox.add(saveFileButton); frame.add(verticalBox, BorderLayout.CENTER); // 创建两个文件对话框对象 FileDialog openD = new FileDialog(frame, "open-target", FileDialog.LOAD); FileDialog saveD = new FileDialog(frame, "save-target", FileDialog.SAVE); // 按钮触发的事件处理 openFileButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { openD.setVisible(true); // 无论打开还是保存的文件对话框,没有点击确认的最终位置,程序只会停留在这里 // 确认之后程序向下执行得到我们需要的文件路径和文件名 String directory = openD.getDirectory(); String file = openD.getFile(); System.out.println("打开的路径 " + directory); System.out.println("打开的文件名 " + file); } }); saveFileButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { saveD.setVisible(true); String directory = saveD.getDirectory(); String file = saveD.getFile(); System.out.println("保存的路径 " + directory); System.out.println("保存的文件名 " + file); } }); frame.pack(); openD.pack(); saveD.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); } }
实际使用时可以发现,如果最后取消了文件选择
那么获取文件路径和文件名的方法返回的值为NULL
打开的路径 C:UsersAdministratorIdeaProjectsGUI-Lesson 打开的文件名 GUI-Lesson.iml 保存的路径 null 保存的文件名 null 打开的路径 null 打开的文件名 null 保存的路径 null 保存的文件名 null