StringBuilder、StringBuffer源码分析
StringBuilder源码分析
类结构
public final class StringBuilder
extends AbstractStringBuilder
implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence
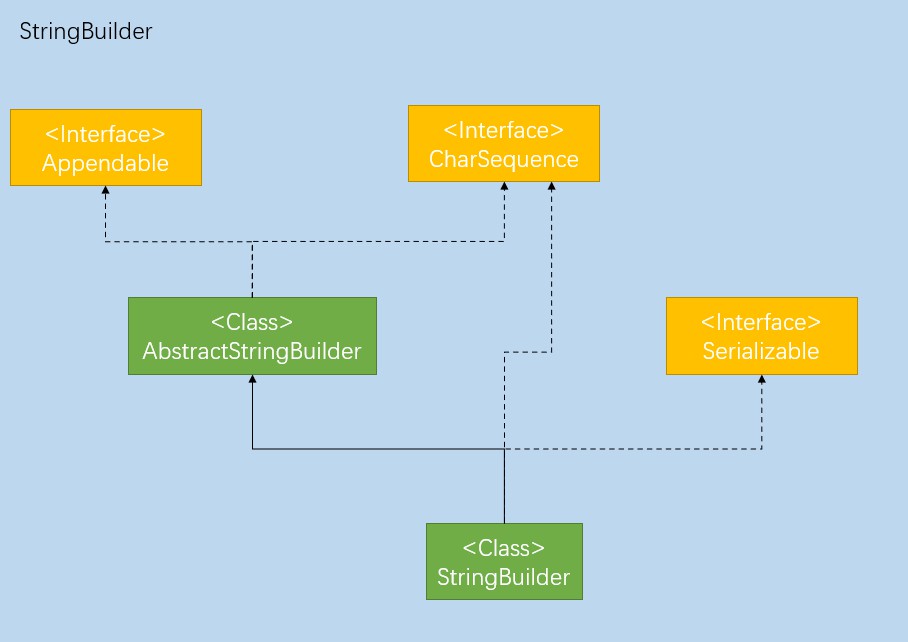
StringBuilder使用final关键字修饰,和String一样不可以被继承
StringBuilder继承AbstractStringBuilder并实现了Serializable和CharSequence,可以被序列化
方法
StringBuilder 的方法多是直接调用父类AbstractStringBuilder的方法,这里找几个典型的方法看一下
StringBuilder append(Object obj)方法重写父类的方法,追加Object类型的元素
@Override
public StringBuilder append(Object obj) {
return append(String.valueOf(obj));//String.valueOf(obj)获取对象转换成的字符串
}
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
@Override
public StringBuilder append(String str) {
super.append(str);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();//如果为null追加字符串“null”
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
//拷贝字符串到数组
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
StringBuilder delete(int start, int end)删除指定起点下标到指定结束下标的字符
@Override
public StringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
super.delete(start, end);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)//如果结束下标>当前保存char的最大下标,直接赋值为最大下标
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int len = end - start;
if (len > 0) {
//把删除尾下标后的元素拷贝到删除起始下标后
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
StringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str)使用字符串替换指定范围内的字符
@Override
public StringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
super.replace(start, end, str);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
int len = str.length();
//计算需要的容量
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
//扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
//删除指定范围的字符
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
//在删除的起始位置插入字符串
str.getChars(value, start);
count = newCount;
return this;
}
StringBuilder insert(int offset, Object obj)在指定位置插入对象
@Override
public StringBuilder insert(int offset, Object obj) {
super.insert(offset, obj);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int offset, Object obj) {
return insert(offset, String.valueOf(obj));//String.valueOf(obj)获取对象转换的字符串
}
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
@Override
public StringBuilder insert(int offset, String str) {
super.insert(offset, str);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int offset, String str) {
if ((offset < 0) || (offset > length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
if (str == null)
str = "null";
int len = str.length();
//扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
//把要插入位置后一定数量的字符(插入字符串长度)串移动后移一定距离(插入字符串长度)
System.arraycopy(value, offset, value, offset + len, count - offset);
//插入要插入的字符串
str.getChars(value, offset);
count += len;
return this;
}
可以看到,StringBuilder的append、insert、replace、delete都是对父类的char数组进行的一些操作,并没有产生新的对象
String toString() 最精髓的一个方法
@Override
public String toString() {
//把进过一些列修改后的最终char数组生成String
return new String(value, 0, count);
}
这里我们看到在toString的时候,把char数组生成了String,这也是为什么StringBuilder比String效率高的原因,String类没做一点修改都会生成新的对象,那么在频繁拼串和截取字符串时,效率当然不如StringBuilder
StringBuffer源码分析
类结构
public final class StringBuffer
extends AbstractStringBuilder
implements java.io.Serializable, CharSequence
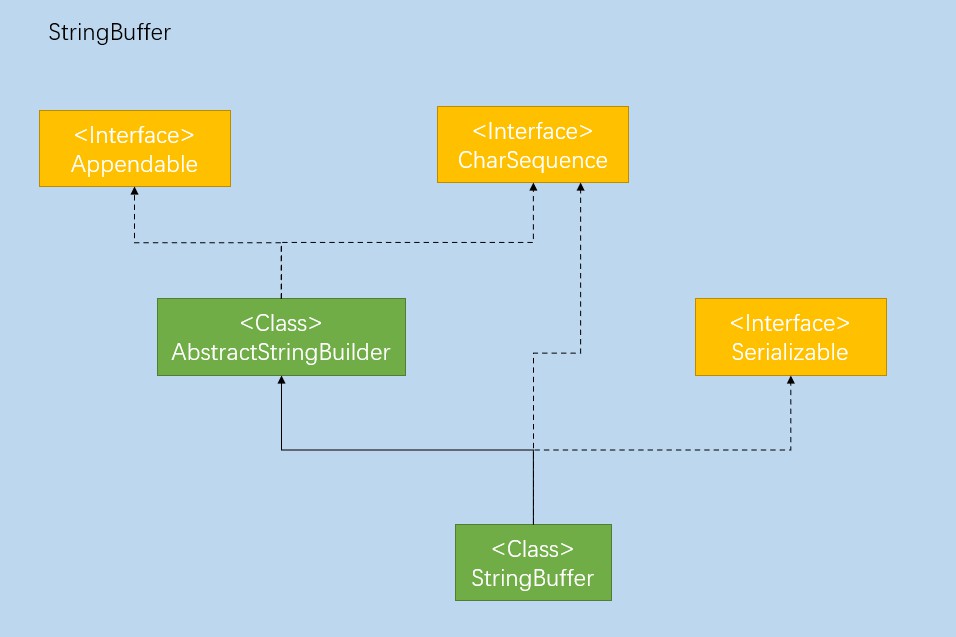
StringBuffer的类结构和StringBuilder的一样
方法
StringBuffer和StringBuilder一样,很多方法都是调用父类AbstractStringBuilder的方法,我们看几个最主要的方法
StringBuffer append(Object obj)向StringBuffer中追加对象,和StringBuilder的追加对象一样的代码
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer append(Object obj) {
toStringCache = null;
super.append(String.valueOf(obj));
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
if (srcBegin < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
}
if (srcEnd > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
}
if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
StringBuffer delete(int start, int end)删除指定范围内的字符,和StringBuilder中delete方法代码一样
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) {
toStringCache = null;
super.delete(start, end);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int len = end - start;
if (len > 0) {
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str)方法使用字符串替换指定范围内的字符,和StringBuilder的replace方法代码一样
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) {
toStringCache = null;
super.replace(start, end, str);
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
int len = str.length();
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
str.getChars(value, start);
count = newCount;
return this;
}
StringBuffer insert(int offset, Object obj)在指定位置插入字符串,也是和StringBuilder的insert方法代码一样
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer insert(int offset, Object obj) {
toStringCache = null;
super.insert(offset, String.valueOf(obj));
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int offset, String str) {
if ((offset < 0) || (offset > length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
if (str == null)
str = "null";
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(value, offset, value, offset + len, count - offset);
str.getChars(value, offset);
count += len;
return this;
}
通过分析这几个方法源码,我们可以看到,StringBuilder和StringBuffer在方法的实现上是一致的,唯一的区别是StringBuffer的所有方法都加了synchronized锁,所以是线程安全的
String toString()把StringBuffer转换成字符串
@Override
public synchronized String toString() {
if (toStringCache == null) {
toStringCache = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, 0, count);
}
return new String(toStringCache, true);
}
StringBuffer与StringBuilder都是在修改的时候并没有产生新的对象,只是在调用toString方法是才转换为字符串。
总结
- StringBuilder和StringBuffer的类结构是一致的,都是使用父类的char数组保存字符。
- StringBuffer的所有方法都加了synchronized锁,所以是线程安全的,但是这也使得它的效率比StringBuilder低。
- StringBuilder和StringBuffer的基本思想是一致的,对StringBuilder、StringBuffer的任何修改都不会产生新对象,这也使得StringBuilder、StringBuffer在进行大量拼串截取时比String的效率高。