configparser模块:
此模块用于生成和修改常见配置文档。
一个常见配置文件(.ini的后缀名)格式如下:
[DEFAULT] # DEFAULT 是指后面的字典里都会默认有的内容 ServerAliveInterval = 45 Compression = yes CompressionLevel = 9 ForwardX11 = yes [bitbucket.org] User = hg [topsecret.server.com] Port = 50022 ForwardX11 = no
解析配置文件:
>>> import configparser >>> config = configparser.ConfigParser() # 开始解析配置文件 # 生成ConfigParser的一个对象config >>> config.sections() # 返回配置文件中的key [] # 没有read之前 config.sections()是个空列表 >>> config.read('example.ini') # read之后, config这个变量就变成了类似字典的数据类型,用法跟字典差不多 # read()之后,就往config这个对象里面添加了 配置文件中的信息 ['example.ini'] >>> config.sections() # read之后就得到了配置文件中的keys ['bitbucket.org', 'topsecret.server.com'] # 判断是否存在某个key >>> 'bitbucket.org' in config True >>> 'bytebong.com' in config False >>> config['bitbucket.org']['User'] 'hg' >>> config['DEFAULT']['Compression'] 'yes' >>> topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com'] >>> topsecret['ForwardX11'] 'no' >>> topsecret['Port'] '50022' >>> for key in config['bitbucket.org']: print(key) # 循环某个key下的value # 由于DEFAULT是每个里面都有的 ,所以也会打印出DEFAULT里面的内容 ... user compressionlevel serveraliveinterval compression forwardx11 >>> config['bitbucket.org']['ForwardX11'] 'yes'
增删改查语法:
配置文件如下:
[group1] k1 = v1 k2:v2 [group2] k1 = v1
对上面的配置文件增删改查(以Python2为例):(和字典的增删改查类似)
import ConfigParser config = ConfigParser.ConfigParser() # 在Python3中改成了小写 configparser config.read('i.cfg') # ########## 读 ########## secs = config.sections() print secs options = config.options('group2') print options item_list = config.items('group2') print item_list val = config.get('group1','key') val = config.getint('group1','key') # ########## 改写 ########## sec = config.remove_section('group1') config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) sec = config.has_section('wupeiqi') sec = config.add_section('wupeiqi') config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) config.set('group2','k1',11111) config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) config.remove_option('group2','age') config.write(open('i.cfg', "w"))
hashlib加密模块:
同一个内容经过 MD5加密后得到结果永远都是唯一的。而且经过MD5处理后的结果是不可逆的, 由密文无法反推明文,只能够利用撞库的方式去尝试反解,所以密码尽量设置的没有规律、复杂一点。
import hashlib m = hashlib.md5() m.update(b'hello') # 如下面关于update的解释, update括号里面必须是二进制格式的bytes,只有这种形式才是可编译的数据类型 m.update(b'neo') print(m.digest()) print(m.hexdigest()) # digest()和hexdigest()的区别看下面的解释 # 打印结果: # b'xadxf1x11xe0&x80;xdax00xd6xfcxb6 xf0&x9c' # adf111e026803bda00d6fcb620f0269c ''' hash.update(arg) Update the hash object with the object arg, which must be interpretable as a buffer of bytes. Repeated calls are equivalent to a single call with the concatenation of all the arguments: m.update(a); m.update(b) is equivalent to m.update(a+b). hash.digest() Return the digest of the data passed to the update() method so far. This is a bytes object of size digest_size( the size of the resulting hash in bytes. ) which may contain bytes in the whole range from 0 to 255. hash.hexdigest() Like digest() except the digest is returned as a string object of double length, containing only hexadecimal digits. This may be used to exchange the value safely in email or other non-binary environments. '''
字符串转成bytes的方法:
一:
a = "abc" b = bytes(a,encoding="utf-8") # 利用bytes()把变量a转换成bytes类型
二:
>>> s = "abc" >>> b = s.encode("utf-8")
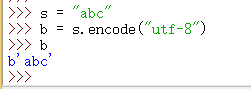
.encode()用法:

subprocess模块:
标准写法:
subprocess.run(['df','-h'],stderr=subprocess.PIPE,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,check=True)
涉及到管道|的命令需要这样写:
subprocess.run('df -h|grep disk1',shell=True) #shell=True的意思是这条命令直接交给系统去执行,不需要python负责解析
Popen()方法
常用参数:
- args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
- stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
- preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
- shell:同上
- cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
- env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
Popen会在发起命令后立刻返回,而不等命令执行结果。
剩下的。。。真的憋不出该怎么写了,,, 以后慢慢学吧