实验二 按键
一、实验目的
1.熟悉linux系统,学会简单linux指令
2.熟悉OK6410-A开发板的烧入步骤
3.熟悉ARM寄存器,地址等。
4.了解中断,定时器,进程等
二、实验仪器
开发机环境
操作系统:ubuntu 20.04
交叉编译环境:arm-linux-gcc 4.6.4
6410板子内核源码:linux-3.0.1
目标板环境
OK6410-A linux-3.0.1
三、实验内容(原理)
1.硬件部分
在驱动模块的初始化函数中实现对按键的初始化,按键的初始化关键是对GPIO引脚的了解,下面是核心板原理图:
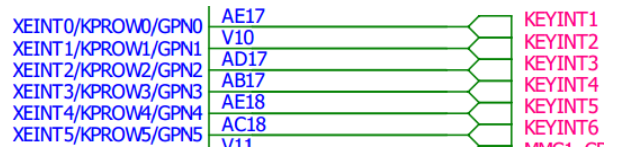
2.寄存器部分
下面的图包括寄存器的bit,输出方式,状态信息等
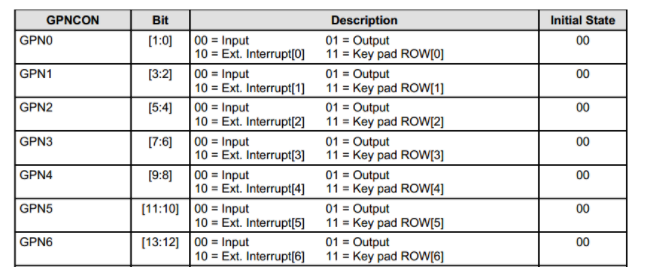
3.中断
这次按键试验使我更加理解了中断这一概念,重点为以下几点:
3.1中断嵌套
所谓的中断嵌套就是,当一种中断正在执行的时候,又产生了另外中断。可以是同类型的,也可以是不同类型的。
慢速中断:是指在进行中断处理的时候,中断的总开关是不关闭的。允许其他类型中断产生。
快速中断:当中断产生的时候,控制位的IF为被置1,别的中断被禁止发生。这样就会产生我们不想看到的情况:中断丢失。
3.2中断分层
上半部:当中断发生时,它进行相应地硬件读写,并“登记”该中断。通常由中断处理程序充当上半部。
下半部:在系统空闲的时候对上半部“登记”的中断进行后续处理。
3.3工作队列
驱动程序中大量运用了工作队列,工作队列是一种将任务推后执行的形式,他把推后的任务交由一个内核线程去执行。这样下半部会在进程上下文执行,它允许重新调度甚至睡眠。 每个被推后的任务叫做“工作”,由这些工作组成的队列称为工作队列
下图为工作队列处理图:
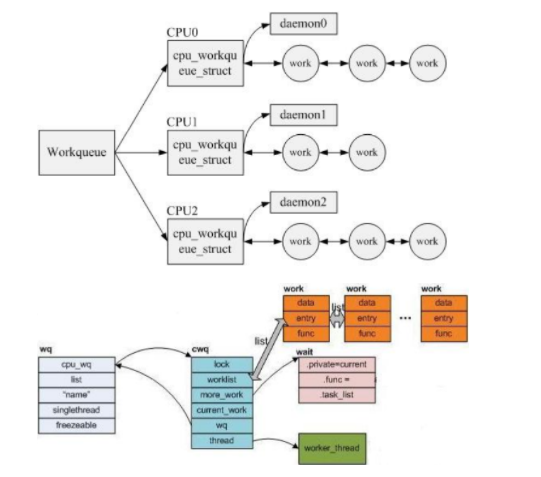
Linux内核使用struct work_struct来描述一个工作队列:
struct workqueue_struct{
struct cpu_workqueue_struct *cpu_wq;
struct list_head list;
const char *name; /*workqueue name*/
int singlethread;
int freezeable; /* Freeze threads during suspend */
int rt;
};
Linux内核使用struct work_struct来描述一个工作项:
struct work_struct{
atomic_long_t data;
struct list_headentry;
work_func_t func;
};
typedef void (*work_func_t)(struct work_struct *work);
4.定时器部分
按键所用开关为机械弹性开关,当机械触点断开、闭合时,由于机械触点的弹性作用,开关不会马上稳定地接通或断开。因而在闭合及断开的瞬间总是伴有一连串的抖动的。按键去抖动的方法主要有两种,一种是硬件电路去抖动;另一种就是软件延时去抖动。而延时又一般分为了两种,一种是for循环等待,另一种是定时器延时。在操作系统中,由于效率方面的原因,一使用定时器。
定时器的使用分为了四个步骤:
1.定义定时器的变量,就是timer_list结构。
2.要对结构进行初始化。Init_timer是系统自动运行的初始化函数,能初始化很大部分timer_list里面的成员。但是,超时函数是需要我们自己设置,就是function。
3.使用add_timer函数注册定时器。
4.mod_timer重启定时器。注意,定时器不是循环的,需要重复调用mod_timer函数。
Linux内核使用struct timer_list来描述一个定时器:
struct timer_list{
struct list_head entry;
unsigned long expires;
void (*function)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
struct tvec_base *base;
};
5.阻塞进程
阻塞进程的概念是正在运行的进程由于提出系统服务请求(如I/O操作),但因为某种原因未得到操作系统的立即响应,或者需要从其他合作进程获得的数据尚未到达等原因,该进程只能调用阻塞原语把自己阻塞,等待相应的事件出现后才被唤醒。
记得吴老师上课讲过,进程阻塞的典型事件有:生产者/消费者问题,理发店问题。
linux内核是采用了一个等待队列的方式来解决进程堵塞的问题,它会将杯堵塞的进程放在一个等待队列,当达到唤醒条件时便唤醒。
队列描述
1、定义等待队列
wait_queue_head_t my_queue
2、初始化等待队列
init_waitqueue_head(&my_queue)
3、定义+初始化等待队列
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(my_queue)
4、进入等待队列,睡眠
4.1 wait_event(queue,condition)
当condition(布尔表达式)为真时,立即返回;否则让进程
进入TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE模式的睡眠,并挂在queue参数所指定的等待队列上。
4.2wait_event_interruptible(queue,condition)
当condition(布尔表达式)为真时,立即返回;否则让
进程进入TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE的睡眠,并挂在queue参数所指定的等待队列上。
4.3int wait_event_killable(queue, condition)
当condition(一个布尔表达式)为真时,立即返回;否则让进程进入TASK_KILLABLE的睡眠,并挂在queue参数所指定的等待队列上。
5、从等待队列中唤醒进程
5.1 wake_up(wait_queue_t *q)
从等待队列q中唤醒状态为TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE,TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,TASK_KILLABLE 的所有进程。
5.2 wake_up_interruptible(wait_queue_t *q)
从等待队列q中唤醒状态为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 的进程
四、实验步骤
1.编写驱动程序
driver_key.c
//driver_key.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <mach/hardware.h>
#include <mach/irqs.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#define DEVICE_NAME "keyint"
#define KEYNUM 6
dev_t devid;
//static DEFINE_SEMAPHORE(key_lock); //declare a mutex lock for keyint
//定义一个信号量
struct semaphore key_lock;
static struct fasync_struct *key_async;
static struct timer_list key_timer;
struct key_irq_desc {
int irq; //irq num
unsigned long flags; //irq flags,identified the way of irq here,eq.edge,level
char *name; //irq name
};
static struct key_irq_desc key_irqs[] = {
//下降沿产生中断
{IRQ_EINT(0), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY1"},
{IRQ_EINT(1), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY2"},
{IRQ_EINT(2), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY3"},
{IRQ_EINT(3), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY4"},
{IRQ_EINT(4), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY5"},
{IRQ_EINT(5), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY6"},
};
/*define a waiting queue here*/
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(key_waitq);
/*define a event flag ev_press*/
static volatile int ev_press = 0;
static volatile int press_cnt[KEYNUM] = {0,0,0,0,0,0};
/*中断处理函数*/
static irqreturn_t keys_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
volatile int *press_cnt = (volatile int *) dev_id;
/*set the pressed key flag(must do here due to not be static value)*/
*press_cnt = *press_cnt + 1;
//延时10ms后执行定时器处理函数
mod_timer(&key_timer,jiffies+HZ/100); //start timer after 10ms
return IRQ_RETVAL(IRQ_HANDLED);
}
//定时器处理函数
static void key_timer_func(unsigned long data)
{
ev_press = 1;
//唤醒等待队列
wake_up_interruptible(&key_waitq);
kill_fasync(&key_async, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
static int key_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int on)
{
printk("Function key_fasync\n");
return fasync_helper(fd,filp,on,&key_async);
}
static unsigned key_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait)
{
unsigned int mask=0;
//指明要使用的等待队列
poll_wait(file,&key_waitq,wait);
//返回掩码
if(ev_press)
mask |= POLL_IN | POLLRDNORM;
printk("poll wait\n");
return mask;
}
static int key_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int num;
if(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {
if(down_trylock(&key_lock)) return -EBUSY;
}
else {
down(&key_lock);
}
//为每个按键注册中断处理程序
for(num=0;num<KEYNUM;num++) {
request_irq(key_irqs[num].irq, keys_interrupt, key_irqs[num].flags, key_irqs[num].name, (void *)&press_cnt[num]);
}
return 0;
}
static int key_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int num;
//释放中断号
for(num=0;num<6;num++) {
free_irq(key_irqs[num].irq, (void *)&press_cnt[num]);
}
up(&key_lock);
printk("key_close free irqs\n");
return 0;
}
static int key_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buff, size_t count, loff_t *offp)
{
// unsigned int err;
//判断是阻塞读还是非阻塞读
if(filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {
if(!ev_press) return -EAGAIN;
}
else {
/*if ev_press==0,then sleep*/
/*阻塞,当有按键按下时(中断)被唤醒*/
wait_event_interruptible(key_waitq,ev_press);
}
//阻塞结束,有键按下了
ev_press = 0;
//拷贝数据到用户空间
copy_to_user(buff,(const void *)press_cnt,min(sizeof(press_cnt),count));
memset((void *)press_cnt,0,sizeof(press_cnt));
// printk("read and clean press_cnt\n");
return 1;
}
static struct file_operations key_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = key_open,
.release = key_close,
.read = key_read,
.poll = key_poll,
.fasync = key_fasync,
};
static struct cdev *cdev_keyint;
static struct class *keyint_class;
//模块初始化函数
static int __init s3c6410_keyint_init(void) {
int val;
/*timer initial */
init_timer(&key_timer);
key_timer.function = key_timer_func;
add_timer(&key_timer);
/*初始化信号量*/
init_MUTEX(&key_lock);
/*register device*/
val = alloc_chrdev_region(&devid,0,1,DEVICE_NAME);
if(val) {
return -1;
printk("register keyint error\n");
}
cdev_keyint = cdev_alloc();
cdev_init(cdev_keyint, &key_ops);
cdev_keyint->owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_keyint->ops = &key_ops;
val = cdev_add(cdev_keyint,devid,1);
if(val) {
return -1;
printk("add device error\n");
}
keyint_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME);
device_create(keyint_class,NULL,devid,NULL,"%s",DEVICE_NAME);
printk("KEY initialezed ^_^\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit s3c6410_keyint_exit(void)
{
cdev_del(cdev_keyint);
device_destroy(keyint_class,devid);
class_destroy(keyint_class);
unregister_chrdev_region(devid,1);
}
module_init(s3c6410_keyint_init);
module_exit(s3c6410_keyint_exit);
2.编写Makefile文件
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := driver_key.o
else
KDIR := /home/kk/Desktop/forlinx/linux-3.0.1
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.mod.o *.mod.c *.symvers
endif
3.编写执行文件
app_key.c
//app_key.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int val;
int i;
int key_value[6];
fd = open("/dev/keyint",0);
if(fd<0) {
printf("open devie error\n");
return -1;
}
while(1) {
val = read(fd,key_value, sizeof(key_value));
if(val<0) {
printf("read error\n");
continue;
}
for (i=0;i<6;i++) {
if(key_value[i])
printf("KEY%d pressed\n",(i+1),key_value[i]);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
4.编译驱动程序与测试程序
#make
将编译生成 driver_key.ko等文件
#arm-linux-gcc app_key.c -o anjian
将生成anjian可执行文件
最后呈现以下文件
5.修改系统内核文件
在原有到内核中,按键的GPIO口被占用,需要进行相应到修改才能达到预期到效果,首先需要做的是安装libncurses 的相关软件,来实现对内核到编写
内核编写过程:
找到内核
make menuconfig
按照下面一路选择
Device Drivers
Input device support
keyboards
有GPIO Buttons
把这个选项去掉
make zImage
生成zImage镜像文件
之后重新烧写
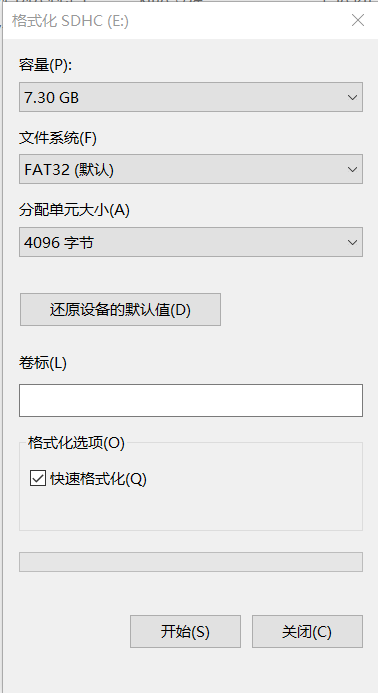
6.格式化SD卡,把 SD 卡格式化为 FAT32 格式。
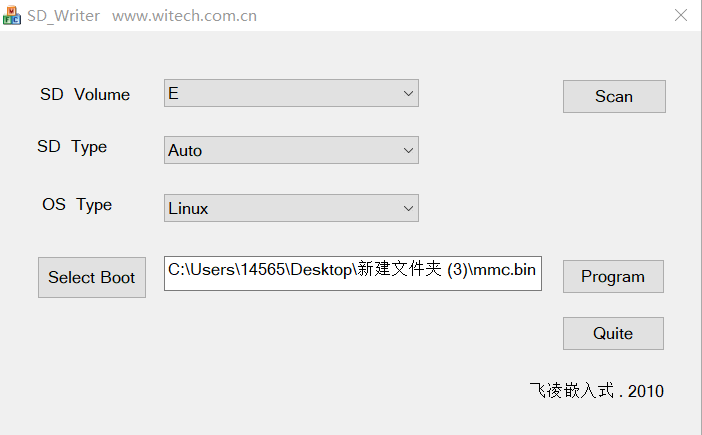
7.用SD_Writer将 mmc.bin 烧写到 SD 卡中
1.以管理员身份运行
2.点击”Scan”,这个步骤是自动搜寻 SD 卡所在盘符。如果"Scan"没有正确设置 SD 卡所在盘符,就需要手动 调整 SD Volume,把盘符号调整为 SD 卡所在盘符(比如说,PC 的 USB 口接了两个或者两个以上的 U 盘或 者 SD 卡,就有可能错误到扫描 SD 卡盘符)。
3.将”SD Type”更改为 auto。这个步骤是为了让 SD_Writer 自动识别 SD 卡类型。
4.将”OS Type”更改为 Linux。这个步骤是选择要烧写的系统类型。
5.点击”Select Boot”, 选择适合自己开发板的 mmc.bin
mmc_ram128.bin 适用于 128M 内存的开发板
mmc_ram256.bin 适用于 256M 内存的开发板
6.点击”Program”,出现”It’s OK”表示操作成功。
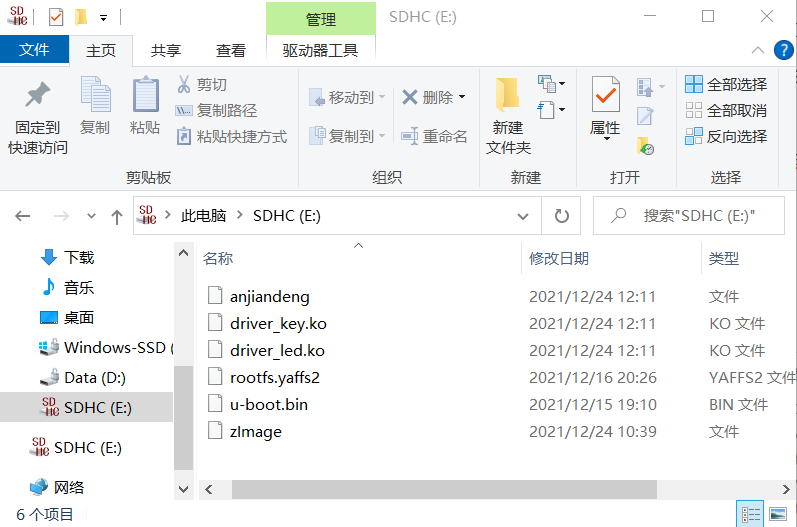
8.拷贝系统文件
首先,将 u-boot.bin 拷贝到 SD 卡中。
u-boot_ram128.bin 专门用于 128M 内存开发板。
u-boot_ram256.bin 专门用于 256M 内存开发板。
将与开发板对应的 u-boot 拷贝到 SD 卡中。接着在 SD 卡中将文件名改为u-boot.bin 即可。
然后,将 zImage 拷贝到 SD 卡中。zImage 是 Linux 的内核映像文件。
最后,将 rootfs.yaffs2 拷贝到 SD 卡中。
rootfs.yaffs2-nand256m 专门用于 128M 内存,256M NandFlash开发板。
rootfs.yaffs2-nand2g 专门用于 256M 内存,1G 或 2G 或者 4G Nandflash 的开发板
9.拷贝驱动程序与测试程序
将driver_led.ko与test拷贝到SD卡上
10.烧写Linux到开发板的NandFlash
步骤 1. 将制作好的 SD 卡插入开发板 SD 的插槽。
步骤 2. 接好 5V 直流电源(飞凌提供此电源,请使用飞凌提供的电源)。
步骤 3. 拨码开关设置为 SD 卡启动。
拨码开关在底板SD 卡启动的拨码开关设置如下:
| 引脚号 | Pin8 | Pin7 | Pin6 | Pin5 | Pin4 | Pin3 | Pin2 | Pin1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 引脚定义 | SELNAND | OM4 | OM3 | OM2 | OM1 | GPN15 | GPN14 | GPN13 |
| SD卡启动 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
11. 测试
1.打开终端
2.加载驱动
#insmod /sdcard/driver_key.ko
3.创建设备文件
#mknod /dev/my_led c 240 0
4.测试
./anjian
5.卸载驱动
#rmmod driver_key

五、实验程序(包括流程图)
1.编写驱动程序
driver_key.c
//driver_key.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <mach/hardware.h>
#include <mach/irqs.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#define DEVICE_NAME "keyint"
#define KEYNUM 6
dev_t devid;
//static DEFINE_SEMAPHORE(key_lock); //declare a mutex lock for keyint
//定义一个信号量
struct semaphore key_lock;
static struct fasync_struct *key_async;
static struct timer_list key_timer;
struct key_irq_desc {
int irq; //irq num
unsigned long flags; //irq flags,identified the way of irq here,eq.edge,level
char *name; //irq name
};
static struct key_irq_desc key_irqs[] = {
//下降沿产生中断
{IRQ_EINT(0), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY1"},
{IRQ_EINT(1), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY2"},
{IRQ_EINT(2), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY3"},
{IRQ_EINT(3), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY4"},
{IRQ_EINT(4), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY5"},
{IRQ_EINT(5), IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "KEY6"},
};
/*define a waiting queue here*/
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(key_waitq);
/*define a event flag ev_press*/
static volatile int ev_press = 0;
static volatile int press_cnt[KEYNUM] = {0,0,0,0,0,0};
/*中断处理函数*/
static irqreturn_t keys_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
volatile int *press_cnt = (volatile int *) dev_id;
/*set the pressed key flag(must do here due to not be static value)*/
*press_cnt = *press_cnt + 1;
//延时10ms后执行定时器处理函数
mod_timer(&key_timer,jiffies+HZ/100); //start timer after 10ms
return IRQ_RETVAL(IRQ_HANDLED);
}
//定时器处理函数
static void key_timer_func(unsigned long data)
{
ev_press = 1;
//唤醒等待队列
wake_up_interruptible(&key_waitq);
kill_fasync(&key_async, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
static int key_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int on)
{
printk("Function key_fasync\n");
return fasync_helper(fd,filp,on,&key_async);
}
static unsigned key_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait)
{
unsigned int mask=0;
//指明要使用的等待队列
poll_wait(file,&key_waitq,wait);
//返回掩码
if(ev_press)
mask |= POLL_IN | POLLRDNORM;
printk("poll wait\n");
return mask;
}
static int key_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int num;
if(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {
if(down_trylock(&key_lock)) return -EBUSY;
}
else {
down(&key_lock);
}
//为每个按键注册中断处理程序
for(num=0;num<KEYNUM;num++) {
request_irq(key_irqs[num].irq, keys_interrupt, key_irqs[num].flags, key_irqs[num].name, (void *)&press_cnt[num]);
}
return 0;
}
static int key_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int num;
//释放中断号
for(num=0;num<6;num++) {
free_irq(key_irqs[num].irq, (void *)&press_cnt[num]);
}
up(&key_lock);
printk("key_close free irqs\n");
return 0;
}
static int key_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buff, size_t count, loff_t *offp)
{
// unsigned int err;
//判断是阻塞读还是非阻塞读
if(filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {
if(!ev_press) return -EAGAIN;
}
else {
/*if ev_press==0,then sleep*/
/*阻塞,当有按键按下时(中断)被唤醒*/
wait_event_interruptible(key_waitq,ev_press);
}
//阻塞结束,有键按下了
ev_press = 0;
//拷贝数据到用户空间
copy_to_user(buff,(const void *)press_cnt,min(sizeof(press_cnt),count));
memset((void *)press_cnt,0,sizeof(press_cnt));
// printk("read and clean press_cnt\n");
return 1;
}
static struct file_operations key_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = key_open,
.release = key_close,
.read = key_read,
.poll = key_poll,
.fasync = key_fasync,
};
static struct cdev *cdev_keyint;
static struct class *keyint_class;
//模块初始化函数
static int __init s3c6410_keyint_init(void) {
int val;
/*timer initial */
init_timer(&key_timer);
key_timer.function = key_timer_func;
add_timer(&key_timer);
/*初始化信号量*/
init_MUTEX(&key_lock);
/*register device*/
val = alloc_chrdev_region(&devid,0,1,DEVICE_NAME);
if(val) {
return -1;
printk("register keyint error\n");
}
cdev_keyint = cdev_alloc();
cdev_init(cdev_keyint, &key_ops);
cdev_keyint->owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_keyint->ops = &key_ops;
val = cdev_add(cdev_keyint,devid,1);
if(val) {
return -1;
printk("add device error\n");
}
keyint_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME);
device_create(keyint_class,NULL,devid,NULL,"%s",DEVICE_NAME);
printk("KEY initialezed ^_^\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit s3c6410_keyint_exit(void)
{
cdev_del(cdev_keyint);
device_destroy(keyint_class,devid);
class_destroy(keyint_class);
unregister_chrdev_region(devid,1);
}
module_init(s3c6410_keyint_init);
module_exit(s3c6410_keyint_exit);
2.编写Makefile文件
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := driver_key.o
else
KDIR := /home/kk/Desktop/forlinx/linux-3.0.1
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.mod.o *.mod.c *.symvers
endif
3.编写执行文件
app_key.c
//app_key.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int val;
int i;
int key_value[6];
fd = open("/dev/keyint",0);
if(fd<0) {
printf("open devie error\n");
return -1;
}
while(1) {
val = read(fd,key_value, sizeof(key_value));
if(val<0) {
printf("read error\n");
continue;
}
for (i=0;i<6;i++) {
if(key_value[i])
printf("KEY%d pressed\n",(i+1),key_value[i]);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
4.流程图
.png)
六、运行结果
按键按下的屏幕显示:

七、心得体会
本次实验使我对中断有了更为深刻的理解,不再是以前学单片机的时候遇到更紧急的事,设一个断点,事完成了,再回到断点,做当前的事,那么简单。而是了解了中断嵌套,中断分层,工作队列技术等等中断的复杂运用。还学会了利用定时器的延时来达到去抖的目的,另一方面,对进程和进程阻塞有了更深入的了解。