Solr4.8.0源码分析(17)之SolrCloud索引深入(4)
前面几节以add为例已经介绍了solrcloud索引链建索引的三步过程,delete以及deletebyquery跟add过程大同小异,这里暂时就不介绍了。由于commit流程较为特殊,那么本节主要简要介绍下commit的流程。
1. SolrCloud的commit流程
SolrCloud的commit流程同样分为三步,本节主要简单介绍下三步过程。
1.1 LogUpdateProcessor
LogUpdateProcessor的commit比较简单,主要包含两个步骤,调用DistributedUpdateProcessor的commit以及将commit信息写入日志。
1 public void processCommit( CommitUpdateCommand cmd ) throws IOException { 2 if (logDebug) { log.debug("PRE_UPDATE " + cmd.toString() + " " + req); } 3 if (next != null) next.processCommit(cmd); 4 5 6 final String msg = cmd.optimize ? "optimize" : "commit"; 7 toLog.add(msg, ""); 8 }
1.2 DistributedUpdateProcessor
DistributedUpdateProcessor的commit过程较前者稍微复杂点,主要有一个判断,如果本节点满足以下几点之一,不是集群,只有一个node且是leader,是被转发过来的,就会进行dolocalcommit,否则的就会进行commit请求的转发。其中dolocalcommit会调用DirectUpdateHandler2的commit。
1 @Override 2 public void processCommit(CommitUpdateCommand cmd) throws IOException { 3 updateCommand = cmd; 4 List<Node> nodes = null; 5 boolean singleLeader = false; 6 if (zkEnabled) { 7 zkCheck(); 8 9 nodes = getCollectionUrls(req, req.getCore().getCoreDescriptor() 10 .getCloudDescriptor().getCollectionName()); 11 if (isLeader && nodes.size() == 1) { 12 singleLeader = true; 13 } 14 } 15 16 if (!zkEnabled || req.getParams().getBool(COMMIT_END_POINT, false) || singleLeader) { 17 doLocalCommit(cmd); 18 } else if (zkEnabled) { 19 ModifiableSolrParams params = new ModifiableSolrParams(filterParams(req.getParams())); 20 if (!req.getParams().getBool(COMMIT_END_POINT, false)) { 21 params.set(COMMIT_END_POINT, true); 22 params.set(DISTRIB_UPDATE_PARAM, DistribPhase.FROMLEADER.toString()); 23 params.set(DISTRIB_FROM, ZkCoreNodeProps.getCoreUrl( 24 zkController.getBaseUrl(), req.getCore().getName())); 25 if (nodes != null) { 26 cmdDistrib.distribCommit(cmd, nodes, params); 27 finish(); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 }
1 private void doLocalCommit(CommitUpdateCommand cmd) throws IOException { 2 if (vinfo != null) { 3 vinfo.lockForUpdate(); 4 } 5 try { 6 7 if (ulog == null || ulog.getState() == UpdateLog.State.ACTIVE || (cmd.getFlags() & UpdateCommand.REPLAY) != 0) { 8 super.processCommit(cmd); 9 } else { 10 log.info("Ignoring commit while not ACTIVE - state: " + ulog.getState() + " replay:" + (cmd.getFlags() & UpdateCommand.REPLAY)); 11 } 12 13 } finally { 14 if (vinfo != null) { 15 vinfo.unlockForUpdate(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
1.3 DirectUpdateHandler2
现在才是commit最关键的流程,DirectUpdateHandler2的commit流程。本步骤的commit包含了对softcommit和hardcommit的处理。
- commit过程包含prepareCommit,Commit,以及postCommit,我们主要关注的是commit
- 当进行commit时,会首先取消等待的softcommit和hardcommit。因为commit的效果是对整个solr的,所以多个commit只会影响性能而不会影响效果。
- 其次solr还会判断是否需要进行索引优化,即optimize。optimize的本质是合并策略中的forcemerge,forcemerge比较暴力,它不管你的合并策略是怎么限制segemnt的大小以及个数,它会一股脑的把所有的segment挤成一个,所以他是很费性能的。关于forcemerge的具体内容将在后续的介绍merge中展开。如果不需要优化optimize,Solr会进行forceMergeDeletes来删除已标记删除的document,它相当于一个小型的forcemerge,对性能的影响较少。当然,forcemerge也会对标记删除的document进行真正的删除。
- Solr存在一种情况,没有进行commit但是索引发生变化了,Solr会进行检查这种情况,如果发生了就会进行一次commit。
- 如果Solr进行的softcommit,首先会对ulog进行一次commit操作,将ulog进行一次清理。同时会调用getSearcher()来重新打开一个SolrIndexSearch满足实时性的要求。SolrIndexSearch是本节的重点,将在第2节重点介绍。
- 如果Solr进行的是hardcommit,那么Solr会删除ulog中最旧的日志(前文中讲到的addOldLog),生成新的日志文件TransactionLog编号。Solr会根据是否需要打开Searcher来调用getSearcher还是openNewSearcher。
- 最后waitSearcher[0].get()会等待新的Searcher打开。
- 以上就是DirectUpdateHandler2 commit的主要步骤,重点是在getSearcher和openNewSearcher上,下一节将重点介绍。
1 public void commit(CommitUpdateCommand cmd) throws IOException { 2 if (cmd.prepareCommit) { 3 prepareCommit(cmd); 4 return; 5 } 6 7 if (cmd.optimize) { 8 optimizeCommands.incrementAndGet(); 9 } else { 10 commitCommands.incrementAndGet(); 11 if (cmd.expungeDeletes) expungeDeleteCommands.incrementAndGet(); 12 } 13 14 Future[] waitSearcher = null; 15 if (cmd.waitSearcher) { 16 waitSearcher = new Future[1]; 17 } 18 19 boolean error=true; 20 try { 21 // only allow one hard commit to proceed at once 22 if (!cmd.softCommit) { 23 solrCoreState.getCommitLock().lock(); 24 } 25 26 log.info("start "+cmd); 27 28 // We must cancel pending commits *before* we actually execute the commit. 29 30 if (cmd.openSearcher) { 31 // we can cancel any pending soft commits if this commit will open a new searcher 32 softCommitTracker.cancelPendingCommit(); 33 } 34 if (!cmd.softCommit && (cmd.openSearcher || !commitTracker.getOpenSearcher())) { 35 // cancel a pending hard commit if this commit is of equal or greater "strength"... 36 // If the autoCommit has openSearcher=true, then this commit must have openSearcher=true 37 // to cancel. 38 commitTracker.cancelPendingCommit(); 39 } 40 41 RefCounted<IndexWriter> iw = solrCoreState.getIndexWriter(core); 42 try { 43 IndexWriter writer = iw.get(); 44 if (cmd.optimize) { 45 writer.forceMerge(cmd.maxOptimizeSegments); 46 } else if (cmd.expungeDeletes) { 47 writer.forceMergeDeletes(); 48 } 49 50 if (!cmd.softCommit) { 51 synchronized (solrCoreState.getUpdateLock()) { // sync is currently needed to prevent preCommit 52 // from being called between preSoft and 53 // postSoft... see postSoft comments. 54 if (ulog != null) ulog.preCommit(cmd); 55 } 56 57 // SolrCore.verbose("writer.commit() start writer=",writer); 58 59 if (writer.hasUncommittedChanges()) { 60 final Map<String,String> commitData = new HashMap<>(); 61 commitData.put(SolrIndexWriter.COMMIT_TIME_MSEC_KEY, 62 String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis())); 63 writer.setCommitData(commitData); 64 writer.commit(); 65 } else { 66 log.info("No uncommitted changes. Skipping IW.commit."); 67 } 68 69 // SolrCore.verbose("writer.commit() end"); 70 numDocsPending.set(0); 71 callPostCommitCallbacks(); 72 } else { 73 callPostSoftCommitCallbacks(); 74 } 75 } finally { 76 iw.decref(); 77 } 78 79 80 if (cmd.optimize) { 81 callPostOptimizeCallbacks(); 82 } 83 84 85 if (cmd.softCommit) { 86 // ulog.preSoftCommit(); 87 synchronized (solrCoreState.getUpdateLock()) { 88 if (ulog != null) ulog.preSoftCommit(cmd); 89 core.getSearcher(true, false, waitSearcher, true); 90 if (ulog != null) ulog.postSoftCommit(cmd); 91 } 92 // ulog.postSoftCommit(); 93 } else { 94 synchronized (solrCoreState.getUpdateLock()) { 95 if (ulog != null) ulog.preSoftCommit(cmd); 96 if (cmd.openSearcher) { 97 core.getSearcher(true, false, waitSearcher); 98 } else { 99 // force open a new realtime searcher so realtime-get and versioning code can see the latest 100 RefCounted<SolrIndexSearcher> searchHolder = core.openNewSearcher(true, true); 101 searchHolder.decref(); 102 } 103 if (ulog != null) ulog.postSoftCommit(cmd); 104 } 105 if (ulog != null) ulog.postCommit(cmd); // postCommit currently means new searcher has 106 // also been opened 107 } 108 109 // reset commit tracking 110 111 if (cmd.softCommit) { 112 softCommitTracker.didCommit(); 113 } else { 114 commitTracker.didCommit(); 115 } 116 117 log.info("end_commit_flush"); 118 119 error=false; 120 } 121 finally { 122 if (!cmd.softCommit) { 123 solrCoreState.getCommitLock().unlock(); 124 } 125 126 addCommands.set(0); 127 deleteByIdCommands.set(0); 128 deleteByQueryCommands.set(0); 129 if (error) numErrors.incrementAndGet(); 130 } 131 132 // if we are supposed to wait for the searcher to be registered, then we should do it 133 // outside any synchronized block so that other update operations can proceed. 134 if (waitSearcher!=null && waitSearcher[0] != null) { 135 try { 136 waitSearcher[0].get(); 137 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 138 SolrException.log(log,e); 139 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 140 SolrException.log(log,e); 141 } 142 } 143 }
2. getSearcher
getSearcher 获取一个现有的SolrIndexSearcher或者创建新的SolrIndexSearcher。每当进行SoftCommit的时候,重新创建一个新的SolrIndexSearcher是实现近实时索引的基础。在重新打开SolrIndexSearcher的时候,Solr不但会进行预热(warn),而且还会新建SolrEventListener。
1 public RefCounted<SolrIndexSearcher> getSearcher(boolean forceNew, boolean returnSearcher, final Future[] waitSearcher, boolean updateHandlerReopens) { 2 }
getSearcher主要包含以下几个参数:
- 如果已有IndexSearcher打开,是否需要强制打开新的IndexSearcher。如果设置为ture,那么每次都会打开新的IndexSearcher,那么刚add的document就是可查讯的,近实时查询需要该值为true。
- waitSearcher 如果该值不为空,那么Solr会得到新的Searcher注册后才会返回新的Searcher。如果在重新打开Searcher的过程中需要进行预热(关于预热下节重点介绍),那么这个waitSearcher就会等到预热完成才返回,而预热的过程往往会占用大量的时间,比较影响索引的性能。
-
returnSearcher 如果设置为ture,则返回SolrIndexSearcher,并引用加1.
接下来通过源码,来学习下Solr是如何获取到一个Seacher。
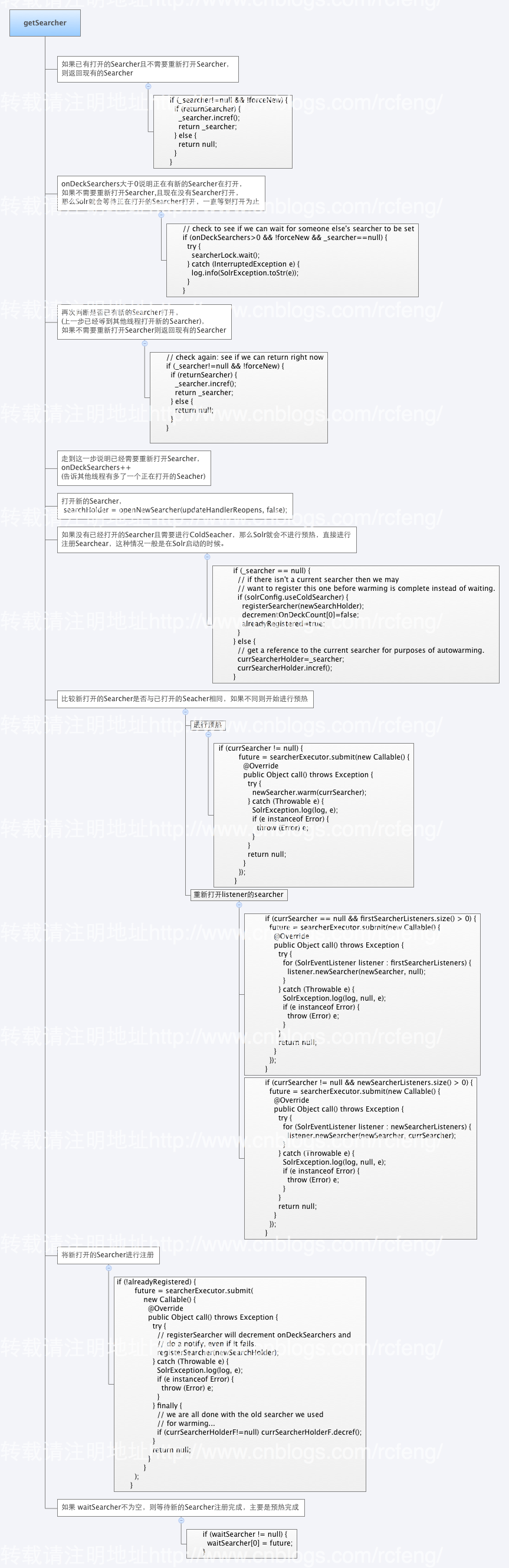
需要补充几点:
-
onDeckSearchers 表示正在准备新建的Searcher。该值在SolrConfig.xml可以进行配置,该值很大程度上制约了多线程建索引的线程数。如果同时用10个线程在建索引,且commit比较频繁,而maxWarmingSearchers设置为8,那么很容出现以下这种错误:
1 Error opening new searcher. exceeded limit of maxWarmingSearchers
而且当多个线程建索引的时候,且commit比较频繁,一直会有warm:
1 PERFORMANCE WARNING: Overlapping onDeckSearchers=2
1 <maxWarmingSearchers>10</maxWarmingSearchers>
1 if (onDeckSearchers < 1) { 2 // should never happen... just a sanity check 3 log.error(logid+"ERROR!!! onDeckSearchers is " + onDeckSearchers); 4 onDeckSearchers=1; // reset 5 } else if (onDeckSearchers > maxWarmingSearchers) { 6 onDeckSearchers--; 7 String msg="Error opening new searcher. exceeded limit of maxWarmingSearchers="+maxWarmingSearchers + ", try again later."; 8 log.warn(logid+""+ msg); 9 // HTTP 503==service unavailable, or 409==Conflict 10 throw new SolrException(SolrException.ErrorCode.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,msg); 11 } else if (onDeckSearchers > 1) { 12 log.warn(logid+"PERFORMANCE WARNING: Overlapping onDeckSearchers=" + onDeckSearchers); 13 }
- 预热即是提升查询性能的一种方式,但是它是以消耗索引性能的,具体的介绍将会在下一节Solr的缓存机制中详细介绍。
- 在getSearcher时候,Solr同样会对一些listener进行预热.在solrconfig.xml上可以配置在newSearcher和firstSearcher的监听器,在事件触发时,可以做某些热身搜索,让Searcher做好准备提供服务,特别是服务重启的时候,如果没有做好热身,开始提供服务搜索时都很勉强。但是通过配置的方式进行listener的预热只对固定的一些查询进行,对于查询比较自由的环境效果可能并不明显。
1 <listener event="newSearcher" class="solr.QuerySenderListener"> 2 <arr name="queries"> 3 <lst><str name="q">美女</str><str name="qt">standard</str><str name="sort">rtsTime desc</str></lst> 4 <lst><str name="q">hadoop</str><str name="qt">standard</str><str name="sort">rtsTime desc</str></lst> 5 <lst><str name="q">zoie</str><str name="qt">standard</str><str name="sort">rts desc</str></lst> 6 <lst><str name="q">lucene</str><str name="qt">standard</str><str name="sort">pubdate desc</str></lst> 7 <lst><str name="q">new searcher</str><str name="qt">standard</str><str name="sort">sourceId desc</str></lst> 8 <lst><str name="q">solr</str><str name="qt">standard</str><str name="sort">price desc</str></lst> 9 </arr> 10 </listener>
- 相比于预热,Solr还提供了另外一种打开Searcher方式即cold Searcher,该方式会直接注册Searcher,并不需要进行预热,因此它会非常迅速,但是由于打开的是完成干净的Searcher,所以一点缓存信息也没有,比较影响一开始的查询性能。
1 <useColdSearcher>false</useColdSearcher>
- 最后讲下注册,注册其实是将新建的Searcher写到一个map结构的变量中private final Map<String, SolrInfoMBean> infoRegistry的过程
1 public void register() { 2 // register self 3 core.getInfoRegistry().put("searcher", this); 4 core.getInfoRegistry().put(name, this); 5 for (SolrCache cache : cacheList) { 6 cache.setState(SolrCache.State.LIVE); 7 core.getInfoRegistry().put(cache.name(), cache); 8 } 9 registerTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); 10 }
- 最后再简单介绍下openNewSearcher,顾名思义该函数就是重新打开新的Searcher。主要代码如下,本质上就是new一个SolrIndexSearcher,只不过会根据是否是近实时模式(nrtmode),是否已有打开的Searcher(判断是否是启动时候打开的searcher),以及是否需要快速打开Searcher(若快速打开Searcher则过滤掉预热过程,在前文中讲到DirectUpdateHandler2的commit过程中也调用了RefCounted<SolrIndexSearcher> searchHolder = core.openNewSearcher(true, true);这里由于设置了true表示需要快速打开,所以是cold模式的searcher。)
1 tmp = new SolrIndexSearcher(this, newIndexDir, getLatestSchema(), getSolrConfig().indexConfig, 2 (realtime ? "realtime":"main"), newReader, true, !realtime, true, directoryFactory);
总结:
本节学习了SolrCloud的commit三步过程,重点介绍了DirectUpdateHandler2的commit和getSearcher的过程,篇幅有限并未深入学习Lucene的commit原理。同时本节提到了Warn预热的内容,那么下节开始将学习下SolrCloud的缓存机制。