今天写一个简单的spring使用例子,遇到这个问题:
项目结构如下:
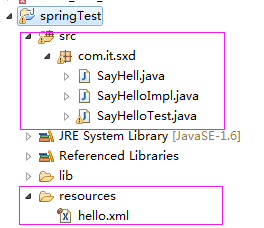
代码如下:

1 package com.it.sxd; 2 3 import java.nio.file.FileSystem; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 7 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 8 import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; 9 10 public class SayHelloTest { 11 12 @Test 13 public void testSayHello(){ 14 //1.读取hello。xml配置文件,实例化一个Ioc容器 15 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("hello.xml"); 16 17 18 //2.从Ioc容器中获取ID为"hello1"的bean ,此处是“面向接口编程 而不是面向实现编程” 19 SayHell sayHell = context.getBean("hello1",SayHell.class); 20 //3.实现功能 21 sayHell.sayHello(); 22 } 23 24 }
代码中使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext获取一个Ioc的实例化对象,但是读取这个"hello.xml"文件,无论怎么修改路径,修改成"resources/hello.xml"或者"hello.xml",总之是没有办法识别,一直报如下的错误:

1 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: IOException parsing XML document from class path resource [resources/hello.xml]; nested exception is java.io.FileNotFoundException: class path resource [resources/hello.xml] cannot be opened because it does not exist 2 at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:344) 3 at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:304) 4 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:181) 5 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:217) 6 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:188) 7 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:252) 8 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java:127) 9 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java:93) 10 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory(AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java:129) 11 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.obtainFreshBeanFactory(AbstractApplicationContext.java:609) 12 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:510) 13 at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:139) 14 at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:83) 15 at com.it.sxd.SayHelloTest.testSayHello(SayHelloTest.java:12) 16 at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) 17 at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57) 18 at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) 19 at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606) 20 at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50) 21 at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12) 22 at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47) 23 at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17) 24 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325) 25 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78) 26 at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57) 27 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290) 28 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71) 29 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288) 30 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58) 31 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268) 32 at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363) 33 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit4.runner.JUnit4TestReference.run(JUnit4TestReference.java:50) 34 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.TestExecution.run(TestExecution.java:38) 35 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:459) 36 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:675) 37 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.run(RemoteTestRunner.java:382) 38 at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.main(RemoteTestRunner.java:192) 39 Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException: class path resource [resources/hello.xml] cannot be opened because it does not exist 40 at org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource.getInputStream(ClassPathResource.java:172) 41 at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:330) 42 ... 36 more
提示这个文件不存在,找不到。
好吧 ,我要爆炸了!!!
听说基友解读了一番,将ClassXmlAplicationContext()方法替换成FileSystemXmlApplicationContext()方法,代码如下:

1 package com.it.sxd; 2 3 import java.nio.file.FileSystem; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 7 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 8 import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; 9 10 public class SayHelloTest { 11 12 @Test 13 public void testSayHello(){ 14 //1.读取hello。xml配置文件,实例化一个Ioc容器 15 ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("resources/hello.xml"); 16 17 18 //2.从Ioc容器中获取ID为"hello1"的bean ,此处是“面向接口编程 而不是面向实现编程” 19 SayHell sayHell = context.getBean("hello1",SayHell.class); 20 //3.实现功能 21 sayHell.sayHello(); 22 } 23 24 }
然后:

效果很好嘛~~!!!然后就好了。
下面就解读一下这两个方法的区别:
Spring容器最基本的接口就是BeanFactory. BeanFactory负责配置、创建、管理Bean,它有一个子接口ApplicationContext,也称为Spring上下文。Spring容器负责管理Bean与Bean之间的信赖关系。
BeanFactory有很多实现类,通常使用org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory类。但对于大部分J2EE应用而言,推荐使用ApplicationContext. ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,其常用实现类是org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext和org.springframework.context.support.ClassXmlAplicationContext。
Springr的配置信息通常采用XML配置文件来设置,因此,创建BeanFactory实例时,应该提供XML配置文件作为参数。、
下面详细介绍ApplicationContext的实际运用:
一:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
1.没有前缀:默认为项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app.spring.xml");
2.前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:app.spring.xml");
3.使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("file:D:/app.spring.xml");
4.可以同时加载多个文件
String[] xmlCfg = new String[] { "classpath:base.spring.xml","app.spring.xml"};
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlCfg);
5.使用通配符加载所有符合要求的文件
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("*.spring.xml");
也就是说呢,这个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext()方法,只能识别源文件夹的范围下的东西。
二:FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
1.默认为项目工作路径 即项目的根目录
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/resources/app.spring.xml");
2.前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:app.spring.xml");
3.使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("file:D:/app.spring.xml");
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D:/app.spring.xml");
4.可以同时加载多个文件
String[] xmlCfg = new String[] { "src/main/resources/base.spring.xml","classpath:app.spring.xml"};
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(xmlCfg);
5.使用通配符加载所有符合要求的文件
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:*.spring.xml");
代码解释:

1 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 2 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 3 import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; 4 import aoplog.LogAfterAdvice; 5 import aoplog.LogBeforeAdvice; 6 /** 7 * @author Michael 8 * 9 */ 10 public class TestApplicationContext { 11 /** 12 * @param args 13 */ 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 /** 16 * ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 17 */ 18 // 没有前缀:默认为项目的classpath下相对路径 19 ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 20 "app.spring.xml"); 21 // 前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径 22 // ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 23 // "classpath:app.spring.xml"); 24 // 使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径 25 // ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 26 // "file:D:/app.spring.xml"); 27 LogBeforeAdvice logBefore = (LogBeforeAdvice) appCt 28 .getBean("logBefore"); 29 System.out.println("ClassPathXmlApplicationContext test:" 30 + logBefore.getClass()); 31 // 利用通配符文件加载 32 ApplicationContext appCtXx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 33 "*.spring.xml"); 34 // 多文件加载 35 String[] xmlCfg = new String[] { "classpath:base.spring.xml", 36 "myapp.spring.xml" }; 37 ApplicationContext appCtMore = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 38 xmlCfg); 39 /* 40 * FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 41 */ 42 // 默认为项目工作路径 即项目的根目录 43 ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( 44 "src/main/resources/app.spring.xml"); 45 // 前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径 46 // ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( 47 // "classpath:app.spring.xml"); 48 // 使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径 49 // ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( 50 // "file:D:/app.spring.xml"); 51 LogAfterAdvice logAfter = (LogAfterAdvice) appCt2.getBean("logAfter"); 52 System.out.println("FileSystemXmlApplicationContext test:" 53 + logAfter.getClass()); 54 } 55 }
附录:
谈一谈什么是ClassPath以及怎么使用它:
首先:
java运行时的类路径,比如导入的类,在运行时需要将jar包放到classpath路径上。
classpath 在classpath路径上寻找指定文件,如果有多个符合的文件,以第一个为准,也就说,只要找到一个,就不在继续搜索
classpath*:会搜索所有满足条件的文件,有多少加载多少
其次:
编写的java源文件经过编译后生成class文件,需要指定目录存放这些文件。web程序默认都在web-info/classes目录下存放我们的java编译后的文件。
但是web-info目录下还有各种jar包和配置文件呢,确切说web-info根目录才是程序运行时classpath。放在根目录下的源代码,在编译之后,会将此文件copy到web-info目录。
JAVA获取classpath路径:
public URL getResource (String name);
public InputStream getResourceAsStream (String name);
这里name是资源的类路径,它是相对与“/”根路径下的位置。getResource得到的是一个URL对象来定位资源,而getResourceAsStream取得该资源输入流的引用保证程序可以从正确的位置抽取数据。
但是真正使用的不是ClassLoader的这两个方法,而是Class的 getResource和getResourceAsStream方法,因为Class对象可以从你的类得到(如YourClass.class或 YourClass.getClass()),而ClassLoader则需要再调用一次YourClass.getClassLoader()方法,不过根据JDK文档的说法,Class对象的这两个方法其实是“委托”(delegate)给装载它的ClassLoader来做的,所以只需要使用 Class对象的这两个方法就可以了。
因此,直接调用 this.getClass().getResourceAsStream(String name) ;获取流,静态化方法中则使用ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream (String name) ; 。
下面是一些得到classpath和当前类的绝对路径的一些方法。你可能需要使用其中的一些方法来得到你需要的资源的绝对路径。
1.this.getClass().getResource("")
得到的是当前类class文件的URI目录。不包括自己!
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/com/test/
2.this.getClass().getResource("/")
得到的是当前的classpath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
3.this.getClass() .getClassLoader().getResource("")
得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
4.ClassLoader.getSystemResource("")
得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
5.Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader ().getResource("")
得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
6.ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath(“/”)
Web应用程序 中,得到Web应用程序的根目录的绝对路径。这样,我们只需要提供相对于Web应用程序根目录的路径,就可以构建出定位资源的绝对路径。
如:file:/D:/workspace/.metadata/.plugins/org.eclipse.wst.server.core/tmp0/wtpwebapps/WebProject
注意点:
1.尽量不要使用相对于System.getProperty("user.dir")当前用户目录的相对路径。这是一颗定时炸 弹,随时可能要你的命。
2.尽量使用URI形式的绝对路径资源。它可以很容易的转变为URI,URL,File对象。
3.尽量使用相对classpath的相对路径。不要使用绝对路径。使用上面ClassLoaderUtil类的public static URL getExtendResource(String relativePath)方法已经能够使用相对于classpath的相对路径定位所有位置的资源。
4.绝对不要使用硬编码的绝对路径。因为,我们完全可以使用ClassLoader类的getResource("")方法得到当前classpath的绝对路径。如果你一定要指定一个绝对路径,那么使用配置文件,也比硬编码要好得多!
