public static void main(String[] args){ final int MAX_VAL = 10000; List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>(); List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { linkedList.add(i); arrayList.add(i); } long time = System.nanoTime(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { linkedList.add(MAX_VAL/2, i); } System.out.println("LL time: " + (System.nanoTime() - time)); time = System.nanoTime(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { arrayList.add(MAX_VAL/2, i); } System.out.println("AL time: " + (System.nanoTime() - time)); }
从中间插入结果:

怎么会这样, 不应该是LinkedList更快吗? ArrayList底层是数组, 添加数据需要移动后面的数据, 而LinkedList使用的是链表, 直接移动指针就行, 按理说应该是LinkedList更快.
再来看
从尾插入
public static void main(String[] args){ final int MAX_VAL = 10000; List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>(); List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { linkedList.add(i); arrayList.add(i); } long time = System.nanoTime(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { linkedList.add(i); } System.out.println("LL time: " + (System.nanoTime() - time)); time = System.nanoTime(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { arrayList.add(i); } System.out.println("AL time: " + (System.nanoTime() - time)); }

从头开始插入
public static void main(String[] args){ final int MAX_VAL = 10000; List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>(); List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { linkedList.add(i); arrayList.add(i); } long time = System.nanoTime(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { linkedList.add(0,i); } System.out.println("LL time: " + (System.nanoTime() - time)); time = System.nanoTime(); for(int i = 0; i < MAX_VAL; i++) { arrayList.add(0,i); } System.out.println("AL time: " + (System.nanoTime() - time)); }
结果
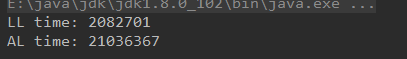
然后从三分之一的位置开始插入
结果
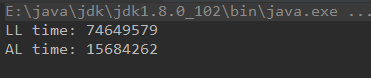
从三分之二的位置插入
结果

源码部分
LinkedList源码
// 在index前添加节点,且节点的值为element public void add(int index, E element) { addBefore(element, (index==size ? header : entry(index))); } // 获取双向链表中指定位置的节点 private Entry<E> entry(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size); Entry<E> e = header; // 获取index处的节点。 // 若index < 双向链表长度的1/2,则从前向后查找; // 否则,从后向前查找。 if (index < (size >> 1)) { for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) e = e.next; } else { for (int i = size; i > index; i--) e = e.previous; } return e; } // 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到entry节点之前。 private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) { // 新建节点newEntry,将newEntry插入到节点e之前;并且设置newEntry的数据是e Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous); // 插入newEntry到链表中 newEntry.previous.next = newEntry; newEntry.next.previous = newEntry; size++; modCount++; return newEntry;
从中,我们可以看出:通过add(int index, E element)向LinkedList插入元素时。先是在双向链表中找到要插入节点的位置index;找到之后,再插入一个新节点。
双向链表查找index位置的节点时,有一个加速动作:若index < 双向链表长度的1/2,则从前向后查找; 否则,从后向前查找。
接着,我们看看ArrayList.java中向指定位置插入元素的代码。如下:
// 将e添加到ArrayList的指定位置 public void add(int index, E element) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size); ensureCapacity(size+1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
ensureCapacity(size+1) 的作用是“确认ArrayList的容量,若容量不够,则增加容量。”
真正耗时的操作是 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);
实际上,我们只需要了解: System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); 会移动index之后所有元素即可。这就意味着,ArrayList的add(int index, E element)函数,会引起index之后所有元素的改变!
结论:
现在大概知道了,插入位置的选取对LinkedList有很大的影响,一直往数据中间部分插入删除的时候,ArrayList比LinkedList更快
原因大概就是当数据量大的时候,system.arraycopy的效率要比每次插入LinkedList都需要从端查找index和分配节点node来的更快。
总之,对于99%或更多的现实情况,ArrayList是更好的选择,并且利用LinkedList的狭隘优势需要非常小心。