jsf标签
JSF标准HTML标签包括了几个共通的属性,整理如下:
|
属性名称 |
适用 |
说明 |
|
id |
所有组件 |
可指定id名称,以让其它卷标或组件参考 |
|
binding |
所有组件 |
绑定至UIComponent |
|
rendered |
所有组件 |
是否显示组件 |
|
styleClass |
所有组件 |
设定Cascading stylesheet (CSS) |
|
value |
输入、输出、命令组件 |
设定值或绑定至指定的值 |
|
valueChangeListener |
输入组件 |
设定值变事件处理者 |
|
converter |
输入、输出组件 |
设定转换器 |
|
validator |
输入组件 |
设定验证器 |
|
required |
输入组件 |
是否验证必填字段 |
|
immediate |
输入、命令组件 |
是否为立即事件 |
除了共通的属性之外,您还可以在某些组件上设定卷标HTML 4.01的属性,像是size、alt、width等属性,或者是设定DHTML事件属性,例如onchange、onclick等等。
HTML组件库 映射标准的HTML输入元素
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h"%>
Core库 辅助常见的应用程序开发任务(如验证/转换数据、事件处理等)
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f"%>
一、输出类标签
输出类的标签包括了outputLabel、outputLink、outputFormat与 outputText
outputLabel
产生<label> HTML卷标,使用for属性指定组件的client ID,例如:
<h:outputLabel for="user" value="用户名">
<h:inputText id="user" value="#{user.name}"/>
outputLink
产生<a> HTML标签,例如:
<h:outputLink value="../index.jsp">
<h:outputText value="Link to Index"/>
<f:param name="name" value="MyName"/>
</h:outputLink>
你可搭配<f:param>帮链接加上参数,所有的参数都会变成 name=value 的型态附加在连结后。
value所指定的内容也可以是JSF EL绑定。
outputFormat
产生指定的文字讯息,可以搭配<f:param>来设定讯息的参数以格式化文字讯息,例如
<f:loadBundle basename="messages" var="msgs"/>
<h:outputFormat value="#{msgs.welcomeText}">
<f:param value="Hello"/>
<f:param value="Guest"/>
</h:outputFormat>
如果您的messages.properties包括以下的内容:
welcomeText={0}, Your name is {1}.
则{0}与{1}会被取代为<f:param>设定的文字,最后显示的文字会是:
Hello, Your name is Guest.
另一个使用的方法则是:
<h:outputFormat value="{0}, Your name is {1}.">
<f:param value="Hello"/>
<f:param value="Guest"/>
</h:outputFormat>
outputText :
简单的显示指定的值或绑定的讯息,例如:
<h:outputText value="#{user.name}"/>
二、输入类标签
输入类标签包括了inputText、inputTextarea、inputSecret、 inputHidden,分别举例说明如下:
inputText
显示单行输入字段,即输出<input> HTML卷标,其type属性设定为text,例如:
<h:inputText value="#{user.name}"/>
inputTextarea
显示多行输入文字区域,即输出<textarea> HTML标签,例如:
<h:inputTextareavalue="#{user.command}"/>
inputSecret
显示密码输入字段,即输出<input> HTML卷标,其type属性设定为password,您可以设定redisplay属性以决定是否要显示密码字段的值,预设是false。例如:
<h:inputSecretvalue="#{user.password}"/>
inputHidden
隐藏字段,即输出<input> HTML卷标,其type属性设定为hidden,隐藏字段的值用于保留一些讯息于客户端,以在下一次发送窗体时一并送出,例如:
<h:inputHiddenvalue="#{user.hiddenInfo}"/>
三、命令类标签
命令类标签包括commandButton与commandLink,其主要作用在于提供一个命令按钮或连结,以下举例说明:
commandButton
显示一个命令按钮,即输出<input> HTML卷标,其type属性可以设定为button、submit或reset,预设是submit,按下按钮会触发 javax.faces.event.ActionEvent,使用例子如下:
<h:commandButton value="送出" action="#{user.verify}"/>
您可以设定image属性,指定图片的URL,
<h:commandButton value="#{msgs.commandText}"
image="images/logowiki.jpg"
action="#{user.verify}"/>
commandLink
产生超级链接,会输出<a> HTML卷标,而href属性会有'#',而onclick属性会含有一段JavaScript程序,这个JavaScript的目的是按下连结后自动提交窗体,具体来说其作用就像按钮,但外观却是超级链接,包括在本体部份的内容都会成为超级链接的一部份,一个使用的例子如下:
<h:commandLink value="#{msgs.commandText}"
action="#{user.verify}"/>
如果搭配<f:param>来使用,则所设定的参数会被当作请求参数一并送出,例如:
<h:commandLink> <h:outputText value="welcome"/> <f:param name="locale" value="zh_CN"/> </h:commandLink>
四、选择类标签
选择类的标签可略分为单选卷标与多选卷标,依外型的不同可以分为单选钮(Radio)、复选框(CheckBox)、列示方块(ListBox)与选单(Menu)。
selectBooleanCheckbox
在视图上呈现一个复选框,例如:
我同意 <h:selectBooleanCheckbox value="#\{user.aggree\}"/>
selectOneRadio selectOneListbox selectOneMenu
这三个标签设定方法类似,作用是让使用者从其所提供的选项中选择一个项目,所不同的就是其外观上的差别,
<h:selectOneRadio value="#{user.education}">
<f:selectItem itemLabel="高中" itemValue="高中"/>
<f:selectItem itemLabel="大学" itemValue="大学"/>
<f:selectItem itemLabel="研究所以上" itemValue="研究所以上"/>
</h:selectOneRadio>
您也可以设定layout属性,可设定的属性是lineDirection、pageDirection,预设是lineDirection,也就是由左到右来排列选项,如果设定为pageDirection,则是由上至下排列选项,例如设定为:
<h:selectOneRadio layout="pageDirection"
value="#{user.education}">
<f:selectItem itemLabel="高中" itemValue="高中"/>
<f:selectItem itemLabel="大学" itemValue="大学"/>
<f:selectItem itemLabel="研究所以上" itemValue="研究所以上"/>
</h:selectOneRadio>
selectManyCheckbox selectManyListbox selectManyMenu
这三个卷标提供使用者复选项目的功能,一个<h:selectManyCheckbox>例子如下:
<h:selectManyCheckbox layout="pageDirection"
value="#{user.preferColors}">
<f:selectItem itemLabel="红" itemValue="false"/>
<f:selectItem itemLabel="黄" itemValue="false"/>
<f:selectItem itemLabel="蓝" itemValue="false"/>
</h:selectManyCheckbox>
value所绑定的属性必须是数组或集合(Collection)对象,在这个例子中所使用的是boolean数组,例如
UserBean.java
public class UserBean {
private boolean[] preferColors;
public boolean[] getPreferColors() {
return preferColors;
}
public void setPreferColors(boolean[] preferColors) {
this.preferColors = preferColors;
}
......
}
<h:selectManyListbox>和<h:selectManyMenu>的设定方法和<h:selectManyCheckbox>类似,其外观分别如下:
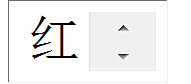
selectItem selectItems
选择类标签可以搭配<f:selectItem>或<f:selectItems>卷标来设定选项,例如:
<f:selectItem itemLabel="高中" itemValue="高中" itemDescription="学历" itemDisabled="true"/>
itemLabel属性设定显示在网页上的文字,itemValue设定发送至伺服端时的值,itemDescription 设定文字描述,它只作用于一些工具程序,对HTML没有什么影响,itemDisabled设定是否选项是否作用,这些属性也都可以使用JSF Expression Language来绑定至一个值。
<f:selectItem>也可以使用value来绑定一个传回javax.faces.model.SelectItem的方法,例如:
<f:selectItem value="#{user.sex}"/>
则绑定的Bean上必须提供下面这个方法:
public SelectItem getSex() {
return new SelectItem("男");
}
如果要一次提供多个选项,则可以使用<f:selectItems>,它的value绑定至一个提供传回SelectItem的数组、集合,或者是Map对象的方法,例如:
<h:selectOneRadio value="#{user.education}">
<f:selectItems value="#{user.educationItems}"/>
</h:selectOneRadio>
这个例子中<f:selectItems>的value绑定至user.educationItems,其内容如下
private SelectItem[] educationItems;
public SelectItem[] getEducationItems() {
if(educationItems == null) {
educationItems = new SelectItem[3];
educationItems[0] = new SelectItem("高中", "高中");
educationItems[1] =new SelectItem("大学", "大学");
educationItems[2] =new SelectItem("研究所以上", "研究所以上");
}
return educationItems;
}
在这个例子中,SelectItem的第一个建构参数用以设定value,而第二个参数用以设定label,SelectItem还提供有数个建构函式,您也可以提供一个传回Map对象的方法,Map的key-value会分别作为选项的label-value,例如:
<h:selectManyCheckbox layout="pageDirection" value="#{user.preferColors}">
<f:selectItems value="#{user.preferColorItems}"/>
</h:selectManyCheckbox>
您要提供下面的程序来搭配上面这个例子:
private Map preferColorItems;
public Map getPreferColorItems() {
if(preferColorItems == null) {
preferColorItems = new HashMap();
preferColorItems.put("红", "Red");
preferColorItems.put("黄", "Yellow");
preferColorItems.put("蓝", "Blue");
}
return preferColorItems;
}
五、表格标签
<h:dataTable>配合<h:column>实现以表格的方式显示数据
<f:facet> header与footer分别表示表头和表尾
使用DataModel处理复杂的数据
<h:dataTable value="#{tableBean.userList}" var="user"
styleClass="orders" headerClass="ordersHeader"
rowClasses="evenColumn,oddColumn">
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Name" />
</f:facet>
<h:outputText value="#{user.name}" />
<f:facet name="footer">
<h:outputText value="****" />
</f:facet>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Password" />
</f:facet>
<h:outputText value="#{user.password}" />
<f:facet name="footer">
<h:outputText value="****" />
</f:facet>
</h:column>
</h:dataTable>
六、其他标签
<h:messages>或<h:message>