目录
- 代码结构
- 调用模型前的设置模块(hparams.py,prepro.py,data_load.py,utils.py)
- transformer代码解析(modules.py , model.py )
- 训练和测试(train.py,eval.py和test.py )
一、代码结构
论文主题模块
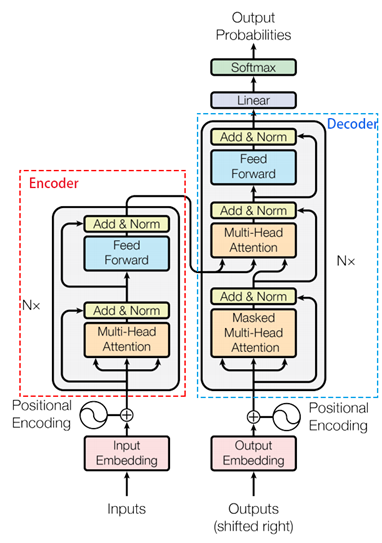
该实现【1】相对原始论文【2】有些许不同,比如为了方便使用了IWSLT 2016德英翻译的数据集,直接用的positional embedding,把learning rate一开始就调的很小等等,不过大同小异,主要模型没有区别.(另外注意最下方的outputs为上面翻译后的词或字)
该实现一共包括以下几个文件

介绍:
download.sh:一个下载 IWSLT 2016 的脚本,需要在Linux环境下,或git bash插件内运行。
hparams.py:该文件包含所有需要用到的参数
prepro.py:从源文件中,提取生成源语言和目标语言的词汇文件。
data_load.py: 该文件包含所有关于加载数据以及批量化数据的函数。
model.py :encode和decode的模型架构,基本是调用到mudules的数据包
modules.py :网络的模型组件,比如FFN,masked mutil-head attetion,LN,Positional Encoding等
train.py :训练模型的代码,定义了模型,损失函数以及训练和保存模型的过程,包含了评估模型的效果
test.py :测试模型
utils.py:调用到的工具类代码,起到一些协助的作用
二、调用模型前的设置模块(hparams.py,prepro.py,data_load.py,utils.py)
2.1 hparams.py
该实现所用到的所又的超参数都在这个文件里面。以下是该文件的所有代码:
import argparse
class Hparams:
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# prepro
parser.add_argument('--vocab_size', default=32000, type=int)
# train
## files
parser.add_argument('--train1', default='iwslt2016/segmented/train.de.bpe',
help="german training segmented data")
parser.add_argument('--train2', default='iwslt2016/segmented/train.en.bpe',
help="english training segmented data")
parser.add_argument('--eval1', default='iwslt2016/segmented/eval.de.bpe',
help="german evaluation segmented data")
parser.add_argument('--eval2', default='iwslt2016/segmented/eval.en.bpe',
help="english evaluation segmented data")
parser.add_argument('--eval3', default='iwslt2016/prepro/eval.en',
help="english evaluation unsegmented data")
## vocabulary
parser.add_argument('--vocab', default='iwslt2016/segmented/bpe.vocab',
help="vocabulary file path")
# training scheme
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', default=128, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=128, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--lr', default=0.0003, type=float, help="learning rate")
parser.add_argument('--warmup_steps', default=4000, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--logdir', default="log/1", help="log directory")
parser.add_argument('--num_epochs', default=20, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--evaldir', default="eval/1", help="evaluation dir")
# model
parser.add_argument('--d_model', default=512, type=int,
help="hidden dimension of encoder/decoder")
parser.add_argument('--d_ff', default=2048, type=int,
help="hidden dimension of feedforward layer")
parser.add_argument('--num_blocks', default=6, type=int,
help="number of encoder/decoder blocks")
parser.add_argument('--num_heads', default=8, type=int,
help="number of attention heads")
parser.add_argument('--maxlen1', default=100, type=int,
help="maximum length of a source sequence")
parser.add_argument('--maxlen2', default=100, type=int,
help="maximum length of a target sequence")
parser.add_argument('--dropout_rate', default=0.3, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--smoothing', default=0.1, type=float,
help="label smoothing rate")
# test
parser.add_argument('--test1', default='iwslt2016/segmented/test.de.bpe',
help="german test segmented data")
parser.add_argument('--test2', default='iwslt2016/prepro/test.en',
help="english test data")
parser.add_argument('--ckpt', help="checkpoint file path")
parser.add_argument('--test_batch_size', default=32, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--testdir', default="test/1", help="test result dir")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument定义变量成为一种趋势;help就是该参数的解释,故基本能够理解参含义,这里挑几个介绍下:
batch_size的大小以及初始学习速率还有日志的目录,batch_size 在后续代码中即所谓的N,参数中常会见到。最后定义了一些模型相关的参数,
maxlen1/2为一句话里最大词的长度为100个,在其他代码中就用的是T来表示,你也可以根据自己的喜好将这个参数调大;
num_epochs被设置为20,该参数表示所有出现次数少于num_epochs次的都会被当作UNK来处理;
hidden_units设置为512,隐藏节点的个数;
num_blocks:重复模块的数量,这里默认为6个
num_heads:multi-head attention 中用到的切分的头的数量
2.2 prepro.py
根据iwslt2016的原始数据,做一个预处理,放到prepro和segment文件中。
2.3 data_load.py
词和序号的转换,源目的词列表,字符串转数字,迭代返回预估值,加载数据以及批量化数据的函数等。
2.4 utils.py
计算计算batches数量def calc_num_batches(total_num, batch_size),
整数tensor转换成string tensor: def convert_idx_to_token_tensor(inputs, idx2token);
处理转换输出def postprocess(hypotheses, idx2token);
保存参数到路径def save_hparams(hparams, path)
加载参数:def load_hparams(parser, path)
保存有关变量的信息,例如它们的名称、形状和参数总数fpath:字符串。输出文件路径:def save_variable_specs(fpath)
得到假设。num_batches、num_samples:标量。sess:对象张量:要获取的目标张量dict:idx2token字典def get_hypotheses(num_batches, num_samples, sess, tensor, dict):
计算bleu(要调用perl文件,我windons进行了删除才跑过去):def calc_bleu(ref, translation)
三、transformer代码解析(modules.py , model.py )
这是最为主要的部分
3.1 modules.py
3.1.1 layer normalization
是 3.1.5 multihead_attention的子模块。归一化数据的一种方式,不过LN 是在每一个样本上计算均值和方差,有点类似CV用到的instance normalization而不是BN那种在批方向计算均值和方差!公式如下:
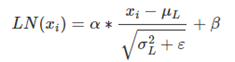
具体代码如下,后面被用在很多模块中都有使用
代码
def ln(inputs, epsilon = 1e-8, scope="ln"):
'''Applies layer normalization. See https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450.
inputs: A tensor with 2 or more dimensions, where the first dimension has `batch_size`.
epsilon: A floating number. A very small number for preventing ZeroDivision Error.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
Returns:
A tensor with the same shape and data dtype as `inputs`.
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
inputs_shape = inputs.get_shape()
params_shape = inputs_shape[-1:]
mean, variance = tf.nn.moments(inputs, [-1], keep_dims=True)
beta= tf.get_variable("beta", params_shape, initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
gamma = tf.get_variable("gamma", params_shape, initializer=tf.ones_initializer())
normalized = (inputs - mean) / ( (variance + epsilon) ** (.5) )
outputs = gamma * normalized + beta
return outputs
3.1.2 get_token_embeddings
初始化嵌入向量,用矩阵表示,目前为[vocab_size, num_units]的矩阵,vocab_size为词的数量,num_units为embedding size,一般根据论文中的设置,为512
代码
def get_token_embeddings(vocab_size, num_units, zero_pad=True):
'''Constructs token embedding matrix.
Note that the column of index 0's are set to zeros.
vocab_size: scalar. V.
num_units: embedding dimensionalty. E.
zero_pad: Boolean. If True, all the values of the first row (id = 0) should be constant zero
To apply query/key masks easily, zero pad is turned on.
Returns
weight variable: (V, E)
'''
with tf.variable_scope("shared_weight_matrix"):
embeddings = tf.get_variable('weight_mat',
dtype=tf.float32,
shape=(vocab_size, num_units),
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
if zero_pad:
embeddings = tf.concat((tf.zeros(shape=[1, num_units]),
embeddings[1:, :]), 0)
return embeddings
3.1.3 scaled_dot_product_attention
缩放的点积注意力机制,是 3.1.5 multihead_attention的子模块
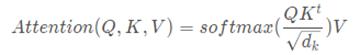
本文attention公式如上所示,和dot-product attention除了没有使用缩放因子,其他和这个一样。
additive attention和dot-product(multi-plicative) attention是最常用的两个attention 函数。为何选择上面的呢?主要为了提升效率,兼顾性能。
效率:在实践中dot-product attention要快得多,而且空间效率更高。这是因为它可以使用高度优化的矩阵乘法代码来实现。
性能:较小时,这两种方法性能表现的相近,当比较大时,addtitive attention表现优于 dot-product attention(点积在数量级上增长的幅度大,将softmax函数推向具有极小梯度的区域 )。所以加上因子拉平性能。
代码
def scaled_dot_product_attention(Q, K, V, key_masks,
causality=False, dropout_rate=0.,
training=True,
scope="scaled_dot_product_attention"):
'''See 3.2.1.
Q: Packed queries. 3d tensor. [N, T_q, d_k].
K: Packed keys. 3d tensor. [N, T_k, d_k].
V: Packed values. 3d tensor. [N, T_k, d_v].
key_masks: A 2d tensor with shape of [N, key_seqlen]
causality: If True, applies masking for future blinding
dropout_rate: A floating point number of [0, 1].
training: boolean for controlling droput
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
d_k = Q.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
# dot product
outputs = tf.matmul(Q, tf.transpose(K, [0, 2, 1])) # (N, T_q, T_k)
# scale
outputs /= d_k ** 0.5
# key masking
outputs = mask(outputs, key_masks=key_masks, type="key")
# causality or future blinding masking
if causality:
outputs = mask(outputs, type="future")
# softmax
outputs = tf.nn.softmax(outputs)
attention = tf.transpose(outputs, [0, 2, 1])
tf.summary.image("attention", tf.expand_dims(attention[:1], -1))
# # query masking
# outputs = mask(outputs, Q, K, type="query")
# dropout
outputs = tf.layers.dropout(outputs, rate=dropout_rate, training=training)
# weighted sum (context vectors)
outputs = tf.matmul(outputs, V) # (N, T_q, d_v)
return outputs
3.1.4 mask
def mask(inputs, key_masks=None, type=None):
"""Masks paddings on keys or queries to inputs
inputs: 3d tensor. (h*N, T_q, T_k)
key_masks: 3d tensor. (N, 1, T_k)
type: string. "key" | "future"
e.g.,
>> inputs = tf.zeros([2, 2, 3], dtype=tf.float32)
>> key_masks = tf.constant([[0., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 1.]])
>> mask(inputs, key_masks=key_masks, type="key")
array([[[ 0.0000000e+00, 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09],
[ 0.0000000e+00, 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09]],
[[ 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09, -4.2949673e+09],
[ 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09, -4.2949673e+09]],
[[ 0.0000000e+00, 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09],
[ 0.0000000e+00, 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09]],
[[ 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09, -4.2949673e+09],
[ 0.0000000e+00, -4.2949673e+09, -4.2949673e+09]]], dtype=float32)
"""
padding_num = -2 ** 32 + 1
if type in ("k", "key", "keys"):
key_masks = tf.to_float(key_masks)
key_masks = tf.tile(key_masks, [tf.shape(inputs)[0] // tf.shape(key_masks)[0], 1]) # (h*N, seqlen)
key_masks = tf.expand_dims(key_masks, 1) # (h*N, 1, seqlen)
outputs = inputs + key_masks * padding_num
elif type in ("f", "future", "right"):
diag_vals = tf.ones_like(inputs[0, :, :]) # (T_q, T_k)
tril = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorLowerTriangular(diag_vals).to_dense() # (T_q, T_k)
future_masks = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tril, 0), [tf.shape(inputs)[0], 1, 1]) # (N, T_q, T_k)
paddings = tf.ones_like(future_masks) * padding_num
outputs = tf.where(tf.equal(future_masks, 0), paddings, inputs)
else:
print("Check if you entered type correctly!")
return outputs
3.1.5 multihead_attention(重要组件)
该部分代码包含了整体框架中的这个部分:
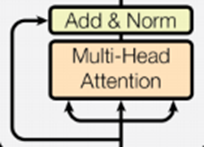
主要公式如下:
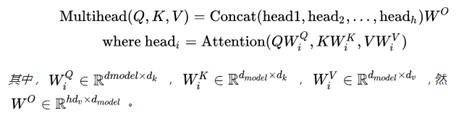
代码:
def multihead_attention(queries, keys, values, key_masks,
num_heads=8,
dropout_rate=0,
training=True,
causality=False,
scope="multihead_attention"):
'''Applies multihead attention. See 3.2.2
queries: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T_q, d_model].
keys: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T_k, d_model].
values: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T_k, d_model].
key_masks: A 2d tensor with shape of [N, key_seqlen]
num_heads: An int. Number of heads.
dropout_rate: A floating point number.
training: Boolean. Controller of mechanism for dropout.
causality: Boolean. If true, units that reference the future are masked.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
Returns
A 3d tensor with shape of (N, T_q, C)
'''
d_model = queries.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# Linear projections
Q = tf.layers.dense(queries, d_model, use_bias=True) # (N, T_q, d_model)
K = tf.layers.dense(keys, d_model, use_bias=True) # (N, T_k, d_model)
V = tf.layers.dense(values, d_model, use_bias=True) # (N, T_k, d_model)
# Split and concat
Q_ = tf.concat(tf.split(Q, num_heads, axis=2), axis=0) # (h*N, T_q, d_model/h)
K_ = tf.concat(tf.split(K, num_heads, axis=2), axis=0) # (h*N, T_k, d_model/h)
V_ = tf.concat(tf.split(V, num_heads, axis=2), axis=0) # (h*N, T_k, d_model/h)
# Attention
outputs = scaled_dot_product_attention(Q_, K_, V_, key_masks, causality, dropout_rate, training)
# Restore shape
outputs = tf.concat(tf.split(outputs, num_heads, axis=0), axis=2 ) # (N, T_q, d_model)
# Residual connection
outputs += queries
# Normalize
outputs = ln(outputs)
return outputs
3.1.6 ff——feed forward(重要组件)
除了attention子层之外,编码器和解码器中的每个层都包含一个完全连接的前馈网络,该网络分别相同地应用于每个位置。 该前馈网络包括两个线性变换,并在第一个的最后使用ReLU激活函数,公式表示如下:

不同position的FFN是一样的,但是不同层是不同的。
描述这种情况的另一种方式是两个内核大小为1的卷积。输入和输出的维度是,内层的维度=2048。
def ff(inputs, num_units, scope="positionwise_feedforward"):
'''position-wise feed forward net. See 3.3
inputs: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T, C].
num_units: A list of two integers.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
Returns:
A 3d tensor with the same shape and dtype as inputs
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# Inner layer
outputs = tf.layers.dense(inputs, num_units[0], activation=tf.nn.relu) #全连接层 相当于添加一个层
# Outer layer
outputs = tf.layers.dense(outputs, num_units[1])
# Residual connection
outputs += inputs
# Normalize
outputs = ln(outputs)
return outputs
3.1.7 label_smoothing
这部分就相当于是使矩阵中的数进行平滑处理。把0改成一个很小的数,把1改成一个比较接近于1的数。论文中说这虽然会使模型的学习更加不确定性,但是提高了准确率和BLEU score。(论文中的5.4部分)
def label_smoothing(inputs, epsilon=0.1):
'''Applies label smoothing. See 5.4 and https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567.
inputs: 3d tensor. [N, T, V], where V is the number of vocabulary.
epsilon: Smoothing rate.
For example,
```
import tensorflow as tf
inputs = tf.convert_to_tensor([[[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]],
[[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0]]], tf.float32)
outputs = label_smoothing(inputs)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run([outputs]))
>>
[array([[[ 0.03333334, 0.03333334, 0.93333334],
[ 0.03333334, 0.93333334, 0.03333334],
[ 0.93333334, 0.03333334, 0.03333334]],
[[ 0.93333334, 0.03333334, 0.03333334],
[ 0.93333334, 0.03333334, 0.03333334],
[ 0.03333334, 0.93333334, 0.03333334]]], dtype=float32)]
```
'''
V = inputs.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # number of channels
return ((1-epsilon) * inputs) + (epsilon / V)
3.1.8 positional_encoding(重要模块)
该模块内如为:
位置编码,论文中3.5的内容,公式如下

其中pos是指当前词在句子中的位置,i是指向量中每个值的维度,位置编码的每个维度对应于正弦曲线。我们选择了这个函数,因为我们假设它允许模型容易地学习相对位置。
def positional_encoding(inputs,
maxlen,
masking=True,
scope="positional_encoding"):
'''Sinusoidal Positional_Encoding. See 3.5
inputs: 3d tensor. (N, T, E)
maxlen: scalar. Must be >= T
masking: Boolean. If True, padding positions are set to zeros.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
returns
3d tensor that has the same shape as inputs.
'''
E = inputs.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # static
N, T = tf.shape(inputs)[0], tf.shape(inputs)[1] # dynamic
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# position indices
position_ind = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tf.range(T), 0), [N, 1]) # (N, T)
# First part of the PE function: sin and cos argument
position_enc = np.array([
[pos / np.power(10000, (i-i%2)/E) for i in range(E)]
for pos in range(maxlen)])
# Second part, apply the cosine to even columns and sin to odds.
position_enc[:, 0::2] = np.sin(position_enc[:, 0::2]) # dim 2i
position_enc[:, 1::2] = np.cos(position_enc[:, 1::2]) # dim 2i+1
position_enc = tf.convert_to_tensor(position_enc, tf.float32) # (maxlen, E)
# lookup
outputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(position_enc, position_ind)
# masks
if masking:
outputs = tf.where(tf.equal(inputs, 0), inputs, outputs)
return tf.to_float(outputs)
3.1.9 noam_scheme
学习率的衰减,在3.2的train(self, xs, ys)模块中会用到,代码如下:
def noam_scheme(init_lr, global_step, warmup_steps=4000.):
'''Noam scheme learning rate decay
init_lr: initial learning rate. scalar.
global_step: scalar.
warmup_steps: scalar. During warmup_steps, learning rate increases
until it reaches init_lr.
'''
step = tf.cast(global_step + 1, dtype=tf.float32)
return init_lr * warmup_steps ** 0.5 * tf.minimum(step * warmup_steps ** -1.5, step ** -0.5)
3.2 model.py
3.2.1 导入包
import tensorflow as tf from data_load import load_vocab from modules import get_token_embeddings, ff, positional_encoding, multihead_attention, label_smoothing, noam_scheme from utils import convert_idx_to_token_tensor from tqdm import tqdm import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
简单介绍:上面提到的大部分模块,基本都在这里用到。
3.2.2 创建Transformer类
class Transformer:
'''
xs: tuple of
x: int32 tensor. (N, T1)
x_seqlens: int32 tensor. (N,)
sents1: str tensor. (N,)
ys: tuple of
decoder_input: int32 tensor. (N, T2)
y: int32 tensor. (N, T2)
y_seqlen: int32 tensor. (N, )
sents2: str tensor. (N,)
training: boolean.
'''
def __init__(self, hp):
self.hp = hp
self.token2idx, self.idx2token = load_vocab(hp.vocab)
self.embeddings = get_token_embeddings(self.hp.vocab_size, self.hp.d_model, zero_pad=True)
类内函数encode部分:按照下图部分一步一步进行。
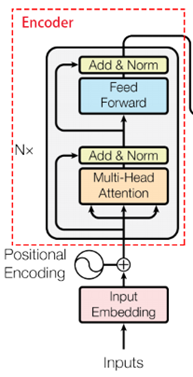
def encode(self, xs, training=True):
'''
Returns
memory: encoder outputs. (N, T1, d_model)
'''
with tf.variable_scope("encoder", reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
x, seqlens, sents1 = xs
# src_masks
src_masks = tf.math.equal(x, 0) # (N, T1)
# embedding
enc = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.embeddings, x) # (N, T1, d_model)
enc *= self.hp.d_model**0.5 # scale
enc += positional_encoding(enc, self.hp.maxlen1)
enc = tf.layers.dropout(enc, self.hp.dropout_rate, training=training)
## Blocks
for i in range(self.hp.num_blocks): #上图中的N,这里默认设置为6
with tf.variable_scope("num_blocks_{}".format(i), reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# self-attention
enc = multihead_attention(queries=enc,
keys=enc,
values=enc,
key_masks=src_masks,
num_heads=self.hp.num_heads,
dropout_rate=self.hp.dropout_rate,
training=training,
causality=False)
# feed forward
enc = ff(enc, num_units=[self.hp.d_ff, self.hp.d_model])
memory = enc
return memory, sents1, src_masks
类内函数decode部分:按照下图部分一步一步进行。
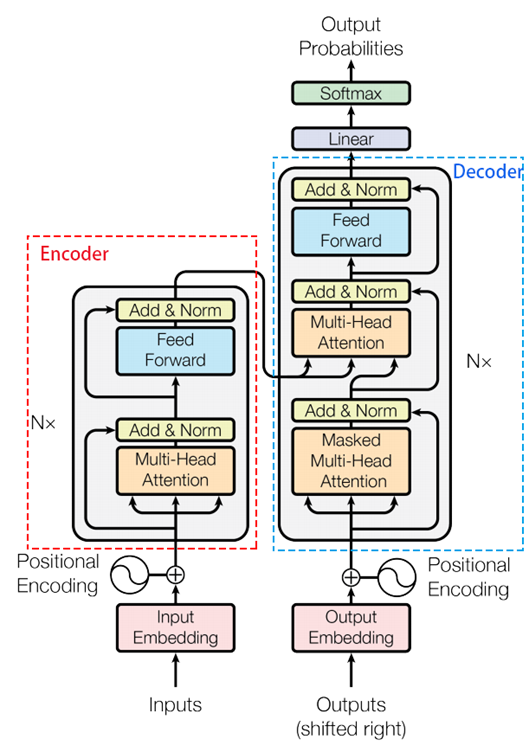
def decode(self, ys, memory, src_masks, training=True):
'''
memory: encoder outputs. (N, T1, d_model)
src_masks: (N, T1)
Returns
logits: (N, T2, V). float32.
y_hat: (N, T2). int32
y: (N, T2). int32
sents2: (N,). string.
'''
with tf.variable_scope("decoder", reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
decoder_inputs, y, seqlens, sents2 = ys
# tgt_masks
tgt_masks = tf.math.equal(decoder_inputs, 0) # (N, T2)
# embedding
dec = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.embeddings, decoder_inputs) # (N, T2, d_model)
dec *= self.hp.d_model ** 0.5 # scale
dec += positional_encoding(dec, self.hp.maxlen2)
dec = tf.layers.dropout(dec, self.hp.dropout_rate, training=training)
# Blocks
for i in range(self.hp.num_blocks):
with tf.variable_scope("num_blocks_{}".format(i), reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
# Masked self-attention (Note that causality is True at this time)
dec = multihead_attention(queries=dec,
keys=dec,
values=dec,
key_masks=tgt_masks,
num_heads=self.hp.num_heads,
dropout_rate=self.hp.dropout_rate,
training=training,
causality=True,
scope="self_attention")
# Vanilla attention
dec = multihead_attention(queries=dec,
keys=memory, #memory: encoder outputs.使用了图中左侧过来的部分
values=memory,
key_masks=src_masks,
num_heads=self.hp.num_heads,
dropout_rate=self.hp.dropout_rate,
training=training,
causality=False,
scope="vanilla_attention")
### Feed Forward
dec = ff(dec, num_units=[self.hp.d_ff, self.hp.d_model])
# Final linear projection (embedding weights are shared)
weights = tf.transpose(self.embeddings) # (d_model, vocab_size)
logits = tf.einsum('ntd,dk->ntk', dec, weights) # (N, T2, vocab_size)
y_hat = tf.to_int32(tf.argmax(logits, axis=-1))
return logits, y_hat, y, sents2
模型训练部分
def train(self, xs, ys):
'''
Returns
loss: scalar.
train_op: training operation
global_step: scalar.
summaries: training summary node
'''
# forward
memory, sents1, src_masks = self.encode(xs)
logits, preds, y, sents2 = self.decode(ys, memory, src_masks)
# train scheme
y_ = label_smoothing(tf.one_hot(y, depth=self.hp.vocab_size))
ce = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=logits, labels=y_)
nonpadding = tf.to_float(tf.not_equal(y, self.token2idx["<pad>"])) # 0: <pad>
loss = tf.reduce_sum(ce * nonpadding) / (tf.reduce_sum(nonpadding) + 1e-7)
global_step = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
lr = noam_scheme(self.hp.lr, global_step, self.hp.warmup_steps)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
tf.summary.scalar('lr', lr)
tf.summary.scalar("loss", loss)
tf.summary.scalar("global_step", global_step)
summaries = tf.summary.merge_all()
return loss, train_op, global_step, summaries
模型训验证部分
def eval(self, xs, ys):
'''Predicts autoregressively
At inference, input ys is ignored.
Returns
y_hat: (N, T2)
'''
decoder_inputs, y, y_seqlen, sents2 = ys
decoder_inputs = tf.ones((tf.shape(xs[0])[0], 1), tf.int32) * self.token2idx["<s>"]
ys = (decoder_inputs, y, y_seqlen, sents2)
memory, sents1, src_masks = self.encode(xs, False)
logging.info("Inference graph is being built. Please be patient.")
for _ in tqdm(range(self.hp.maxlen2)):
logits, y_hat, y, sents2 = self.decode(ys, memory, src_masks, False)
if tf.reduce_sum(y_hat, 1) == self.token2idx["<pad>"]: break
_decoder_inputs = tf.concat((decoder_inputs, y_hat), 1)
ys = (_decoder_inputs, y, y_seqlen, sents2)
# monitor a random sample
n = tf.random_uniform((), 0, tf.shape(y_hat)[0]-1, tf.int32)
sent1 = sents1[n]
pred = convert_idx_to_token_tensor(y_hat[n], self.idx2token)
sent2 = sents2[n]
tf.summary.text("sent1", sent1)
tf.summary.text("pred", pred)
tf.summary.text("sent2", sent2)
summaries = tf.summary.merge_all()
return y_hat, summaries
四、训练和测试(train.py,eval.py和test.py)
4.1 train.py
训练模型的代码,定义了模型,损失函数以及训练和保存模型的过程 包含了评估模型的效果
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
from model import Transformer
from tqdm import tqdm
from data_load import get_batch
from utils import save_hparams, save_variable_specs, get_hypotheses, calc_bleu
import os
from hparams import Hparams
import math
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logging.info("# hparams")
hparams = Hparams()
parser = hparams.parser
hp = parser.parse_args()
save_hparams(hp, hp.logdir)
logging.info("# Prepare train/eval batches")
train_batches, num_train_batches, num_train_samples = get_batch(hp.train1, hp.train2,
hp.maxlen1, hp.maxlen2,
hp.vocab, hp.batch_size,
shuffle=True)
eval_batches, num_eval_batches, num_eval_samples = get_batch(hp.eval1, hp.eval2,
100000, 100000,
hp.vocab, hp.batch_size,
shuffle=False)
# create a iterator of the correct shape and type
iter = tf.data.Iterator.from_structure(train_batches.output_types, train_batches.output_shapes)
xs, ys = iter.get_next()
#迭代器需要初始化
train_init_op = iter.make_initializer(train_batches)
eval_init_op = iter.make_initializer(eval_batches)
logging.info("# Load model")
m = Transformer(hp)
loss, train_op, global_step, train_summaries = m.train(xs, ys)
y_hat, eval_summaries = m.eval(xs, ys)
# y_hat = m.infer(xs, ys)
logging.info("# Session")
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=hp.num_epochs)
with tf.Session() as sess:
ckpt = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(hp.logdir)
if ckpt is None:
logging.info("Initializing from scratch")
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
save_variable_specs(os.path.join(hp.logdir, "specs"))
else:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt)
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(hp.logdir, sess.graph) #定义一个写入summary的目标文件,hp.logdir为写入文件地址
sess.run(train_init_op)
total_steps = hp.num_epochs * num_train_batches
_gs = sess.run(global_step)
for i in tqdm(range(_gs, total_steps+1)):
_, _gs, _summary = sess.run([train_op, global_step, train_summaries])
epoch = math.ceil(_gs / num_train_batches)
summary_writer.add_summary(_summary, _gs)#调用train_writer的add_summary方法将训练过程以及训练步数保存
if _gs and _gs % num_train_batches == 0:
logging.info("epoch {} is done".format(epoch))
_loss = sess.run(loss) # train loss
logging.info("# test evaluation")
_, _eval_summaries = sess.run([eval_init_op, eval_summaries])
summary_writer.add_summary(_eval_summaries, _gs)
logging.info("# get hypotheses")
hypotheses = get_hypotheses(num_eval_batches, num_eval_samples, sess, y_hat, m.idx2token)
logging.info("# write results")
model_output = "iwslt2016_E%02dL%.2f" % (epoch, _loss)
if not os.path.exists(hp.evaldir): os.makedirs(hp.evaldir)
translation = os.path.join(hp.evaldir, model_output)
with open(translation, 'w') as fout:
fout.write("
".join(hypotheses))
logging.info("# calc bleu score and append it to translation")
calc_bleu(hp.eval3, translation)
logging.info("# save models")
ckpt_name = os.path.join(hp.logdir, model_output)
saver.save(sess, ckpt_name, global_step=_gs)
logging.info("after training of {} epochs, {} has been saved.".format(epoch, ckpt_name))
logging.info("# fall back to train mode")
sess.run(train_init_op)
summary_writer.close()
logging.info("Done")
4.2 test.py
测试模型,若是windowns上跑模型,注意将最后两句计算Bleu部分注释掉。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from data_load import get_batch
from model import Transformer
from hparams import Hparams
from utils import get_hypotheses, calc_bleu, postprocess, load_hparams
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logging.info("# hparams")
hparams = Hparams()
parser = hparams.parser
hp = parser.parse_args()
load_hparams(hp, hp.ckpt)
logging.info("# Prepare test batches")
test_batches, num_test_batches, num_test_samples = get_batch(hp.test1, hp.test1,
100000, 100000,
hp.vocab, hp.test_batch_size,
shuffle=False)
iter = tf.data.Iterator.from_structure(test_batches.output_types, test_batches.output_shapes)
xs, ys = iter.get_next()
test_init_op = iter.make_initializer(test_batches)
logging.info("# Load model")
m = Transformer(hp)
y_hat, _ = m.eval(xs, ys)
logging.info("# Session")
with tf.Session() as sess:
ckpt_ = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(hp.ckpt)
ckpt = hp.ckpt if ckpt_ is None else ckpt_ # None: ckpt is a file. otherwise dir.
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, ckpt)
sess.run(test_init_op)
logging.info("# get hypotheses")
hypotheses = get_hypotheses(num_test_batches, num_test_samples, sess, y_hat, m.idx2token)
logging.info("# write results")
model_output = ckpt.split("/")[-1]
if not os.path.exists(hp.testdir): os.makedirs(hp.testdir)
translation = os.path.join(hp.testdir, model_output)
with open(translation, 'w') as fout:
fout.write("
".join(hypotheses))
logging.info("# calc bleu score and append it to translation")
calc_bleu(hp.test2, translation)
结果
参考文献
【1】本次实现解读的代码:https://github.com/Kyubyong/transformer
【2】论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
【3】老版本代码解读 https://blog.csdn.net/mijiaoxiaosan/article/details/74909076