不得不说,js变得越来越像 python 了,其实我想吐槽的是功能是越来越强了,就是语法糖越多,代码就越凌乱不堪,写法多了,代码就很难统一规范. 对比一下 java,人家实例化都还要在前面指定类型,如: Object obj = new Object'() 哈哈,是不是很标准,
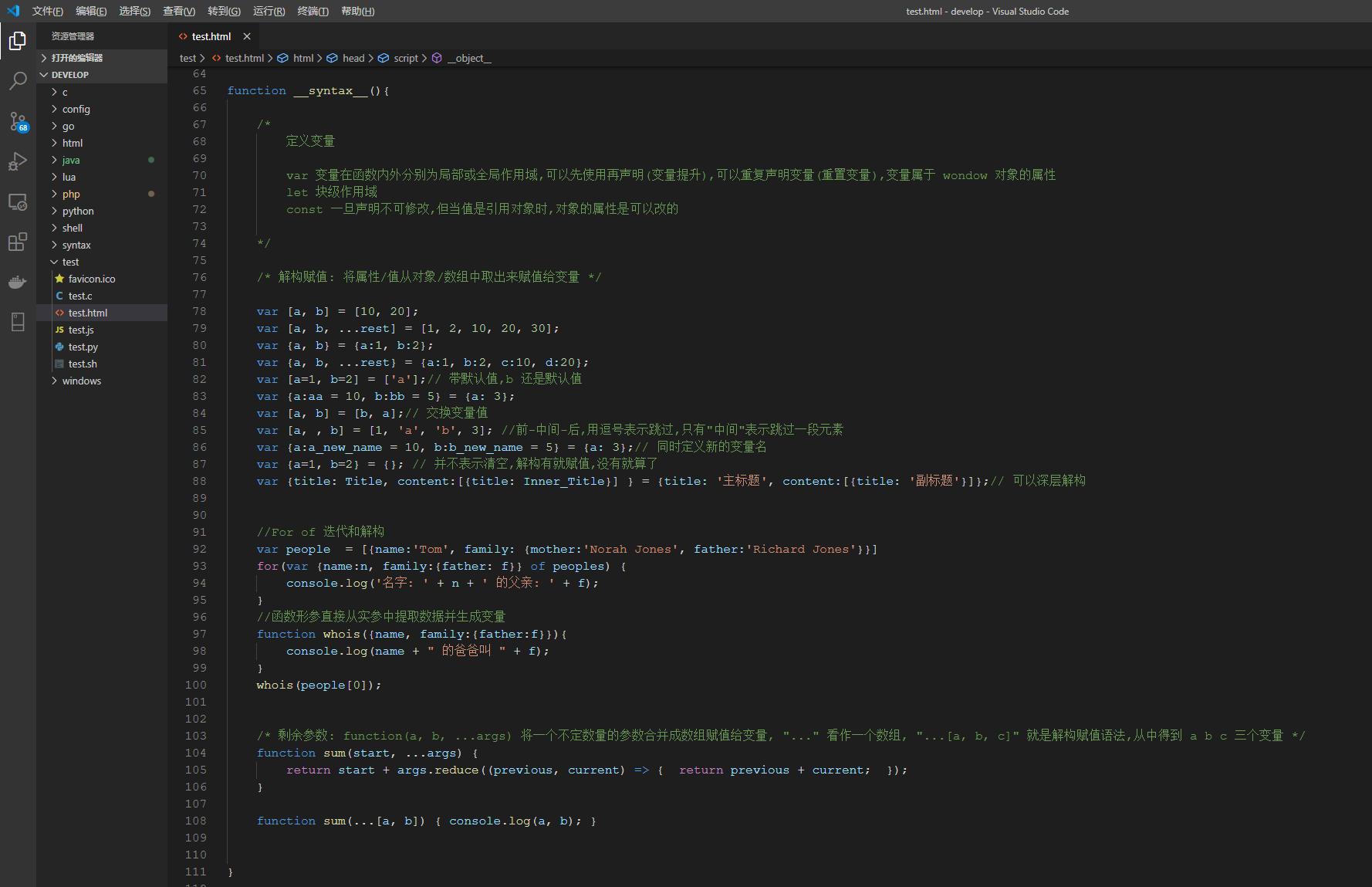
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Jstacipt 标准</title> <script type="text/javascript"> const tools = { window:{ vars(){ if(arguments.length != 0){ for(let index in arguments) { console.log(arguments[index]); } return; } let i = 1; for (var value in window){ if (window.hasOwnProperty(value)){ if(i++ < 200 || typeof window[value] == 'function') continue; attr = window[value]; if(typeof attr == 'object'){ attr.__var_name__ = value; console.log(attr); }else{ console.log(value + ' = ' + attr); } } } }, attr(value){ if (window.hasOwnProperty(value)){ attr = window[value]; if(typeof attr == 'object'){ attr.__var_name__ = value; console.log(attr); }else{ console.log(value + ' = ' + attr); } }else{ console.log('window 对象不包含该 '+value+' 属性'); } } }, } function __syntax__(){ /* 定义变量 var 变量在函数内外分别为局部或全局作用域,可以先使用再声明(变量提升),可以重复声明变量(重置变量),变量属于 wondow 对象的属性 let 块级作用域 const 一旦声明不可修改,但当值是引用对象时,对象的属性是可以改的 */ /* 解构赋值: 将属性/值从对象/数组中取出来赋值给变量 */ var [a, b] = [10, 20]; var [a, b, ...rest] = [1, 2, 10, 20, 30]; var {a, b} = {a:1, b:2}; var {a, b, ...rest} = {a:1, b:2, c:10, d:20}; var [a=1, b=2] = ['a'];// 带默认值,b 还是默认值 var {a:aa = 10, b:bb = 5} = {a: 3}; var [a, b] = [b, a];// 交换变量值 var [a, , b] = [1, 'a', 'b', 3]; //前-中间-后,用逗号表示跳过,只有"中间"表示跳过一段元素 var {a:a_new_name = 10, b:b_new_name = 5} = {a: 3};// 同时定义新的变量名 var {a=1, b=2} = {}; // 并不表示清空,解构有就赋值,没有就算了 var {title: Title, content:[{title: Inner_Title}] } = {title: '主标题', content:[{title: '副标题'}]};// 可以深层解构 //For of 迭代和解构 var people = [{name:'Tom', family: {mother:'Norah Jones', father:'Richard Jones'}}] for(var {name:n, family:{father: f}} of peoples) { console.log('名字: ' + n + ' 的父亲: ' + f); } //函数形参直接从实参中提取数据并生成变量 function whois({name, family:{father:f}}){ console.log(name + " 的爸爸叫 " + f); } whois(people[0]); /* 剩余参数: function(a, b, ...args) 将一个不定数量的参数合并成数组赋值给变量, "..." 看作一个数组, "...[a, b, c]" 就是解构赋值语法,从中得到 a b c 三个变量 */ function sum(start, ...args) { return start + args.reduce((previous, current) => { return previous + current; }); } function sum(...[a, b]) { console.log(a, b); } } function __object__(){ new Object(); Object.create(); let object = { property: "value", property(parameters){}, property: function(parameters){}, get property() {}, set property(value) {} }; let attr = 'name' object = { [attr]: '张三', ['a'+'g'+'e']: 20 } let a = 'foo', b = 42, c = {}; object = {a, b, c} // {a: "foo", b: 42, c:{}} name = {a, b, c}.a; // 扩展属性:返回对象所有属性 var clone = { ...obj1 }; var merge = { ...obj1, ...obj2 }; } function __arguments__(){ /* alt + shift + a arguments对象 是所有(非箭头)函数中都可用的局部变量 是一个对应于传递给函数的参数的类似于数组的对象 属性 arguments.callee 当前执行的函数 arguments.length 参数数量 arguments[@@iterator] 返回一个新的Array迭代器对象,该对象包含参数中每个索引的值。 */ console.log(typeof arguments); console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arguments)); /* To Array */ // 对参数使用slice会阻止某些JavaScript引擎中的优化 var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); var args = [].slice.call(arguments); // Array构造函数作为一个函数 var args = (arguments.length === 1 ? [arguments[0]] : Array.apply(null, arguments)); // ES2015 var args = Array.from(arguments); var args = [...arguments]; /* Iterate */ for(let item of arguments) { console.log(item); } } </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> <script type="text/javascript"> class Position { #watch = false;//属性与方法不能同名,这里前面加个#号也表示私有变量 #id; #error; #success; options = { enableHighAccuracy: false, // 高精度 timeout: 5000, maximumAge: 10 // 缓存时间 }; constructor(options = {}){ Object.assign(this.options, options); if(!this.constructor.support()) console.error("浏览器不支持定位功能!") } // 静态方法和属性可通过类名访问,也可以在其他静态方法中用 this 访问, 但不能在动态方法用 this 访问, 但可以变通, this.constructor 对象指向的就是类 static support(){ return "geolocation" in navigator; } watch(value = true){ this.#watch = value; return this; } position(options = {}){ Object.assign(this.options, options); if(this.#watch){ this.#id = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(this.#success, this.#error, this.options); }else{ navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(this.#success, this.#error, this.options); } } clear(){ if(this.#id) navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(this.#id); } success(callback){ if(typeof callback != 'function'){ callback = function(position){ console.success(position); } } this.#success = callback; return this; } error(callback){ if(typeof callback != 'function'){ callback = function(error){ console.error(error); } } this.#error = callback; return this; } } let square = new Position(); square.watch().success().error().position(); console.log(square); </script>