A famous sculptor Cicasso goes to a world tour!
Well, it is not actually a world-wide. But not everyone should have the opportunity to see works of sculptor, shouldn't he? Otherwise there will be no any exclusivity. So Cicasso will entirely hold the world tour in his native country — Berland.
Cicasso is very devoted to his work and he wants to be distracted as little as possible. Therefore he will visit only four cities. These cities will be different, so no one could think that he has "favourites". Of course, to save money, he will chose the shortest paths between these cities. But as you have probably guessed, Cicasso is a weird person. Although he doesn't like to organize exhibitions, he likes to travel around the country and enjoy its scenery. So he wants the total distance which he will travel to be as large as possible. However, the sculptor is bad in planning, so he asks you for help.
There are n cities and m one-way roads in Berland. You have to choose four different cities, which Cicasso will visit and also determine the order in which he will visit them. So that the total distance he will travel, if he visits cities in your order, starting from the first city in your list, and ending in the last, choosing each time the shortest route between a pair of cities — will be the largest.
Note that intermediate routes may pass through the cities, which are assigned to the tour, as well as pass twice through the same city. For example, the tour can look like that: 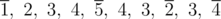 . Four cities in the order of visiting marked as overlines: [1, 5, 2, 4].
. Four cities in the order of visiting marked as overlines: [1, 5, 2, 4].
Note that Berland is a high-tech country. So using nanotechnologies all roads were altered so that they have the same length. For the same reason moving using regular cars is not very popular in the country, and it can happen that there are such pairs of cities, one of which generally can not be reached by car from the other one. However, Cicasso is very conservative and cannot travel without the car. Choose cities so that the sculptor can make the tour using only the automobile. It is guaranteed that it is always possible to do.
In the first line there is a pair of integers n and m (4 ≤ n ≤ 3000, 3 ≤ m ≤ 5000) — a number of cities and one-way roads in Berland.
Each of the next m lines contains a pair of integers ui, vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n) — a one-way road from the city ui to the city vi. Note that ui and viare not required to be distinct. Moreover, it can be several one-way roads between the same pair of cities.
Print four integers — numbers of cities which Cicasso will visit according to optimal choice of the route. Numbers of cities should be printed in the order that Cicasso will visit them. If there are multiple solutions, print any of them.
8 9
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 5
2 1 8 7
Let d(x, y) be the shortest distance between cities x and y. Then in the example d(2, 1) = 3, d(1, 8) = 7, d(8, 7) = 3. The total distance equals 13.
题目大意:给定一张边权均为1的有向图,求四个不同的点A,B,C,D,使得dis[A][B]+dis[B][C]+dis[C][D]尽可能大。
分析:典型的枚举题.要确定很多东西,没有很好的方法,就只能通过枚举。
那么枚举什么?一般对于枚举题,枚举在复杂度要求内,最有“特点”的东西. 在本题中对应B点和C点.接下来就比较容易有思路了,我们肯定是选尽可能远的路径长度走到B,并且从C走尽可能远的路径长度,但是要防止冲突,比如4个点会有重复,需要记录最大,次大和第三大的值. 那么对于每个点,bfs预处理一下就好了.
看错题了gg,以为b和c只用通过一条边相连.
#include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 10010,inf = 0x7ffffff; int n,m,head1[maxn],to1[maxn],nextt1[maxn],tot1 = 1; int head2[maxn],to2[maxn],nextt2[maxn],tot2 = 1; int ans1[maxn][3],pos1[maxn][3],d1[3010][3010],d2[3010][3010],pos2[maxn][3]; int vis1[maxn],vis2[maxn],a[3010][3010],ans[4],maxx,ans2[maxn][3]; void add1(int x,int y) { to1[tot1] = y; nextt1[tot1] = head1[x]; head1[x] = tot1++; } void add2(int x,int y) { to2[tot2] = y; nextt2[tot2] = head2[x]; head2[x] = tot2++; } void push1(int d,int x,int y) { if (d > ans1[x][0]) { ans1[x][2] = ans1[x][1]; pos1[x][2] = pos1[x][1]; ans1[x][1] = ans1[x][0]; pos1[x][1] = pos1[x][0]; ans1[x][0] = d; pos1[x][0] = y; } else if (d > ans1[x][1]) { ans1[x][2] = ans1[x][1]; pos1[x][2] = pos1[x][1]; ans1[x][1] = d; pos1[x][1] = y; } else if (d > ans1[x][2]) { ans1[x][2] = d; pos1[x][2] = y; } } void push2(int d,int x,int y) { if (d > ans2[x][0]) { ans2[x][2] = ans2[x][1]; pos2[x][2] = pos2[x][1]; ans2[x][1] = ans2[x][0]; pos2[x][1] = pos2[x][0]; ans2[x][0] = d; pos2[x][0] = y; } else if (d > ans2[x][1]) { ans2[x][2] = ans2[x][1]; pos2[x][2] = pos2[x][1]; ans2[x][1] = d; pos2[x][1] = y; } else if (d > ans2[x][2]) { ans2[x][2] = d; pos2[x][2] = y; } } void bfs(int x) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d1[x][i] = d2[x][i] = inf; memset(vis1,0,sizeof(vis1)); memset(vis2,0,sizeof(vis2)); queue <int> q; q.push(x); vis1[x] = 1; d1[x][x] = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); vis1[u] = 0; for (int i = head1[u]; i; i = nextt1[i]) { int v = to1[i]; if (d1[x][v] > d1[x][u] + 1) { d1[x][v] = d1[x][u] + 1; if (!vis1[v]) { vis1[v] = 1; //push1(d1[v],x,v); q.push(v); } } } } while (!q.empty()) q.pop(); q.push(x); vis2[x] = 1; d2[x][x] = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); vis2[u] = 0; for (int i = head2[u]; i; i = nextt2[i]) { int v = to2[i]; if (d2[x][v] > d2[x][u] + 1) { d2[x][v] = d2[x][u] + 1; if (!vis2[v]) { vis2[v] = 1; //push2(d2[v],x,v); q.push(v); } } } } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //printf("%d %d ",d1[i],d2[i]); if (d1[x][i] != inf) push1(d1[x][i],x,i); if (d2[x][i] != inf) push2(d2[x][i],x,i); } } int check(int x,int y,int k1,int k2) { int a1 = pos2[x][k1]; int a2 = pos1[y][k2]; if (x == 0 || y == 0 || a1 == 0 || a2 == 0) return -1; if (a1 != a2 && a2 != x && x != y && y != a1) return ans2[x][k1] + ans1[y][k2] + d1[x][y]; return -1; } int main() { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); a[x][y] = 1; add1(x,y); add2(y,x); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) bfs(i); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if (i == j || d1[i][j] >= inf) continue; for (int k1 = 0; k1 < 3; k1++) { for (int k2 = 0; k2 < 3; k2++) { int temp = check(i,j,k1,k2); if (temp > maxx) { ans[0] = pos2[i][k1]; ans[1] = i; ans[2] = j; ans[3] = pos1[j][k2]; maxx = temp; } } } } } for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]); printf(" "); return 0; }