第一部分:总结教材14.1-14.3知识内容
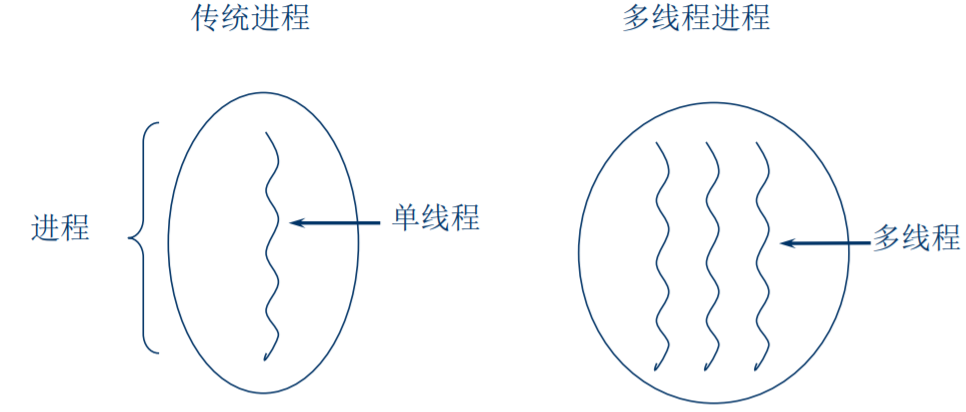
并发
• 线程的概念
• 中断线程
• 线程状态
• 多线程调度
• 线程同步
一、线程的概念
1. 程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本。
2. 进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载、执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程。
3. 操作系统为每个进程分配一段独立的内存空间和系统资源,包括:代码数据以及堆栈等资源。每一个进程的内部数据和状态都是完全独立的。
4. 多任务操作系统中,进程切换对CPU资源消耗较大。
二、多线程的概念
1. 多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索。 ‐线程是比进程执行更小的单位。
2. 线程不能独立存在,必须存在于进程中,同一进 程的各线程间共享进程空间的数据。
3. 每个线程有它自身的产生、存在和消亡的过程, 是一个动态的概念。
4. 多线程意味着一个程序的多行语句可以看上去几 乎在同一时间内同时运行。
5. 线程创建、销毁和切换的负荷远小于进程,又称 为轻量级进程(lightweight process)。
6. Java实现多线程有两种途径:
• 创建Thread类的子类
• API :
➢ Therad (Runnable traget) 构造一个新线程,用于调用给定目标的run() 方法
➢ void start() 启动这个线程,讲引发调用 run() 方法 。这个方法将立即返回,并且新线程将并发运行。
➢ void run() 调用关联 Runnable 的 run 方法
➢ static void sleep (long millis) 休眠给定的毫秒数
• 在程序中定义实现Runnable接口的类
➢ void run ( ) 必须覆盖这个方法中提供索要执行的任务指令。
三、.中断线程
• 当线程的 run方法 执行方法体中最后一条语句后, 或者出现了在 run方法 中没有捕获的异常时,线程将终止,让出CPU使用权。
• 调用 interrupt() 方法也可终止线程
• 当对一个线程调用 interrupt() 方法时,线程的中断状态将被置位。 这是每一个线程都具有的 boolean 标志 。每个线程都应该不时的检查这个标志,以判断线程是否被中断。
• 要想弄清中断状态是否被置位,首先调用静态的 Thread.currentThread 方法获得当前线程,然后调用 isInterrupted 方法。
• 如果线程被阻塞, 就无法检测中断状态 。这是产生 Interrupted Exception 异常的地方。
• API :
➢ void interrupt () 像线程发送中断请求。 现成的中断状态将被设置为 true. 如果目前该线程被一个sleep 调用阻塞, 那么,InterruptedException 异常抛出。
➢ static boolean interupted () 测试当前线程 (及正在执行这一命令的线程) 是否被中断。 注意, 这是一个静态方法。 这一调用会产生副作用------它将当前线程的中断状态重置为flase.
➢ boolean isInterrupted() 测试线程是否被终止。 不像静态的中断方法, 这一调用不改变线程的中断状态。
➢ static Thread currentThread () 返回代表当执行线程的 Thread 对象。
四、. 线程状态
• 利用各线程的状态变换,可以控制各个线程轮流 使用CPU,体现多线程的并行性特征。
• 线程有如下7种状态:
➢ New (新建)
➢ Runnable (可运行)
➢ Running(运行)
➢ Blocked (被阻塞)
➢ Waiting (等待)
➢ Timed waiting (计时等待)
➢ Terminated (被终止)
1、新创建线程
• new(新建)线程对象刚刚创建,还没有启动,此时线程还处于不可运行状态。
2、可运行线程
➢ 一旦调用start方法,线程处于 runnable(可运行状态)
➢ 此时线程已经启动,处于线程的run()方法之中。
➢ 此时的线程可能运行,也可能不运行,只要 CPU一空闲,马上就会运行。
3、被阻塞线程和等待线程
- blocked (被阻塞)
➢ 一个正在执行的线程因特殊原因,被暂停执行, 进入阻塞状态。
➢ 当线程处于阻塞或等待状态,它暂时不活动。 它不运行任何代码且消耗最少资源,直到线程调度器重新激活他。
➢ sleep(),wait()是两个常用引起线程阻塞的方法。
4、被终止的线程
Terminated (被终止) 线程被终止的原因有二:
➢ run()方法中最后一个语句执行完毕而自然死亡。
➢ 因为一个没有捕获的异常终止了run方法而意外死亡。
API:
➢ void join() 等待终止线程
➢ void join(long millis) 等待指定的线程死亡或者经过指定的毫秒数
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第13章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
在elipse IDE中调试运行教材585页程序13-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
将所生成的JAR文件移到另外一个不同的目录中,再运行该归档文件,以便确认程序是从JAR文件中,而不是从当前目录中读取的资源。
掌握创建JAR文件的方法;
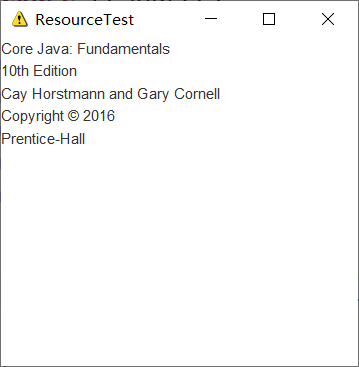
1 package 第十六周; 2 import java.awt.*; 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.net.*; 5 import java.util.*; 6 import javax.swing.*; 7 /** 8 * @version 1.41 2015-06-12 9 * @author Cay Horstmann 10 */ 11 public class ResourceTest 12 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) 14 { 15 EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { 16 JFrame frame = new ResourceTestFrame(); 17 frame.setTitle("ResourceTest"); 18 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 19 frame.setVisible(true); 20 }); 21 } 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * A frame that loads image and text resources. 26 */ 27 class ResourceTestFrame extends JFrame 28 { 29 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; 30 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; 31 32 public ResourceTestFrame() 33 { 34 setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); 35 ///在找到ResourceTest类的地方查找about.gif文件 36 URL aboutURL = getClass().getResource("about.gif"); 37 // //将此图像设置为框架的图标 38 Image img = new ImageIcon(aboutURL).getImage(); 39 setIconImage(img); 40 41 JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(); 42 InputStream stream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("about.txt");//通过"about.txt"地址调用 getClass()方法,对文本资源进行加载 43 try (Scanner in = new Scanner(stream, "UTF-8")) 44 { 45 while (in.hasNext()) 46 textArea.append(in.nextLine() + " ");//讲读到的内容显示在文本域 47 } 48 add(textArea); 49 } 50 }



运行结果:
测试程序2:
在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
掌握线程概念;
掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
1. Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法:
1 package 第十六周; 2 3 // 创建Thread类的子类实现多线程 4 5 class Lefthand extends Thread { 6 public void run() 7 { 8 for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) 9 { System.out.println("You are Students!"); 10 try{ sleep(500); } //每500ms 休眠一次 11 catch(InterruptedException e) 12 { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 class Righthand extends Thread { //创建Thread类的子类实现多线程 17 public void run() 18 { 19 for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) 20 { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); 21 try{ sleep(300); } //每300ms 休眠一次 22 catch(InterruptedException e) 23 { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 public class ThreadTest 28 { 29 static Lefthand left; 30 static Righthand right; 31 public static void main(String[] args) 32 { left=new Lefthand(); 33 right=new Righthand(); 34 left.start(); 35 right.start(); 36 } 37 }
2. 用Runnable接口创建线程的方法:
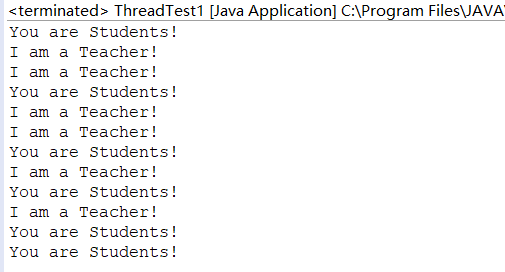
1 // 实现Runnable接口的来实现多线程 2 class Lefthand implements Runnable { 3 public void run() { 4 for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { 5 System.out.println("You are Students!"); 6 try { 7 Thread.sleep(500);//调用Thread类的sleep方法 每500ms 休眠一次 8 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 9 System.out.println("Lefthand error."); 10 } 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 15 class Righthand implements Runnable { // 实现Runnable接口的来实现多线程 16 public void run() { 17 for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { 18 System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); 19 try { 20 Thread.sleep(300);//调用Thread类的sleep方法 每500ms 休眠一次 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 System.out.println("Righthand error."); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 public class ThreadTest1 { 29 static Lefthand left; 30 static Righthand right; 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) { 33 Runnable left1 = new Lefthand(); 34 Runnable right1 = new Righthand() ; 35 Thread left = new Thread(left1); 36 Thread right = new Thread(right1); 37 left.start(); 38 right.start(); 39 } 40 }
运行结果如下:
测试程序3:
在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
1 package 第十六周; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.awt.event.*; 5 import javax.swing.*; 6 7 /** 8 * Shows an animated bouncing ball. 9 * @version 1.34 2015-06-21 10 * @author Cay Horstmann 11 */ 12 public class Bounce 13 { 14 public static void main(String[] args) 15 { 16 EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { 17 JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); 18 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 19 frame.setVisible(true); 20 }); 21 } 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * The frame with ball component and buttons. 26 */ 27 class BounceFrame extends JFrame 28 { 29 private BallComponent comp; 30 public static final int STEPS = 1000; 31 public static final int DELAY = 3; 32 33 /** 34 * Constructs the frame with the component for showing the bouncing ball and 35 * Start and Close buttons 36 */ 37 public BounceFrame() //构造包含用于显示弹跳球和启动和关闭按钮 38 { 39 setTitle("Bounce"); 40 comp = new BallComponent(); 41 add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); 42 JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
//为按钮添加标题,监听器,并将按钮添加到面板 43 addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall()); 44 addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); 45 add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 46 pack(); 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * Adds a button to a container. 51 * @param c the container 52 * @param title the button title 53 * @param listener the action listener for the button 54 */ 55 public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) 56 { 57 JButton button = new JButton(title); 58 c.add(button); 59 button.addActionListener(listener); 60 } 61 62 /** 63 * Adds a bouncing ball to the panel and makes it bounce 1,000 times. 64 */ 65 public void addBall() //在面板中添加一个弹跳球,使其弹跳1000次 66 { 67 try 68 { 69 Ball ball = new Ball(); 70 comp.add(ball); 71 72 for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) 73 { 74 ball.move(comp.getBounds()); 75 comp.paint(comp.getGraphics()); 76 Thread.sleep(DELAY); 77 } 78 } 79 catch (InterruptedException e) 80 { 81 } 82 } 83 }
1 package 第十六周; 2 3 import java.awt.geom.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A ball that moves and bounces off the edges of a rectangle 7 * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class Ball 11 { 12 private static final int XSIZE = 15; 13 private static final int YSIZE = 15; 14 private double x = 0; 15 private double y = 0; 16 private double dx = 1; 17 private double dy = 1; 18 19 /** 20 * Moves the ball to the next position, reversing direction if it hits one of the edges 21 */ 22 public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) //将球移动到下一个位置,如果碰到其中一个边,则反转方向 23 { 24 x += dx; //x y方向上依次加位移增量 25 y += dy;
//宽度上的最小位置 26 if (x < bounds.getMinX()) 27 { 28 x = bounds.getMinX(); 29 dx = -dx; 30 }
//宽度上的最大位置 31 if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) 32 { 33 x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; 34 dx = -dx; 35 }
//高度上的最小位置 36 if (y < bounds.getMinY()) 37 { 38 y = bounds.getMinY(); 39 dy = -dy; 40 }
//高度上的最大位置 41 if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) 42 { 43 y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; 44 dy = -dy; 45 } 46 } 47 48 /** 49 * Gets the shape of the ball at its current position. 50 */ 51 public Ellipse2D getShape() //获取球在其当前位置的形状。 52 { 53 return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); 54 } 55 }
1 package 第十六周; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.util.*; 5 import javax.swing.*; 6 7 /** 8 * The component that draws the balls. 9 * @version 1.34 2012-01-26 10 * @author Cay Horstmann 11 */ 12 public class BallComponent extends JPanel 13 { 14 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; 15 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; 16 17 private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); 18 19 /** 20 * Add a ball to the component. 21 * @param b the ball to add 22 */ 23 public void add(Ball b) //将球添加到组件 24 { 25 balls.add(b); 26 } 27 28 public void paintComponent(Graphics g) 29 { 30 super.paintComponent(g); // 删除背景 31 Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; 32 for (Ball b : balls) 33 { 34 g2.fill(b.getShape()); 35 } 36 } 37 38 public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } 39 }
运行结果如下:

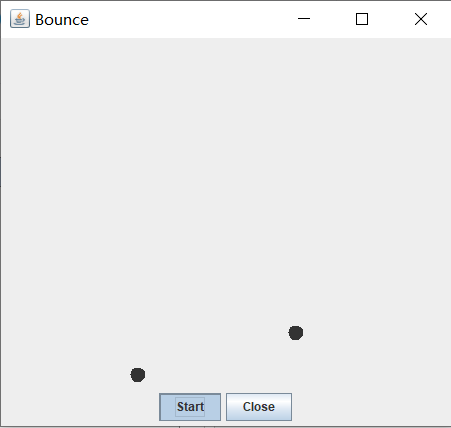
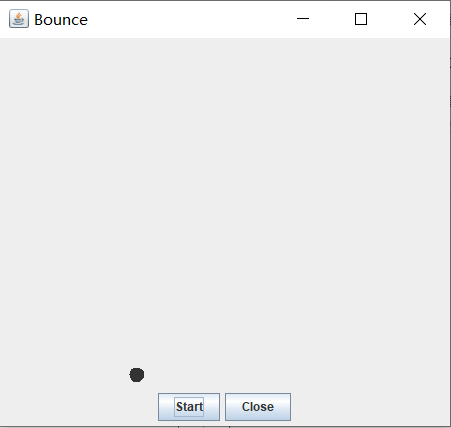
在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
1 import java.awt.geom.*; 2 3 /** 4 * 在长方形边缘上移动和反弹的球 5 * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class Ball 9 { 10 private static final int XSIZE = 15; 11 private static final int YSIZE = 15; 12 private double x = 0; 13 private double y = 0; 14 private double dx = 1; 15 private double dy = 1; 16 17 /** 18 * 将球移动到下一个位置,如果碰到其中一个边,则反转方向 19 */ 20 public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) 21 { 22 x += dx; 23 y += dy; 24 //宽度上的最小位置 25 if (x < bounds.getMinX()) 26 { 27 x = bounds.getMinX(); 28 dx = -dx; 29 } 30 //宽度上的最大位置 31 if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) 32 { 33 x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; 34 dx = -dx; 35 } 36 //高度上的最小位置 37 if (y < bounds.getMinY()) 38 { 39 y = bounds.getMinY(); 40 dy = -dy; 41 } 42 //宽度上的最大位置 43 if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) 44 { 45 y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; 46 dy = -dy; 47 } 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * 获取球在其当前位置的形状 52 */ 53 public Ellipse2D getShape() 54 { 55 return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); 56 } 57 }
1 import java.awt.*; 2 import java.util.*; 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 5 /** 6 * 画弹力球的部件. 7 * @version 1.34 2012-01-26 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class BallComponent extends JPanel 11 { 12 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; 13 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; 14 15 private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>() 21 22 //将球添加到组件 23 public void add(Ball b) 24 { 25 balls.add(b); 26 } 27 30 public void paintComponent(Graphics g) 31 { 32 super.paintComponent(g); // 使用背景色绘制面板 33 Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; 34 35 //获取每一个球的位置和形状并使用默认颜色进行填充 36 for (Ball b : balls) 37 { 38 g2.fill(b.getShape()); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } 43 }
1 import java.awt.*; 2 import java.awt.event.*; 3 4 import javax.swing.*; 5 6 /** 7 * 显示动画弹跳球。 8 * @version 1.34 2015-06-21 9 * @author Cay Horstmann 10 */ 11 public class BounceThread 12 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) 14 { 15 EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { 16 JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); 17 frame.setTitle("BounceThread"); 18 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 19 frame.setVisible(true); 20 }); 21 } 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 有面板和按钮的框架。 26 */ 27 class BounceFrame extends JFrame 28 { 29 private BallComponent comp; 30 public static final int STEPS = 1000; 31 public static final int DELAY = 5; 32 33 34 /** 35 * 构造包含用于显示弹跳球和开始和关闭按钮的组件的框架 36 */ 37 public BounceFrame() 38 { 39 comp = new BallComponent(); 40 add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); 41 JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); 42 addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall()); 43 addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); 44 add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 45 pack(); 46 } 47 54 public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) 55 { 56 JButton button = new JButton(title); 57 c.add(button); 58 button.addActionListener(listener); 59 } 60 61 /** 62 * 在画布上添加一个弹跳球并开始一条线使其弹跳 63 */ 64 public void addBall() 65 { 66 Ball ball = new Ball(); 67 comp.add(ball); 71 Runnable r = () -> { 72 try 73 { 74 for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) 75 { 76 ball.move(comp.getBounds()); 77 //调用组件的repaint方法,重新绘制组件 78 comp.repaint(); 79 Thread.sleep(DELAY); 80 } 81 } 82 catch (InterruptedException e) 83 { 84 } 85 }; 86 87 //将Runnable对象作为入口参数传入Thread的构造函数,再调用start方法就可以启动线程 88 Thread t = new Thread(r); 89 t.start(); 90 } 91 }
运行结果如下:
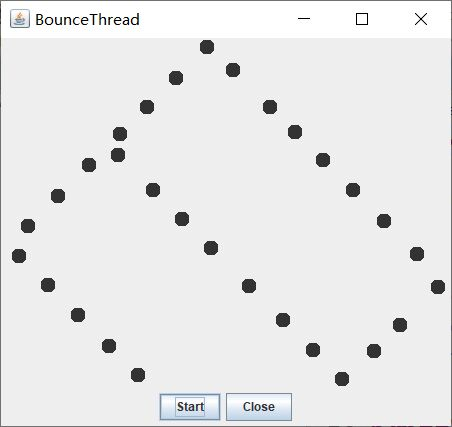
实验2:结对编程练习:采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并创建程序归档文件。
设计一个100以内整数小学生四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
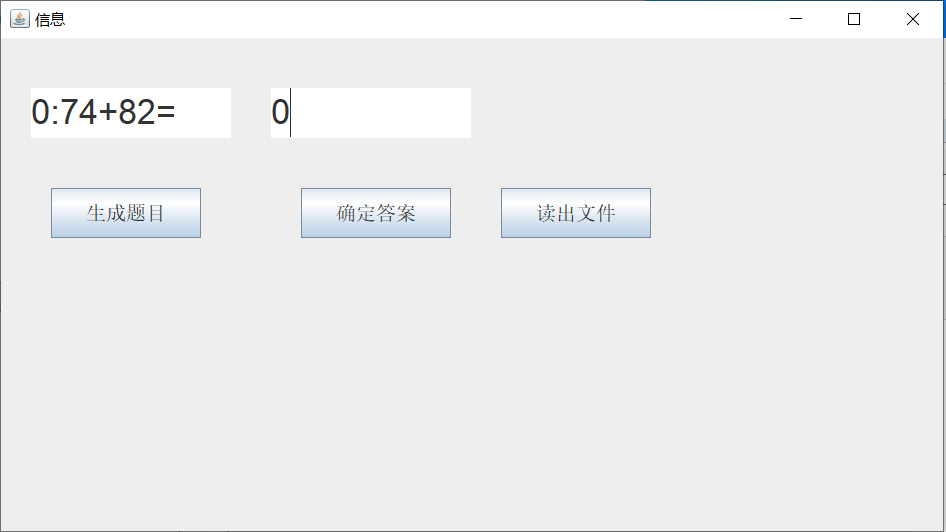
1 package add; 2 import java.awt.Font; 3 import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; 4 import java.awt.event.ActionListener; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.PrintWriter; 7 import java.util.Collections; 8 import java.util.Scanner; 9 10 import javax.swing.*; 11 12 import java.math.*; 13 14 15 public class Culu extends JFrame { 16 17 private String[] c=new String[10]; 18 private String[] c1=new String[10]; 19 private int[] list=new int[10]; 20 int i=0,i1=0,sum = 0; 21 private PrintWriter out = null; 22 private JTextArea text,text1; 23 private int counter; 24 25 public Culu() { 26 JPanel Panel = new JPanel(); 27 Panel.setLayout(null); 28 JLabel JLabel1=new JLabel(""); 29 JLabel1.setBounds(500, 800, 400, 30); 30 JLabel1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); 31 JButton Button = new JButton("生成题目"); 32 Button.setBounds(50,150,150,50); 33 Button.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); 34 Button.addActionListener(new Action()); 35 JButton Button2 = new JButton("确定答案"); 36 Button2.setBounds(300,150,150,50); 37 Button2.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); 38 Button2.addActionListener(new Action1()); 39 JButton Button3 = new JButton("读出文件"); 40 Button3.setBounds(500,150,150,50); 41 Button3.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); 42 Button3.addActionListener(new Action2()); 43 text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(30, 50, 200, 50); 44 text.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); 45 text1=new JTextArea(30,80); 46 text1.setBounds(270, 50, 200, 50); 47 text1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); 48 49 Panel.add(text); 50 Panel.add(text1); 51 52 Panel.add(Button); 53 Panel.add(Button2); 54 Panel.add(Button3); 55 Panel.add(JLabel1); 56 add(Panel); 57 } 58 59 private class Action implements ActionListener 60 { 61 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 62 { 63 text1.setText("0"); 64 if(i<10) { 65 66 int a = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); 67 int b = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); 68 int m= (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); 69 switch(m) 70 { 71 case 0: 72 while(a<b){ 73 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 74 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 75 } 76 c[i]=(i+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); 77 list[i]=Math.floorDiv(a, b); 78 text.setText(i+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); 79 i++; 80 break; 81 case 1: 82 c[i]=(i+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); 83 list[i]=Math.multiplyExact(a, b); 84 text.setText(i+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); 85 i++; 86 break; 87 case 2: 88 c[i]=(i+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); 89 list[i]=Math.addExact(a, b); 90 text.setText(i+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); 91 i++; 92 break ; 93 case 3: 94 while(a<=b){ 95 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 96 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 97 } 98 c[i]=(i+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); 99 text.setText(i+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); 100 list[i]=Math.subtractExact(a, b); 101 i++; 102 break ; 103 } 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 private class Action1 implements ActionListener 108 { 109 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 110 { 111 if(i<10) { 112 text.setText(null); 113 String daan=text1.getText().toString().trim(); 114 int a = Integer.parseInt(daan); 115 if(text1.getText()!="") { 116 if(list[i1]==a) sum+=10; 117 } 118 c1[i1]=daan; 119 i1++; 120 } 121 } 122 } 123 124 125 private class Action2 implements ActionListener 126 { 127 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 128 { 129 130 try { 131 out = new PrintWriter("text.txt"); 132 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 133 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 134 e.printStackTrace(); 135 } 136 for(int counter=0;counter<10;counter++) 137 { 138 out.println(c[counter]+c1[counter]); 139 } 140 out.println("成绩"+sum); 141 out.close(); 142 143 } 144 145 } 146 }
1 package add; 2 import java.awt.Dimension; 3 import java.awt.EventQueue; 4 import java.awt.Toolkit; 5 6 import javax.swing.JFrame; 7 8 public class Main { 9 10 public static void main (String args[]) 11 { 12 Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); 13 Dimension s=t.getScreenSize(); 14 EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { 15 JFrame frame = new Culu(); 16 frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth()/2,(int)s.getHeight()/2); 17 frame.setTitle("信息"); 18 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 19 frame.setVisible(true); 20 }); 21 } 22 23 }
运行结果如下:
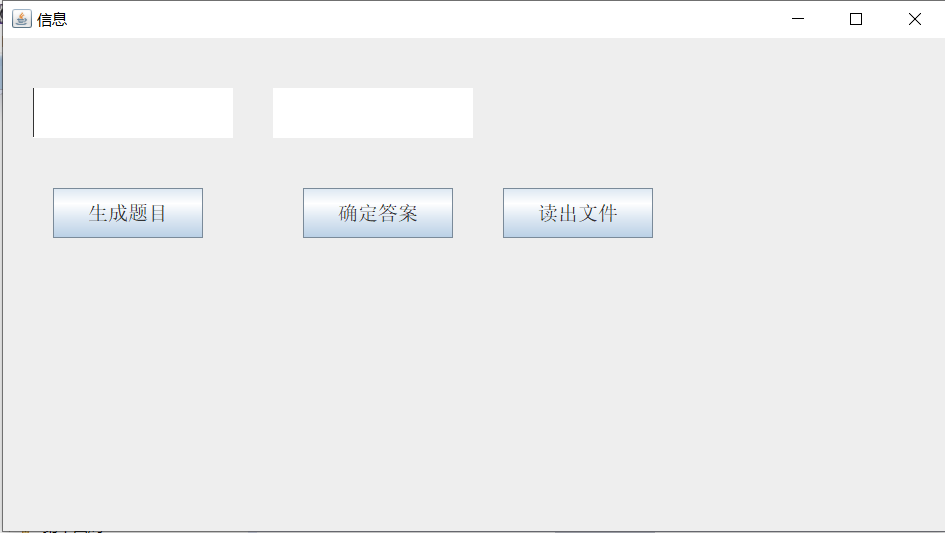

实验总结:本周实验主要学了线程。区分了程序,进程,和线程的概念区别。多线程是并发的 ,多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索,多线程是一个程序的多行语句同时执行 ,线程是比进程执行更小的单位。本周学习的内容还是比较难的,特别难懂,我觉得掌握的不好,课后就多看看书,尽量多理解理解。本周的结对编程难度还是很大的我觉得,自己掌握的不多,编起来就很困难,程序也是用来很长的时间来琢磨消化的,但还是模模糊糊的。