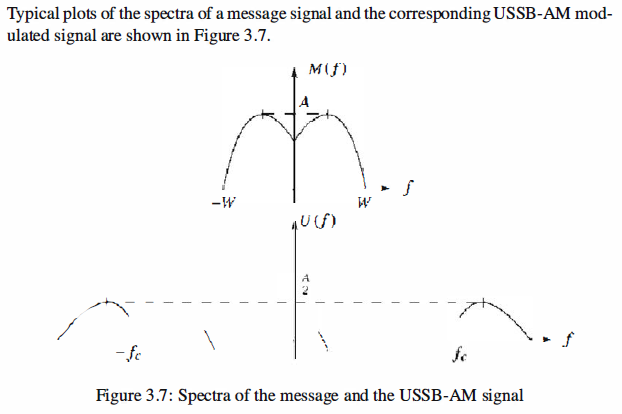
SSB-AM
SSB-AM is derived from DSB-AM by eliminating one of the sidebands. Therefore,
it occupies half the bandwidth of DSB-AM. Depending on the sideband that remains,
either the upper or the lower sideband, there exist two types of SSB-AM: Upper SingleSideband
AM (USSB-AM) and Lower Single-Sideband AM (LSSB-AM).
The time representation for these signals is given by


Matlab Coding

Solution

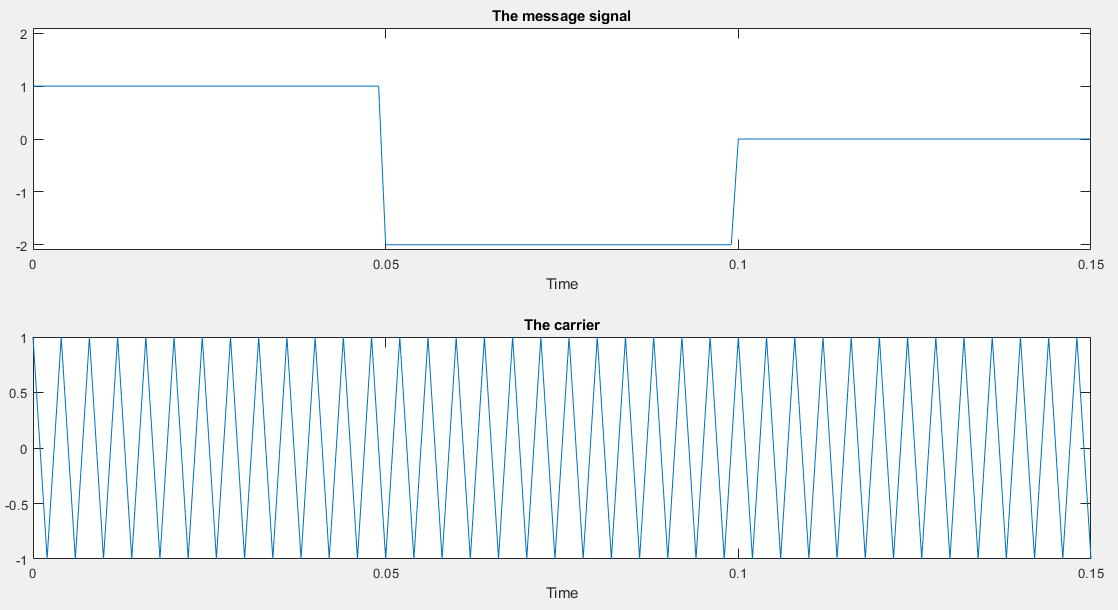
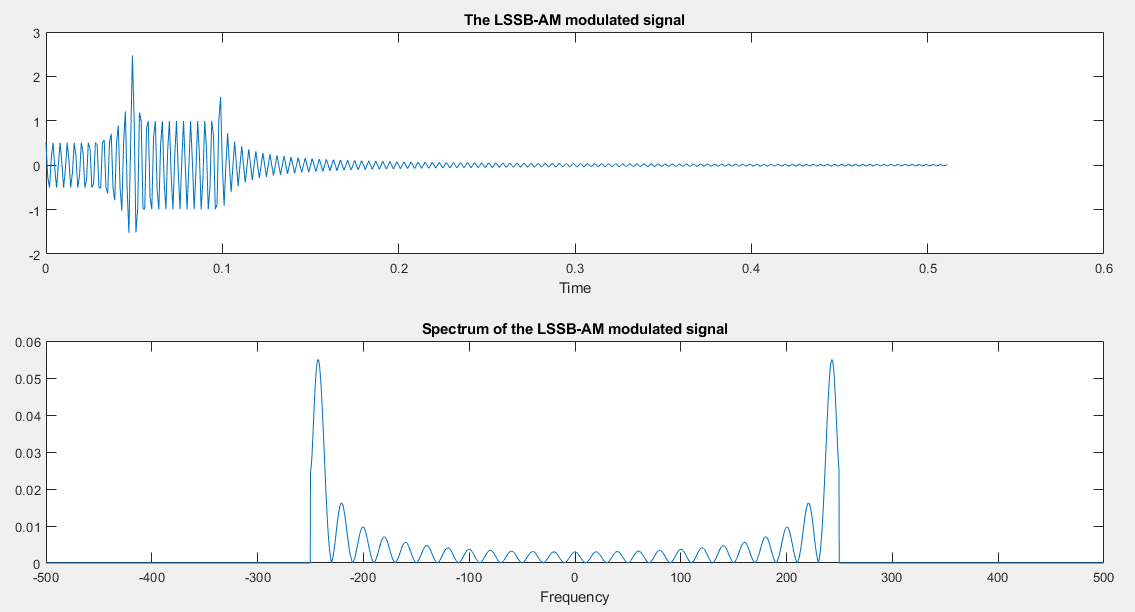
1 % MATLAB script for Illustrative Problem 3.4. 2 % Demonstration script for LSSB-AM modulation. The message signal 3 % is +1 for 0 < t < t0/3, -2 for t0/3 < t < 2t0/3, and zero otherwise. 4 echo on 5 t0=.15; % signal duration 6 ts=0.001; % sampling interval 7 fc=250; % carrier frequency 8 snr=10; % SNR in dB (logarithmic) 9 fs=1/ts; % sampling frequency 10 df=0.25; % desired freq. resolution 11 t=[0:ts:t0]; % time vector 12 snr_lin=10^(snr/10); % SNR 13 % the message vector 14 m=[ones(1,t0/(3*ts)),-2*ones(1,t0/(3*ts)),zeros(1,t0/(3*ts)+1)]; 15 c=cos(2*pi*fc.*t); % carrier vector 16 udsb=m.*c; % DSB modulated signal 17 [UDSB,udssb,df1]=fftseq(udsb,ts,df); % Fourier transform 18 UDSB=UDSB/fs; % scaling 19 f=[0:df1:df1*(length(udssb)-1)]-fs/2; % frequency vector 20 n2=ceil(fc/df1); % location of carrier in freq. vector
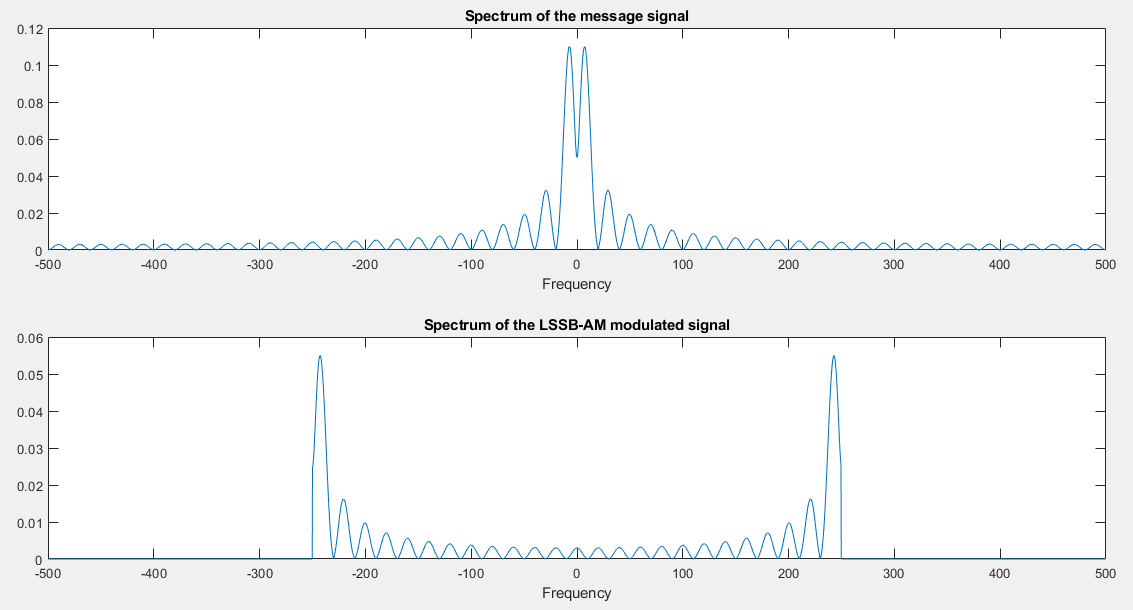
21 % Remove the upper sideband from DSB. 22 UDSB(n2:length(UDSB)-n2)=zeros(size(UDSB(n2:length(UDSB)-n2))); 23 ULSSB=UDSB; % Generate LSSB-AM spectrum. 24 [M,m,df1]=fftseq(m,ts,df); % Fourier transform 25 M=M/fs; % scaling 26 u=real(ifft(ULSSB))*fs; % Generate LSSB signal from spectrum. 27 signal_power=spower(udsb(1:length(t)))/2; 28 % % Compute signal power. 29 noise_power=signal_power/snr_lin; % Compute noise power. 30 noise_std=sqrt(noise_power); % Compute noise standard deviation. 31 noise=noise_std*randn(1,length(u)); % Generate noise vector. 32 r=u+noise; % Add the signal to noise. 33 [R,r,df1]=fftseq(r,ts,df); % Fourier transform 34 R=R/fs; % scaling 35 pause % Press a key to show the modulated signal power. 36 signal_power 37 pause % Press any key to see a plot of the message signal. 38 clf 39 subplot(2,1,1) 40 plot(t,m(1:length(t))) 41 axis([0,0.15,-2.1,2.1]) 42 xlabel('Time') 43 title('The message signal') 44 pause % Press any key to see a plot of the carrier. 45 subplot(2,1,2) 46 plot(t,c(1:length(t))) 47 xlabel('Time') 48 title('The carrier') 49 pause % Press any key to see a plot of the modulated signal and its spectrum. 50 clf 51 subplot(2,1,1) 52 plot([0:ts:ts*(length(u)-1)/8],u(1:length(u)/8)) 53 xlabel('Time') 54 title('The LSSB-AM modulated signal') 55 subplot(2,1,2) 56 plot(f,abs(fftshift(ULSSB))) 57 xlabel('Frequency') 58 title('Spectrum of the LSSB-AM modulated signal') 59 pause % Press any key to see the spectra of the message and the modulated signals. 60 clf 61 subplot(2,1,1) 62 plot(f,abs(fftshift(M))) 63 xlabel('Frequency') 64 title('Spectrum of the message signal') 65 subplot(2,1,2) 66 plot(f,abs(fftshift(ULSSB))) 67 xlabel('Frequency') 68 title('Spectrum of the LSSB-AM modulated signal') 69 pause % Press any key to see a noise sample. 70 subplot(2,1,1) 71 plot(t,noise(1:length(t))) 72 title('Noise sample') 73 xlabel('Time') 74 pause % Press a key to see the modulated signal and noise. 75 subplot(2,1,2) 76 plot(t,r(1:length(t))) 77 title('Modulated signal and noise') 78 xlabel('Time') 79 subplot(2,1,1) 80 pause % Press any key to see the spectrum of the modulated signal. 81 plot(f,abs(fftshift(ULSSB))) 82 title('Modulated signal spectrum') 83 xlabel('Frequency') 84 subplot(2,1,2) 85 pause % Press a key to see the modulated signal noise in freq. domain. 86 plot(f,abs(fftshift(R))) 87 title('Modulated signal noise spectrum') 88 xlabel('Frequency')
The modulated signal power
signal_power =
0.4139
The message signal, and the carrier
The modulated signal and its spectrum
The spectra of the message and the modulated signals
The noise sample
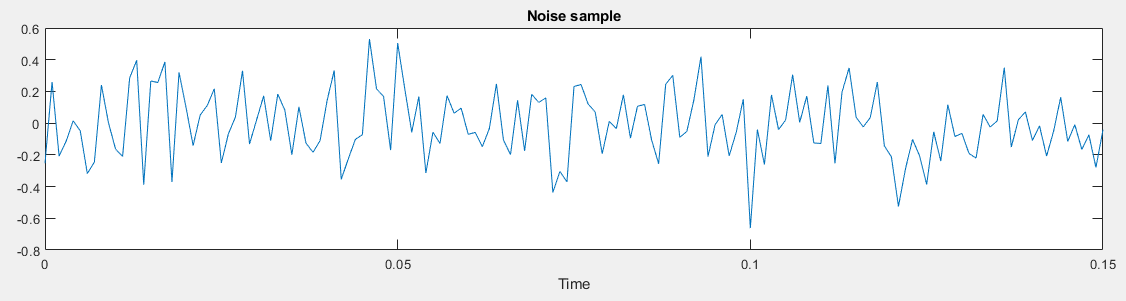
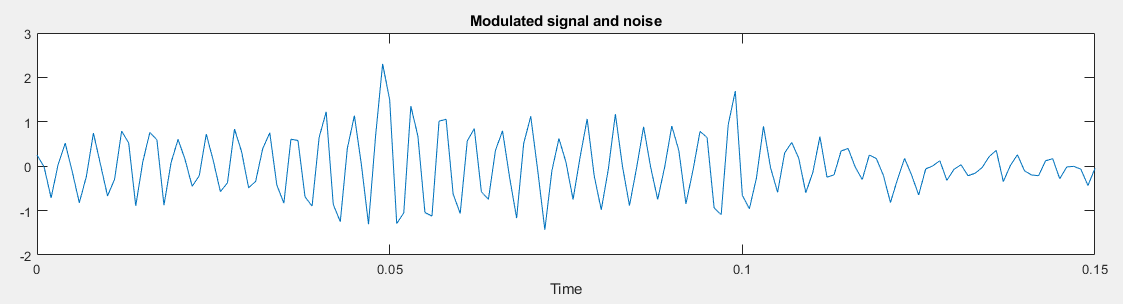
The modulated signal and noise
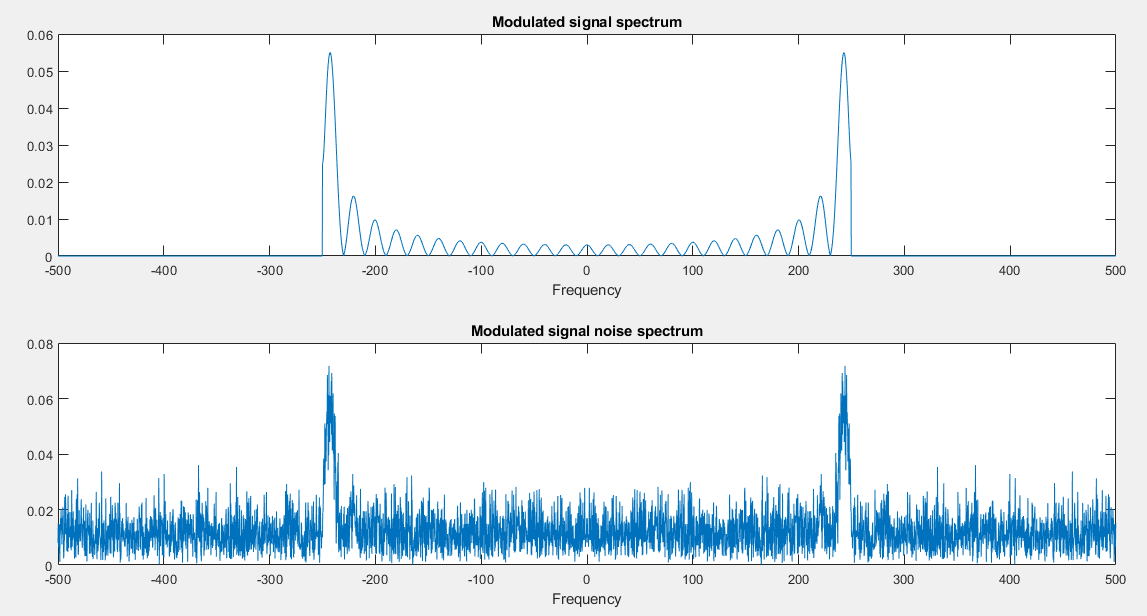
The spectrum of the modulated signal and the modulated signal noise in frequency domain
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis