1.最大/小值
#min max 返回最大、小值 a = [0, -1, 2, 3] print(min(a)) print(max(a))
2.判断列表里的值真假
#all any bool 判断列表内所有的值是否为真,只要有一个为0则假 b = [0, -1, 2, 3] print(all(b)) # 判断内的值为真——有0为假 print(any(b)) # 用法与all判断相反 #bool判断值的真假, 0为False, 其他为True print(bool(1)) # 0为False, 其他为True
3.用内置函数进行列表切片
myslice = slice(5) # 设置截取5个元素的切片 slice(5)#切片第0~4个元素 slice(3, 9, None) #myslice = slice(3, 9, None) #设置切片第4~9个元素 ls = list(range(10)) # 生成一个10个元素的列表 print(ls[myslice])
4.十进制转换各种进制
#hex、bin、oct 16进制 2进制 8进制 print(hex(24), bin(26), oct(28)) # 返回数字的各种进制格式
5.返回除数的余和值
#divmod() # 返回除数的值和余 print(divmod(10, 3)) #=10/3 余1 输出: (3, 1)
6.列表进行排序
# sorted 列表排序 a = list(range(10)) # 生成一个0-9的列表 a[4] = 99 # 把第5个值修改 a2 = sorted(a) # 将列表进行排序 print(a2) 输出:
#通过sorted 把字典排序 d = {} # 生成一个字典 for i in range(10): d[i] = i-50 #print(d) d[0] = 399 # 更新key=0的值 #print(d) d.items() # 字典转换成列表 b = sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]) # 元组由小到大排序 print(b) c = sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # 元组的由大到小排序 print(c) 输出:
7.中文字符串转ASCII码 ,单个英文字符返回ASCII:
#ascii 返回ascii字符编码 s = 'abc你好' print(ascii(s))
#ord 通过字符串返回ascii print(ord('a'))

8.eval
#eval 按解析器规则把字符串转代码 #有返回值 f = '1+3/2' print('eval', eval(f)) eval("print('hello world')") # 只能处理单行代码
输出:
9.exec
#exec 没返回值 code = ''' def foo(): print('run') return 1234 foo() ''' res = exec(code) res2 = eval('1+2+3') print('exec', res, 'eval', res2)
输出:
10.map 列表里的值自相乘
#map 列表内的值自相乘 print(list(map(lambda x: x*x, [1, 2, 3, 4])))
11.filter把列表里值过滤
#filter 把符合条件的值过滤出来 print(list(filter(lambda x: x > 3, [1, 5, 3, 4])))
12.reduce列表里的值自相加
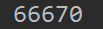
#reduce 列表内的值自相加 import functools print(functools.reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1, 66667, 2]))
13.tuple字符串转换成元组
#tuple() 字符串编程元组 print(tuple('abc'))
14.callable判断是否可调用
def f2(): print('crm') print(callable(f)) # 判断是否可调用,函数不能调用 a = [0, 1, 2, 3] print(callable(a)) # 列表也是不可调用
15.halp 帮助函数(略)
16.frozenset冻结
l2 = {2, 3, 4, 4} # 集合
l2.discard(2) # 删除一个元素
print(l2)
print(type(l2))
s = frozenset(s) # 使用frozenset函数后,集合的值不能删
17. vars locals globals
def abc(): ab = 2 print(vars()) #打印变量名和变量值 print(locals()) # 打印局部变量 print(globals()) # 打印全局变量和值 print(ab) abc()
18.列表转换成字典
#两个列表转换成字典 g = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] c = ['x', 'y', 'f', 'z'] print(list(zip(g, c))) # 没对应上的值丢弃 eg.5 print(dict(zip(g, c)))