SpringBoot (1)
启动
Springboot版本2.1.6
Springboot入口
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemospringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemospringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringApplication.run方法
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
run方法中做了几个事情
context = createApplicationContext();
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
这几件事情,完成了核心SpringContext的创建,初始化,刷新等,如果需要详细了解,可以自行查阅Spring源码。
createApplicationContext
/**
* Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this
* method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context
* class before falling back to a suitable default.
* @return the application context (not yet refreshed)
* @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class)
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
...
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
createApplicationContext会根据this.webApplicationType来选择初始化哪种类型的ConfigurableApplicationContext。this.webApplicationType值是在之前env设置的时候确定的。
prepareContext
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
load是用来处理BeanDefinitionLoader,即Bean的加载
refresh
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
refresh(context)就是对context进行了一次激活操作
@SpringBootApplication注解
//此坑待填
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
...
}
SpringBootApplication注解集合了SpringBootConfiguration,EnableAutoConfiguration,ComponentScan
。其中EnableAutoConfiguration是核心。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
...
}
EnableAutoConfiguration 使用了@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)注解,并且import了AutoConfigurationImportSelector,其中的isEnabled方法,启用了starter
protected boolean isEnabled(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
if (getClass() == AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) {
return getEnvironment().getProperty(EnableAutoConfiguration.ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY, Boolean.class, true);
}
return true;
}
调用isEnable方法的地方有2个selectImports,getAutoConfigurationEntry
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,
annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
/**
* Return the {@link AutoConfigurationEntry} based on the {@link AnnotationMetadata}
* of the importing {@link Configuration @Configuration} class.
* @param autoConfigurationMetadata the auto-configuration metadata
* @param annotationMetadata the annotation metadata of the configuration class
* @return the auto-configurations that should be imported
*/
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
获取配置
/**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
此处可以看出需要在META-INF/下准备spring.factories,并且实现放好配置信息。所以不要问为什么要有spring.facotries,问就是被硬编码写死了。
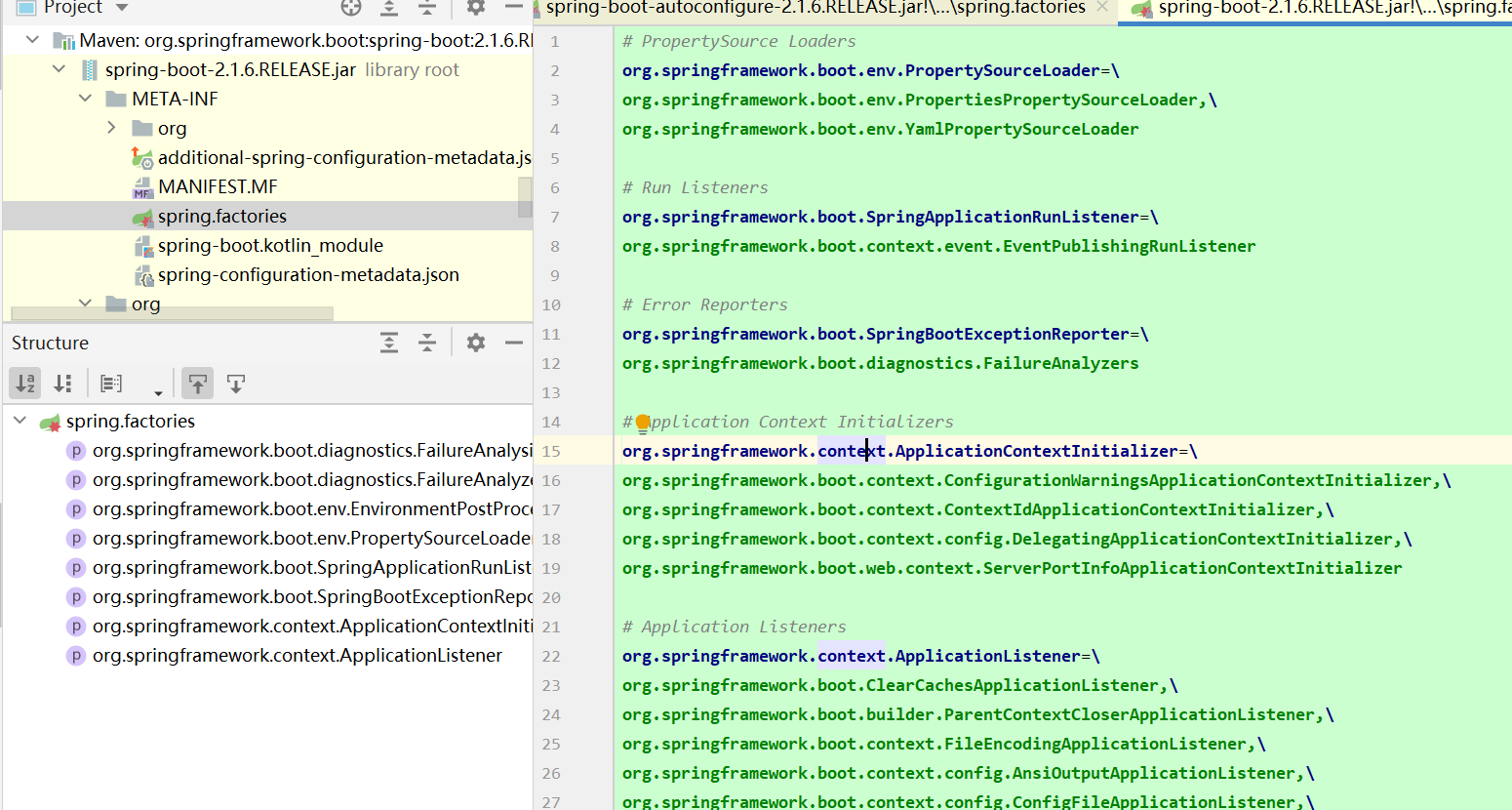
从spring.factories文件中获取到接口对应的实现类,然后按需加载。
listeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
在run方法中,一开始就已经准备了SpringApplicationRunListeners的监听器。EventPublishingRunListener
starting方法就开始了对之前加载的listener进行了广播multicastEvent。所有的ApplicationListener都会starting
prepareEnvironment
准备环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
在执行environmentPrepared方法时,会去发布监听事件,加载相应的配置文件,然后env就准备ok了
总的来说,springapplication.run 中的比较核心的
1 environment的创建
2 ioc容器的创建
3 回调callrunners,用来处理扩展