Problem UVA211-The Domino Effect
Accept:536 Submit:2504
Time Limit: 3000 mSec
 Problem Description
Problem Description
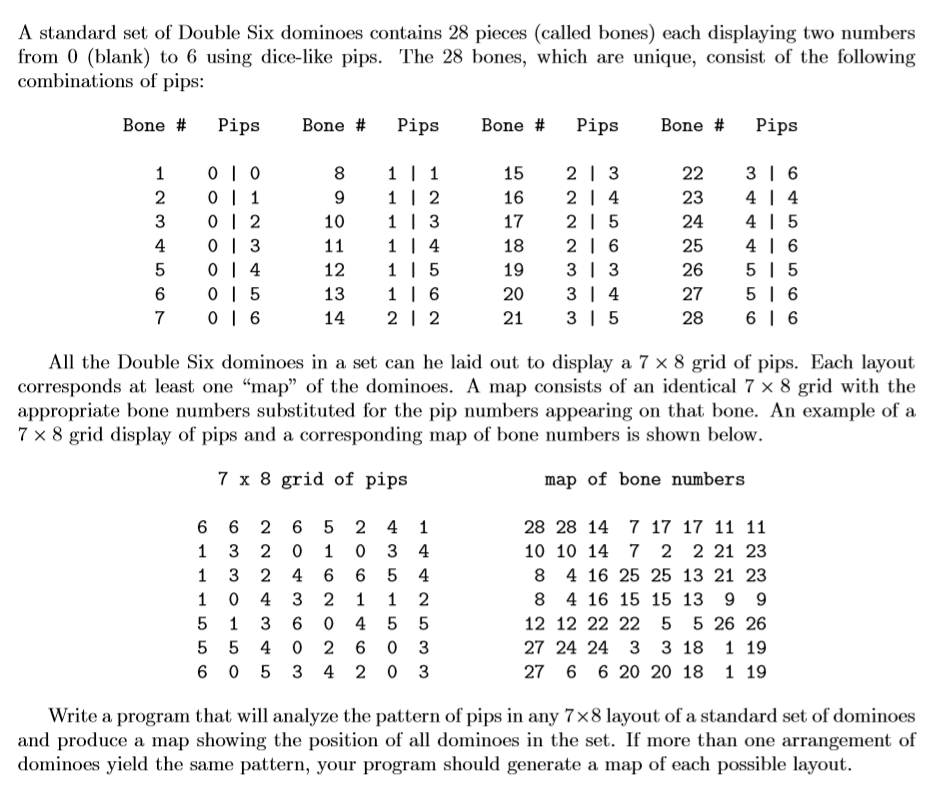
 Input
Input
The input file will contain several of problem sets. Each set consists of seven lines of eight integers from 0 through 6, representing an observed pattern of pips. Each set is corresponds to a legitimate configuration of bones (there will be at least one map possible for each problem set). There is no intervening data separating the problem sets.
 Output
Output
Correct output consists of a problem set label (beginning with Set #1) followed by an echo printing of the problem set itself. This is followed by a map label for the set and the map(s) which correspond to the problem set. (Multiple maps can be output in any order.) After all maps for a problem set have been printed, a summary line stating the number of possible maps appears. At least three lines are skipped between the output from different problem sets while at least one line separates the labels, echo printing, and maps within the same problem set.
Note: A sample input file of two problem sets along with the correct output are shown.
 Sample Input
Sample Input
0 6 0 1 2 3 1 1
3 2 6 5 0 4 2 0
5 3 6 2 3 2 0 6
4 0 4 1 0 0 4 1
5 2 2 4 4 1 6 5
5 5 3 6 1 2 3 1
4 2 5 2 6 3 5 4
5 0 4 3 1 4 1 1
1 2 3 0 2 2 2 2
1 4 0 1 3 5 6 5
4 0 6 0 3 6 6 5
4 0 1 6 4 0 3 0
6 5 3 6 2 1 5 3
 Sample Ouput
Sample Ouput
0 6 0 1 2 3 1 1
3 2 6 5 0 4 2 0
5 3 6 2 3 2 0 6
4 0 4 1 0 0 4 1
5 2 2 4 4 1 6 5
5 5 3 6 1 2 3 1
6 18 2 2 3 19 8 8
21 18 28 17 3 16 16 7
21 4 28 17 15 15 5 7
24 4 11 11 1 1 5 12
24 14 14 23 23 13 13 12
26 26 22 22 9 9 10 10
5 0 4 3 1 4 1 1
1 2 3 0 2 2 2 2
1 4 0 1 3 5 6 5
4 0 6 0 3 6 6 5
4 0 1 6 4 0 3 0
6 5 3 6 2 1 5 3
6 6 24 10 10 20 12 11
8 15 15 3 3 17 14 14
8 5 5 2 19 17 28 26
23 1 13 2 19 7 28 26
23 1 13 25 25 7 4 4
27 27 22 22 9 9 21 21
6 6 24 10 10 20 12 11
8 15 15 3 3 17 14 14
8 5 5 2 19 17 28 26
23 1 13 2 19 7 28 26
23 1 13 25 25 7 21 4
27 27 22 22 9 9 21 4
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 const int maxn = 10; 6 const int n = 7,m = 8; 7 8 int table[maxn][maxn]; 9 int gra[maxn][maxn],ans[maxn][maxn]; 10 int _count; 11 bool vis[maxn][maxn]; 12 bool used[maxn<<2]; 13 int dx[] = {0,1}; 14 int dy[] = {1,0}; 15 16 void init(){ 17 memset(table,0,sizeof(table)); 18 memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis)); 19 memset(used,false,sizeof(used)); 20 int i = 0,j = 0,cnt = 1; 21 for(int len = 7;len >= 0;len--){ 22 for(int p = j;p < 7;p++){ 23 table[i][p] = table[p][i] = cnt++; 24 } 25 i++,j++; 26 } 27 } 28 29 void dfs(int x,int y,int cnt){ 30 if(cnt == 28){ 31 _count++; 32 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ 33 for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){ 34 printf("%4d",ans[i][j]); 35 } 36 printf(" "); 37 } 38 printf(" "); 39 return; 40 } 41 42 if(y == m) x++,y = 0; 43 if(vis[x][y]) dfs(x,y+1,cnt); 44 else{ 45 for(int i = 0;i < 2;i++){ 46 int xx = x+dx[i],yy = y+dy[i]; 47 if(xx>=n || yy>=m) continue; 48 if(vis[xx][yy] || used[table[gra[x][y]][gra[xx][yy]]]) continue; 49 50 ans[x][y] = ans[xx][yy] = table[gra[x][y]][gra[xx][yy]]; 51 vis[x][y] = vis[xx][yy] = used[table[gra[x][y]][gra[xx][yy]]] = true; 52 dfs(x,y+1,cnt+1); 53 vis[x][y] = vis[xx][yy] = used[table[gra[x][y]][gra[xx][yy]]] = false; 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 int main() 59 { 60 #ifdef GEH 61 freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); 62 #endif 63 init(); 64 int iCase = 0; 65 while(~scanf("%d",&gra[0][0])){ 66 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ 67 for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){ 68 if(i==0 && j==0) continue; 69 scanf("%d",&gra[i][j]); 70 } 71 } 72 73 if(iCase) printf(" "); 74 printf("Layout #%d: ",++iCase); 75 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ 76 for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){ 77 printf("%4d",gra[i][j]); 78 } 79 printf(" "); 80 } 81 printf(" "); 82 printf("Maps resulting from layout #%d are: ",iCase); 83 _count = 0; 84 dfs(0,0,0); 85 printf("There are %d solution(s) for layout #%d. ",_count,iCase); 86 } 87 return 0; 88 }