一、前言
之前用java实现堆结构,一直用的优先队列,但是在实际的面试中,可能会要求用数组实现,所以还是用java老老实实的实现一遍堆结构吧。
二、概念
堆,有两种形式,一种是大根堆,另一种是小根堆。堆,一般是二叉树,这个概念当然也可以扩展到k叉树。大根堆指的是根节点的值要大于左子树和右子树所有节点值,堆的子树也是堆。小根堆的概念同理可知。
三、实现过程
堆的形式是一棵树,但是我们可以用数组来实现它,父节点和孩子节点的父子关系通过数组下标来确定。
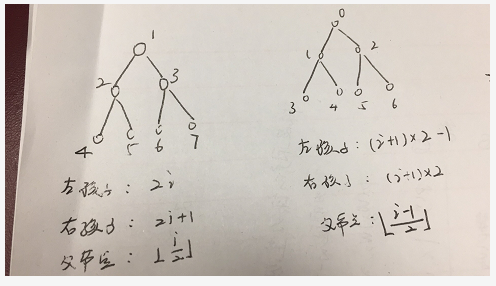
它的左右孩子节点和父节点的位置,如上图所示。
在接下来的实现过程,我们使用第二种表示方式,也就是说节点的编号是从0开始。
(1)首先我们需要定义一个节点的左右孩子的位置和根节点的位置。
// find the index of left children public static int left(int i){ return (i+1)*2 -1; } // find the index of right children public static int right(int i){ return (i+1)*2; } // find the index of parent public static int parent(int i){ return (i-1)/2; }
(2)其次我们需要保持堆的结构。所谓保持堆结构,指的是:让它的根节点始终比它的左右子树大(大顶堆)或者小(小顶堆)。具体做法就是在根节点和左右子树的根节点的值进行对比,如果根节点就是最大的话,就结束;否则就将根节点和最大值的位置互换,然后递归的变更最大值。
//keep the max heap structure public static void heapkeep(int[] a, int i, int heaplength){ int l = left(i); int r = right(i); int largest = i; if(l<heaplength&&a[i]<a[l]){ largest = l; } if(r<heaplength&&a[largest]<a[r]){ largest = r; } if(largest!=i){ int temp = a[largest]; a[largest] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; heapkeep(a, largest, heaplength); } }
(3)构建堆。构建堆的方法很简单,就是自底向上的构建堆。
// create the heap public static int heapcreate(int[] a, int length){ if(a.length<length){ return -1; }else{ int pr = parent(length-1); for(int i = pr;i>=0;i--){ heapkeep(a, i, length); } return 0; } }
上述实现过程,实现的大顶堆,如果想要实现小顶堆的话只需要修改一下heapkeep函数的判断条件。