一、常见题型
1. 求两个节点的最近公共祖先;
2. 求二叉树中最远的两个节点的距离;
3. 由前序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树(如:前序序列:1 2 3 4 5 6 - 中序序列 :3 2 4 1 6 5);
4. 判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树 ;
5. 将二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向;
6.求二叉树的宽度;
7. 判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树;
8.判断一颗二叉树是否是另一颗树的子树。
二、解题思路分析
1.两个节点的最近公共祖先
求两个节点的最近公共祖先可分为三种情况,分别为:
(1)搜索二叉树,根据搜索二叉树的性质,左子树的所有节点比根节点小,右子树的所有节点比跟节点大。
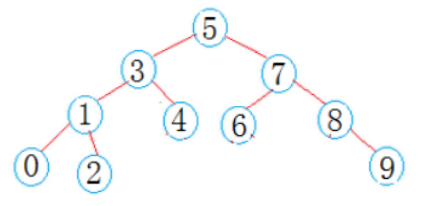
如果两个节点都比根节点小,则递归左子树 ;
如果两个节点都比跟节点大,则递归右子树 ;
否则,两个节点一个在左子树,一个在右子树,则当前节点就是最近公共祖先节点。
1 Node* GetAncestor(Node* root, Node* x1, Node* x2)//1.该二叉树为搜索二叉树 2 { 3 assert(x1 && x2); 4 if (x1->_data <= root->_data && x2->_data <= root->_data) 5 { 6 return GetAncestor(root->_left, x1, x2);//两个节都小于根节点,最近公共祖先在左子树中 7 } 8 else if (x1->_data > root->_data && x2->_data > root->_data) 9 { 10 return GetAncestor(root->_right, x1, x2);//两个节都大于根节点,最近公共祖先在左子树中 11 } 12 else 13 return root; //一个在左子树,一个在右子树,找到公共祖先 14 15 }
(2)三叉链,二叉树节点有指向父节点的指针。首先给出node1的父节点node1->_parent,然后将node1的所有父节点依次和node2->parent作比较,如果发现两个节点相等,则该节点就是最近公共祖先,直接将其返回。如果没找到相等节点,则将node2的所有父节点依次和node1->_parent->_parent作比较......直到node1->_parent==NULL。代码如下:
1 struct BinaryNode //节点的结构
2 {
3 BinaryNode* _left;
4 BinaryNode* _right;
5 BinaryNode* _parent;
6 int _data;
7
8 BinaryNode(const int& data)
9 :_data(data)
10 , _left(NULL)
11 , _right(NULL)
12 , _parent(NULL)
13 {}
14 };
1 Node * GetLastCommonAncestor(Node * root, Node * node1, Node * node2) 2 { 3 Node * temp; 4 while (node1 != NULL) 5 { 6 node1 = node1->_parent; 7 temp = node2; 8 while (temp != NULL) 9 { 10 if (node1 == temp->_parent) 11 return node1; 12 temp = temp->_parent; 13 } 14 } 15 }
该算法时间复杂度为O(n^2),可用另一种O(n)的算法:
给定的两个节点都含有父节点,因此,可将这两个节点看做是两个链表的头结点,将求两个节点的最近公共祖先节点转化为求两链表的交点,这两个链表的尾节点都是根节点。
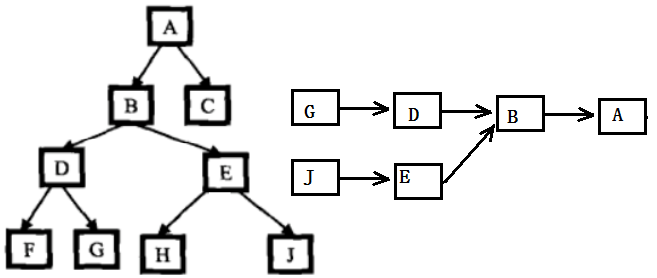
1 int Hight(BinaryNode* root, BinaryNode* node) 2 { 3 int len = 0; 4 for (; node != NULL; node = node->_parent) 5 len++; 6 7 return len; 8 } 9 BinaryNode* GetLastCommonAncestor(BinaryNode* root, BinaryNode* node1, BinaryNode* node2) 10 { 11 12 if (root == NULL || node1 == NULL || node2==NULL) 13 return NULL; 14 15 int len1 = Hight(root,node1); 16 int len2 = Hight(root,node2); 17 19 for (; len1 > len2; len1--) 20 node1 = node1->_parent; 21 for (; len2 > len1; len2--) 22 node2 = node2->_parent; 23 24 while (node1 && node2 && node1 != node2) 25 { 26 node1 = node1->_parent; 27 node2 = node2->_parent; 28 } 29 30 if (node1 == node2) 31 return node1; 32 else 33 return NULL; 34 }
(3)普通二叉树,这种情况可采用与搜索二叉树类似的解法
从根节点开始遍历,如果node1和node2中的任一个和root匹配,那么与root匹配的节点就是最低公共祖先。 如果都不匹配,则分别递归左、右子树,如果有一个 节点出现在左子树,并且另一个节点出现在右子树,则root就是最低公共祖先. 如果两个节点都出现在左子树,则说明最低公共祖先在左子树中,否则在右子树。
1 Node* GetAncestor(Node* root, Node* x1, Node* x2) 2 { 3 assert(x1 && x2); 4 if (root == NULL) { 5 return NULL; 6 } 7 if (root == x1 || root == x2) //如果两个节点是父子关系,其中的一个节点为公共祖先 8 { 9 return root; 10 } 11 bool x1inleft, x2inleft, x1inright, x2inright; 12 x1inleft = JudgeNode(root->_left, x1); //判断x1是否在左子树 13 x1inright = JudgeNode(root->_right x1); //判断x1是否在右子树 14 assert(x1inleft || x1inright); //至少有一个为真 15 x2inleft = JudgeNode(root->_left, x2); //判断x2是否在左子树 16 x2inright = JudgeNode(root->_right, x2); //判断x2是否在右子树 17 assert(x2inleft || x2inright); //至少有一个为真 18 if ((x1inleft && x2inright) || (x1inright && x2inright)) 19 { 20 return root; //一个在左子树,一个在右子树,找到公共祖先 21 } 22 else if (x1inleft && x2inleft) //两个节都在左子树中,最近公共祖先在左子树中 23 { 24 return GetAncestor(root->_left, x1, x2); 25 } 26 else { //两个节都在右子树中,最近公共祖先在右子树中 27 return GetAncestor(root->_right, x1, x2); 28 } 29 }
上述方法时间复杂度为O(N^2),下面的方法时间复杂度为O(N),但是需要额外的空间来存储路径。
1) 找到从根到node1的路径,并存储在一个向量或数组中。
2)找到从根到node2的路径,并存储在一个向量或数组中。
3) 遍历这两条路径,直到遇到一个不同的节点,则前面的那个即为最低公共祖先.
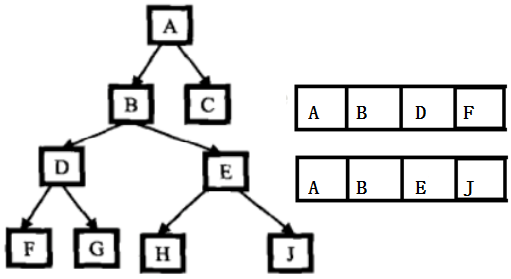
1 bool GetNodePaths(Node* root, Node* node, stack<Node *>& s) 2 { 3 if (root == NULL) 4 { 5 return false; 6 } 7 s.push(root); 8 if (root == node) 9 { 10 return true; 11 } 12 bool inleft = GetNodePaths(root->_left, node, s); 13 if (inleft) 14 { 15 return true; 16 } 17 bool inright = GetNodePaths(root->_right, node, s); 18 if (inright) 19 { 20 return true; 21 } 22 s.pop(); 23 return false; 24 } 25 Node* GetAncestor(Node* root, Node* x1, Node* x2); 26 { 27 assert(x1 && x2); 28 stack<Node*> paths1, paths2; 29 if (!GetNodePaths(root->_left, x1, paths1) || !GetNodePaths(root->_right, x2, paths2)) 30 { 31 return NULL; 32 }
else{
while(paths1.size()>paths2.size()){
paths1.pop();
}
while(paths1.size()<paths2.size()){
paths2.pop();
}
while(!paths1.empty() && !paths2.empty() && paths1.top()!=paths2.top()){
if(paths1.top()==paths2.top())
return paths1.top();
paths1.pop();
paths2.pop();
}
}
return NULL; 33 }
2.最远的两个节点的距离
第一种情况最远的两个节点的距离为它们到根节点的路径长度之和,又有可能距离最远的两个节点之间的路径不经过根节点,如图所示:
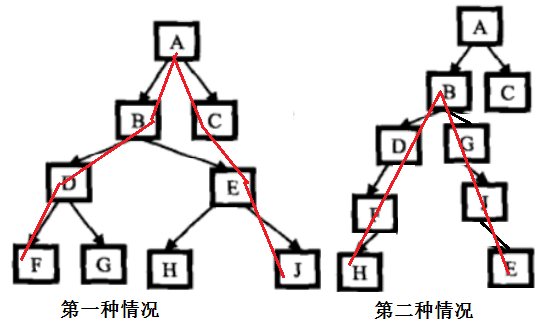
所以不要考虑不全,直接用两个子树的的高度相加来表示最远的两个节点的距离。有两种方法求解:
还是要借助两个子树的高度求解,但是要递归整棵树,如果子树中出现第二种情况要更新最大距离,时间复杂度为O(N^2)。
1 //求二叉树中最远的两个节点的距离 2 size_t MaxLen() 3 { 4 size_t maxlen = 0; 5 _MaxLen(_root, maxlen); 6 return maxlen; 7 } 8 void _MaxLen(Node* root, size_t maxlen) //O(N^2) 9 { 10 if (root == NULL) 11 { 12 return 0; 13 } 14 int leftdepth = Depth(root->_left); 15 int rightdepth = Depth(root->_right); 16 if (leftdepth + rightdepth > maxlen) 17 { 18 maxlen = leftdepth + rightdepth; 19 } 20 _MaxLen(root->_left, maxlen); 21 _MaxLen(root->_right, maxlen); 22 }
另一种时间复杂度为O(N)的解法:
1 size_t _MaxLen(Node* root, size_t maxlen) //O(N) 2 { 3 if (root == NULL) 4 { 5 return; 6 } 7 size_t left = _MaxLen(root->_left, maxlen); 8 size_t right = _MaxLen(root->_right, maxlen); 9 if (right+left>maxlen) 10 { 11 maxlen = right + left; 12 } 13 return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1; 14 }
3. 前序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
这个题是要用一颗二叉树的前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列,如:前序序列:1 2 3 4 5 6 - 中序序列 :3 2 4 1 6 5,来重新构建二叉树。可以利用前序序列和中序序列中根节点的位置特性作为重建依据。图示解析过程如下:
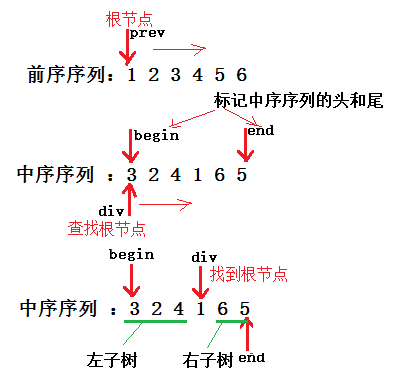

创建右子树的方法与左子树的方法完全相同。当 prev 遍历完前序序列,即二叉树创建完成。代码如下:
1 //由前序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树(如:前序序列:1 2 3 4 5 6 - 中序序列 :3 2 4 1 6 5) 2 Node* RebulidTree(char* prev, char* inbgein, char* inend) 3 { 4 assert(prev && inbgein && inend); 5 if (inbgein > inend || prev == '�') 6 { 7 return NULL; 8 } 9 Node* root = new Node(*prev); //先创建根节点 10 char* div = inbgein; //让div查找根节点 11 while (div <= inend) { 12 if (*div == *prev) 13 { 14 if (inbgein <= div -1) 15 { 16 root->_left = RebulidTree(++prev, inbgein, div - 1);//递归创建左子树 17 } 18 else { 19 root->_left = NULL; 20 } 21 if (div + 1 <= inend) 22 { 23 root->_right = RebulidTree(++prev, div + 1, inend);//递归创建右子树 24 } 25 else { 26 root->_right = NULL; 27 } 28 break; 29 } 30 ++div; 31 } 32 return root; 33 }
4. 判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
完全二叉树: 前n-1层都是满的,第n层如有空缺,则是缺在右边,即第n层的最右边的节点,它的左边是满的,右边是空的。
这是一个层序遍历非递归法的变型题,同样要借助额外空间来临时存储节点。按照层序遍历二叉树,找到第一个只有非满结点(这个节点只有两种情况,孩子为空或者只有左没有右),如果之后的节点还有非满结点,则不是。
1 bool IsComplateTree(Node* root) 2 { 3 queue<Node*> q; 4 if (root) 5 { 6 q.push(root); //先将节点压入队列中 7 } 8 //这里给一个tag是标记是否出现非满节点 9 bool tag = true; 10 while (!q.empty()) 11 { 12 Node* front = q.front(); 13 q.pop(); 14 //如果已经出现过非满结点,则后面再出现有孩子的结点则一定不是完全二叉树。 15 if (front->_left) 16 { 17 if (tag == false) 18 { 19 return false; 20 } 21 q.push(front->_left); 22 } 23 else { 24 tag = false; 25 } 26 if (front->_right) 27 { 28 if (tag == false) 29 { 30 return false; 31 } 32 q.push(front->_right); 33 } 34 else { 35 tag = false; 36 } 37 } 38 return true; 39 }
第二种思路:将所有的结点全部押入队列中,每次判断队列的头如果队列头为空了则跳出循环,如果此后队列中还有元素则不是完全二叉树。
1 bool IsCompleteTree(BinaryTreeNode *pRoot) 2 { 3 if(pRoot == NULL) 4 return false; 5 6 queue<BinaryTreeNode*> q; 7 q.push(pRoot); 8 BinaryTreeNode* pCur = q.front(); 9 while(pCur != NULL) 10 { 11 q.pop(); 12 q.push(pCur -> left); 13 q.push(pCur -> right); 14 pCur = q.front(); 15 } 16 17 q.pop();//把空pop出来 18 //因为以经有一个空了,所以只要头不为空就不是完全二叉树 19 while(! q.empty()) 20 { 21 if(q.front() != NULL) 22 return false; 23 q.pop(); 24 } 25 return true; 26 }
5. 将二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表
与二叉树的线索花化雷同
1 void _ToList(Node* cur, Node*& prev) 2 { 3 if (cur == NULL) 4 return; 5 6 _ToList(cur->_left, prev); 7 // 8 cur->_left = prev; 9 if(prev) 10 prev->_right = cur; 11 12 prev = cur; 13 14 _ToList(cur->_right, prev); 15 } 16 17 Node* ToList(Node* root) 18 { 19 Node* prev = NULL; 20 _ToList(root, prev); 21 22 Node* head = root; 23 while (head && head->_left) 24 { 25 head = head->_left; 26 } 27 28 return head; 29 }
6.求二叉树的宽度
所谓二叉树的宽度是指:二叉树各层节点个数的最大值。
我们知道层序遍历二叉树是使用 queue 来实现的:每次打印一个节点之后,如果存在左右子树,则把左右子树压入 queue,那么此时的队列中可能既包含当前层的节点,也包含下一层的节点。
而我们要求的是对于特定某一层的节点的个数,因此我们需要从头结点开始,记录每一层的个数,对于当前层的每一个节点,在弹出自身之后把其左右子树压入 queue,当把当前层全部弹出队列之后,在队列中剩下的就是下一层的节点。然后比较队列的size和之前得到的maxWidth,取最大值即为队列的宽度。最终队列为空,得到的maxWidth就是二叉树的宽度!
1 int Width(Node* root) 2 { 3 queue<Node*> q; 4 if (root) 5 q.push(root); 6 int maxwidth = 1; 7 while (!q.empty()) 8 { 9 int length = q.size(); 10 while (length-- > 0) 11 { 12 Node* front = q.front(); 13 q.pop(); 14 if (front->_left) 15 { 16 q.push(front->_left); 17 } 18 if (front->_right) 19 { 20 q.push(front->_right); 21 } 22 } 23 maxwidth = maxwidth > q.size() ? maxwidth : q.size(); 24 } 25 return maxwidth; 26 }
7. 二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
二叉树中每一个节点的左右子树高度之差均小于2即为平衡二叉树。那么当一颗二叉树的所有子树都是平衡二叉树时,它本身必定为平衡二叉树,用此思想可递归判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。代码如下:
1 //--判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树 2 bool IsBalance(Node* root) //O(N^2) 3 { 4 if (root == NULL) 5 { 6 return false; 7 } 8 int left = Depth(root->_left); 9 int right = Depth(root->_right); 10 return abs(right - left) < 2 && IsBalance(root->_left) && IsBalance(root->_right); 11 }
这种方法借助左右的高度比较来确定是否为二叉树,需多次遍历二叉树,时间复杂度为O(N^2)。下面是一种O(N)的算法:
1 bool IsBalance(Node* root, int& depth) //O(N) 2 { 3 if (root == NULL) 4 { 5 depth = 0; 6 return true; 7 } 8 int leftdepth = 0; 9 if (IsBalance(root->_left, leftdepth) == false) 10 { 11 return false; 12 } 13 int rightdepth = 0; 14 if (IsBalance(root->_right, rightdepth) == false) 15 { 16 return false; 17 } 18 depth = rightdepth > leftdepth ? rightdepth + 1 : leftdepth + 1; 19 return abs(leftdepth - rightdepth) < 2; 20 }
8.二叉树是否为另一颗树的子树
判断一颗二叉树是否是另一颗树的子树。
先在找二叉树里找根节点,找到之后判断后续的节点是否相等,如果相等,则为子树。
1 bool JudgeNextTree(Node* next, Node* child) //两棵树的起始节点的值已经相等,在判断其他节点是否相等 2 { 3 if (child == NULL) 4 { 5 return true; 6 } 7 if (next == NULL) 8 { 9 return false; 10 } 11 if (next->_data == child->_data) // 12 { 13 return JudgeNextTree(next->_left, child->_left) && JudgeNextTree(next->_right, child->_right); 14 } 15 else { 16 return false; //如果左右孩子都相等,则是子树,否则不是 17 } 18 } 19 bool JudgeTree(Node* parent, Node* child) //判断child是否为parent的子树 20 { 21 if (child == NULL) //空树是任何树的子树 22 { 23 return true; 24 } 25 if (parent == NULL) //空树没有除空树的任何子树 26 { 27 return false; 28 } 29 if (parent->_data == child->_data) //当前节点与要查找子树的根节点相同时 30 { 31 return JudgeNextTree(parent, child); //从相等节点开始判断是否为子树 32 } 33 else if (JudgeTree(parent->_left, child->_left) == true) //判断当前节点的左子树是否与要查找子树的根节点相同 34 { 35 return true; 36 } 37 else { 38 return JudgeTree(parent->_right, child->_right); //判断当前节点的右子树是否与要查找子树的根节点相同 39 } 40 }