推荐博文,博客。写得很好,给个赞。
Reference Link : http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/7829481
一阶导数法:梯度算子
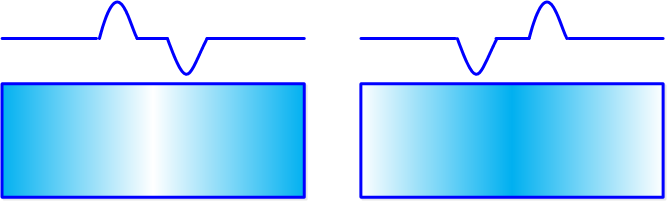
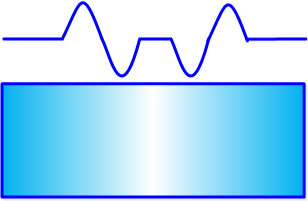
对于左图,左侧的边是正的(由暗到亮),右侧的边是负的(由亮到暗)。对于右图,结论相反。常数部分为零。用来检测边是否存在。
梯度算子 Gradient operators
函数f(x,y)在(x,y)处的梯度为一个向量:
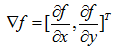
计算这个向量的大小为:
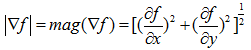
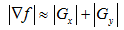
梯度的方向角为:
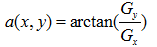
Sobel算子
sobel算子的表示:

梯度幅值:
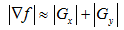
用卷积模板来实现:
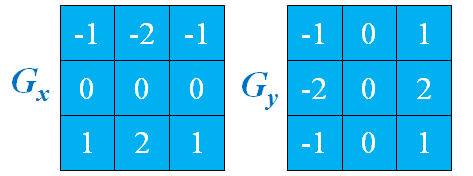
【相关代码】
- CV_EXPORTS_W Sobel( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, ddepth,
- ksize=3,
- double scale=1, double delta=0,
- borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );
CV_EXPORTS_W void Sobel( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth,
int dx, int dy, int ksize=3,
double scale=1, double delta=0,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );
- /////////////////////////// Sobe l////////////////////////////////////
- /// Generate grad_x and grad_y
- Mat grad_x, grad_y;
- Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y;
- /// Gradient X
- //Scharr( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT );
- //Calculates the first, second, third, or mixed image derivatives using an extended Sobel operator.
- Sobel( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT );
- convertScaleAbs( grad_x, abs_grad_x );
- /// Gradient Y
- //Scharr( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT );
- Sobel( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT );
- convertScaleAbs( grad_y, abs_grad_y );
- /// Total Gradient (approximate)
- addWeighted( abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, grad );
/////////////////////////// Sobe l//////////////////////////////////// /// Generate grad_x and grad_y Mat grad_x, grad_y; Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y; /// Gradient X //Scharr( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); //Calculates the first, second, third, or mixed image derivatives using an extended Sobel operator. Sobel( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_x, abs_grad_x ); /// Gradient Y //Scharr( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); Sobel( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_y, abs_grad_y ); /// Total Gradient (approximate) addWeighted( abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, grad );
二阶微分法:拉普拉斯
二阶微分在亮的一边是负的,在暗的一边是正的。常数部分为零。可以用来确定边的准确位置,以及像素在亮的一侧还是暗的一侧。
LapLace 拉普拉斯算子
二维函数f(x,y)的拉普拉斯是一个二阶的微分,定义为:
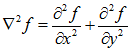
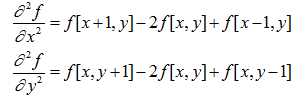
可以用多种方式将其表示为数字形式。对于一个3*3的区域,经验上被推荐最多的形式是:

定义数字形式的拉普拉斯要求系数之和必为0
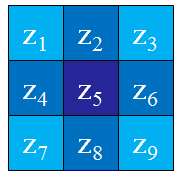
【相关代码】
- CV_EXPORTS_W Laplacian( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, ddepth,
- ksize=1, double scale=1, double delta=0,
- borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );
CV_EXPORTS_W void Laplacian( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth,
int ksize=1, double scale=1, double delta=0,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );
- Mat abs_dst,dst;
- scale = 1;
- delta = 0;
- ddepth = CV_16S;
- kernel_size = 3;
- Laplacian( src_gray, dst, ddepth, kernel_size, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT );
- convertScaleAbs( dst, abs_dst );
- namedWindow( window_name2, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
Mat abs_dst,dst; int scale = 1; int delta = 0; int ddepth = CV_16S; int kernel_size = 3; Laplacian( src_gray, dst, ddepth, kernel_size, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( dst, abs_dst ); namedWindow( window_name2, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );

注意,边缘检测对噪声比较敏感,需要先用高斯滤波器对图像进行平滑。参考博文:【OpenCV】邻域滤波:方框、高斯、中值、双边滤波
Sobel 边缘检测
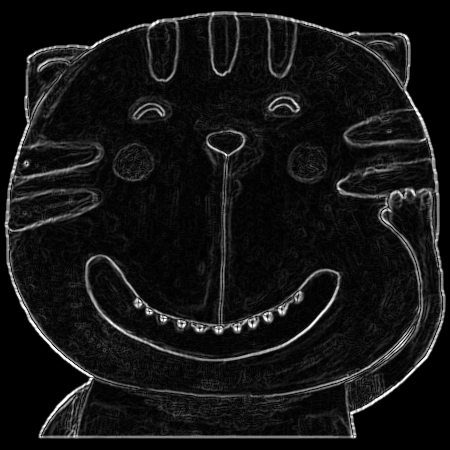

Sobel算子可以直接计算Gx 、Gy可以检测到边的存在,以及从暗到亮,从亮到暗的变化。仅计算| Gx |,产生最强的响应是正交 于x轴的边; | Gy |则是正交于y轴的边。
Laplace边缘检测
拉普拉斯对噪声敏感,会产生双边效果。不能检测出边的方向。通常不直接用于边的检测,只起辅助的角色,检测一个像素是在边的亮的一边还是暗的一边利用零跨越,确定边的位置。