转载地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/p/9550648.html
前言
pytest配置文件可以改变pytest的运行方式,它是一个固定的文件pytest.ini文件,读取配置信息,按指定的方式去运行。
ini配置文件
pytest里面有些文件是非test文件
- pytest.ini pytest的主配置文件,可以改变pytest的默认行为
- conftest.py 测试用例的一些fixture配置
- __init__.py 识别该文件夹为python的package包
- tox.ini 与pytest.ini类似,用tox工具时候才有用
- setup.cfg 也是ini格式文件,影响setup.py的行为
ini文件基本格式
# 保存为pytest.ini文件 [pytest] addopts = -rsxX xfail_strict = true
使用pytest --help指令可以查看pytest.ini的设置选项
[pytest] ini-options in the first pytest.ini|tox.ini|setup.cfg file found: markers (linelist) markers for test functions empty_parameter_set_mark (string) default marker for empty parametersets norecursedirs (args) directory patterns to avoid for recursion testpaths (args) directories to search for tests when no files or dire console_output_style (string) console output: classic or with additional progr usefixtures (args) list of default fixtures to be used with this project python_files (args) glob-style file patterns for Python test module disco python_classes (args) prefixes or glob names for Python test class discover python_functions (args) prefixes or glob names for Python test function and m xfail_strict (bool) default for the strict parameter of addopts (args) extra command line options minversion (string) minimally required pytest version
--rsxX 表示pytest报告所有测试用例被跳过、预计失败、预计失败但实际被通过的原因
mark标记
如下案例,使用了2个标签:webtest和hello,使用mark标记功能对于以后分类测试非常有用处
# content of test_mark.py import pytest @pytest.mark.webtest def test_send_http(): print("mark web test") def test_something_quick(): pass def test_another(): pass @pytest.mark.hello class TestClass: def test_01(self): print("hello :") def test_02(self): print("hello world!") if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-v", "test_mark.py", "-m=hello"])
运行结果
============================= test session starts ============================= platform win32 -- Python 3.6.0, pytest-3.6.3, py-1.5.4, pluggy-0.6.0 -- D:softpython3.6python.exe cachedir: .pytest_cache metadata: {'Python': '3.6.0', 'Platform': 'Windows-7-6.1.7601-SP1', 'Packages': {'pytest': '3.6.3', 'py': '1.5.4', 'pluggy': '0.6.0'}, 'Plugins': {'metadata': '1.7.0', 'html': '1.19.0', 'allure-adaptor': '1.7.10'}, 'JAVA_HOME': 'D:\soft\jdk18\jdk18v'} rootdir: D:YOYO, inifile: plugins: metadata-1.7.0, html-1.19.0, allure-adaptor-1.7.10 collecting ... collected 5 items / 3 deselected test_mark.py::TestClass::test_01 PASSED [ 50%] test_mark.py::TestClass::test_02 PASSED [100%] =================== 2 passed, 3 deselected in 0.11 seconds ====================
有时候标签多了,不容易记住,为了方便后续执行指令的时候能准确使用mark的标签,可以写入到pytest.ini文件
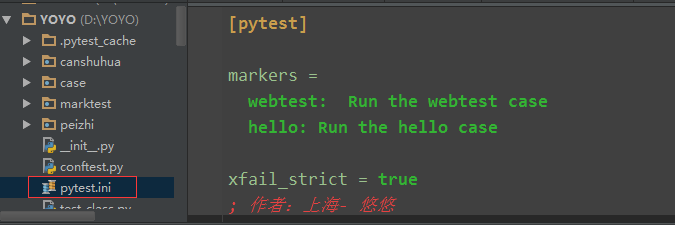
# pytest.ini [pytest] markers = webtest: Run the webtest case hello: Run the hello case
标记好之后,可以使用pytest --markers查看到
$ pytest --markers
D:YOYO>pytest --markers @pytest.mark.webtest: Run the webtest case @pytest.mark.hello: Run the hello case @pytest.mark.skip(reason=None): skip the given test function with an optional re ason. Example: skip(reason="no way of currently testing this") skips the test. @pytest.mark.skipif(condition): skip the given test function if eval(condition) results in a True value. Evaluation happens within the module global context. E xample: skipif('sys.platform == "win32"') skips the test if we are on the win32 platform. see http://pytest.org/latest/skipping.html @pytest.mark.xfail(condition, reason=None, run=True, raises=None, strict=False): mark the test function as an expected failure if eval(condition) has a True val ue. Optionally specify a reason for better reporting and run=False if you don't even want to execute the test function. If only specific exception(s) are expect ed, you can list them in raises, and if the test fails in other ways, it will be reported as a true failure. See http://pytest.org/latest/skipping.html @pytest.mark.parametrize(argnames, argvalues): call a test function multiple tim es passing in different arguments in turn. argvalues generally needs to be a lis t of values if argnames specifies only one name or a list of tuples of values if argnames specifies multiple names. Example: @parametrize('arg1', [1,2]) would l ead to two calls of the decorated test function, one with arg1=1 and another wit h arg1=2.see http://pytest.org/latest/parametrize.html for more info and example s. @pytest.mark.usefixtures(fixturename1, fixturename2, ...): mark tests as needing all of the specified fixtures. see http://pytest.org/latest/fixture.html#usefix tures @pytest.mark.tryfirst: mark a hook implementation function such that the plugin machinery will try to call it first/as early as possible. @pytest.mark.trylast: mark a hook implementation function such that the plugin m achinery will try to call it last/as late as possible.
最上面两个就是刚才写入到pytest.ini的配置了
禁用xpass
设置xfail_strict = true可以让那些标记为@pytest.mark.xfail但实际通过的测试用例被报告为失败
什么叫标记为@pytest.mark.xfail但实际通过,这个比较绕脑,看以下案例
# content of test_xpass.py import pytest ** 作者:上海-悠悠 QQ交流群:588402570** def test_hello(): print("hello world!") assert 1 @pytest.mark.xfail() def test_yoyo1(): a = "hello" b = "hello world" assert a == b @pytest.mark.xfail() def test_yoyo2(): a = "hello" b = "hello world" assert a != b if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-v", "test_xpass.py"])
测试结果
collecting ... collected 3 items test_xpass.py::test_hello PASSED [ 33%] test_xpass.py::test_yoyo1 xfail [ 66%] test_xpass.py::test_yoyo2 XPASS [100%] =============== 1 passed, 1 xfailed, 1 xpassed in 0.27 seconds ================
test_yoyo1和test_yoyo2这2个用例一个是a == b一个是a != b,两个都标记失败了,我们希望两个用例不用执行全部显示xfail。实际上最后一个却显示xpass.为了让两个都显示xfail,那就加个配置
xfail_strict = true
# pytest.ini [pytest] markers = webtest: Run the webtest case hello: Run the hello case xfail_strict = true
再次运行,结果就变成
collecting ... collected 3 items test_xpass.py::test_hello PASSED [ 33%] test_xpass.py::test_yoyo1 xfail [ 66%] test_xpass.py::test_yoyo2 FAILED [100%] ================================== FAILURES =================================== _________________________________ test_yoyo2 __________________________________ [XPASS(strict)] ================ 1 failed, 1 passed, 1 xfailed in 0.05 seconds ================
这样标记为xpass的就被强制性变成failed的结果
配置文件如何放
一般一个工程下方一个pytest.ini文件(不要瞎jb拍脑袋乱命名,瞎jb命名是找不到的)就可以了,放到顶层文件夹下
addopts
addopts参数可以更改默认命令行选项,这个当我们在cmd输入指令去执行用例的时候,会用到,比如我想测试完生成报告,指令比较长
$ pytest -v --rerun 1 --html=report.html --self-contained-html
每次输入这么多,不太好记住,于是可以加到pytest.ini里
# pytest.ini [pytest] markers = webtest: Run the webtest case hello: Run the hello case xfail_strict = true addopts = -v --rerun 1 --html=report.html --self-contained-html
这样我下次打开cmd,直接输入pytest,它就能默认带上这些参数了