Mathematicians are interesting (sometimes, I would say, even crazy) people. For example, my friend, a mathematician, thinks that it is very fun to play with a sequence of integer numbers. He writes the sequence in a row. If he wants he increases one number of the sequence, sometimes it is more interesting to decrease it (do you know why?..) And he likes to add the numbers in the interval [l;r]. But showing that he is really cool he adds only numbers which are equal some mod (modulo m).
Guess what he asked me, when he knew that I am a programmer? Yep, indeed, he asked me to write a program which could process these queries (n is the length of the sequence):
- + p r It increases the number with index p by r. (
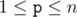 ,
, 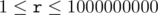 )
)
You have to output the number after the increase.
- - p r It decreases the number with index p by r. (
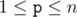 ,
, 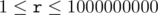 ) You must not decrease the number if it would become negative.
) You must not decrease the number if it would become negative.
You have to output the number after the decrease.
- s l r mod You have to output the sum of numbers in the interval
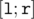 which are equal mod (modulo m). (
which are equal mod (modulo m). (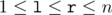 ) (
) (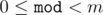 )
)
The first line of each test case contains the number of elements of the sequence n and the number m. (1 ≤ n ≤ 10000) (1 ≤ m ≤ 10)
The second line contains n initial numbers of the sequence. (0 ≤ number ≤ 1000000000)
The third line of each test case contains the number of queries q (1 ≤ q ≤ 10000).
The following q lines contains the queries (one query per line).
Output q lines - the answers to the queries.
3 4
1 2 3
3
s 1 3 2
+ 2 1
- 1 2
2
3
1
题目大意:
s 求 l~r中 对m取模==mod 的 和
+ 单点修改
- 单点修改,如果减后小于0直接输出
树状数组
屠龙宝刀点击就送
#include <ctype.h> #include <cstdio> #define N 10005 typedef long long LL; void read(LL &x) { x=0;bool f=0; char ch=getchar(); for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar()) if(ch=='-') f=1; for(;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; x=f?(~x)+1:x; } LL dis[N],n,m,q; struct node { LL tag[N]; int n; int lowbit(int x) {return x&((~x)+1);} void plus(int x,int y) { for(;x<=n;x+=lowbit(x)) tag[x]+=y; } LL query(int x) { LL ans=0; for(;x;x-=lowbit(x)) ans+=tag[x]; return ans; } }a[25]; int main() { read(n);read(m); for(int i=0;i<m;i++) a[i].n=n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { read(dis[i]); a[dis[i]%m].plus(i,dis[i]); } char str[5]; read(q); for(LL x,y,z;q--;) { scanf("%s",str+1);read(x);read(y); switch(str[1]) { case 's': { read(z); printf("%lld ",a[z].query(y)-a[z].query(x-1)); break; } case '+': { a[dis[x]%m].plus(x,-dis[x]); dis[x]+=y; a[dis[x]%m].plus(x,dis[x]); printf("%lld ",dis[x]); break; } case '-': { if(dis[x]<y) {printf("%lld ",dis[x]);} else { a[dis[x]%m].plus(x,-dis[x]); dis[x]-=y; a[dis[x]%m].plus(x,dis[x]); printf("%lld ",dis[x]); } break; } } } return 0; }