多线程的问题中的经典问题是生产者和消费者的问题,就是如何让线程有序的进行执行,获取CPU执行时间片的过程是随机的,如何能够让线程有序的进行,Java中提供了等待唤醒机制很好的解决了这个问题!
生产者消费者经典的线程中的问题其实是解决线程中的通讯问题,就是不同种类的线程针对同一资源的操作,这里其实有一张图很好的阐述了这其中的问题:

1 //代码中的实体类 2 public class Student { 3 String name; 4 int age; 5 boolean flag; // 默认情况是没有数据,如果是true,说明有数据 6 } 7 8 public class SetThread implements Runnable { 9 10 private Student s; 11 private int x = 0; 12 13 public SetThread(Student s) { 14 this.s = s; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public void run() { 19 while (true) { 20 synchronized (s) { 21 //判断有没有 22 if(s.flag){ 23 try { 24 s.wait(); //t1等着,释放锁 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 } 29 30 if (x % 2 == 0) { 31 s.name = "林青霞"; 32 s.age = 27; 33 } else { 34 s.name = "刘意"; 35 s.age = 30; 36 } 37 x++; //x=1 38 39 //修改标记 40 s.flag = true; 41 //唤醒线程 42 s.notify(); //唤醒t2,唤醒并不表示你立马可以执行,必须还得抢CPU的执行权。 43 } 44 //t1有,或者t2有 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 public class GetThread implements Runnable { 50 private Student s; 51 52 public GetThread(Student s) { 53 this.s = s; 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 public void run() { 58 while (true) { 59 synchronized (s) { 60 if(!s.flag){ 61 try { 62 s.wait(); //t2就等待了。立即释放锁。将来醒过来的时候,是从这里醒过来的时候 63 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } 67 68 System.out.println(s.name + "---" + s.age); 69 //林青霞---27 70 //刘意---30 71 72 //修改标记 73 s.flag = false; 74 //唤醒线程 75 s.notify(); //唤醒t1 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 81 /* 82 * 分析: 83 * 资源类:Student 84 * 设置学生数据:SetThread(生产者) 85 * 获取学生数据:GetThread(消费者) 86 * 测试类:StudentDemo 87 * 88 * 问题1:按照思路写代码,发现数据每次都是:null---0 89 * 原因:我们在每个线程中都创建了新的资源,而我们要求的时候设置和获取线程的资源应该是同一个 90 * 如何实现呢? 91 * 在外界把这个数据创建出来,通过构造方法传递给其他的类。 92 * 93 * 问题2:为了数据的效果好一些,我加入了循环和判断,给出不同的值,这个时候产生了新的问题 94 * A:同一个数据出现多次 95 * B:姓名和年龄不匹配 96 * 原因: 97 * A:同一个数据出现多次 98 * CPU的一点点时间片的执行权,就足够你执行很多次。 99 * B:姓名和年龄不匹配 100 * 线程运行的随机性 101 * 线程安全问题: 102 * A:是否是多线程环境 是 103 * B:是否有共享数据 是 104 * C:是否有多条语句操作共享数据 是 105 * 解决方案: 106 * 加锁。 107 * 注意: 108 * A:不同种类的线程都要加锁。 109 * B:不同种类的线程加的锁必须是同一把。 110 * 111 * 问题3:虽然数据安全了,但是呢,一次一大片不好看,我就想依次的一次一个输出。 112 * 如何实现呢? 113 * 通过Java提供的等待唤醒机制解决。 114 * 115 * 等待唤醒: 116 * Object类中提供了三个方法: 117 * wait():等待 118 * notify():唤醒单个线程 119 * notifyAll():唤醒所有线程 120 * 为什么这些方法不定义在Thread类中呢? 121 * 这些方法的调用必须通过锁对象调用,而我们刚才使用的锁对象是任意锁对象。 122 * 所以,这些方法必须定义在Object类中。 123 */ 124 public class StudentDemo { 125 public static void main(String[] args) { 126 //创建资源 127 Student s = new Student(); 128 129 //设置和获取的类 130 SetThread st = new SetThread(s); 131 GetThread gt = new GetThread(s); 132 133 //线程类 134 Thread t1 = new Thread(st); 135 Thread t2 = new Thread(gt); 136 137 //启动线程 138 t1.start(); 139 t2.start(); 140 }
141 }
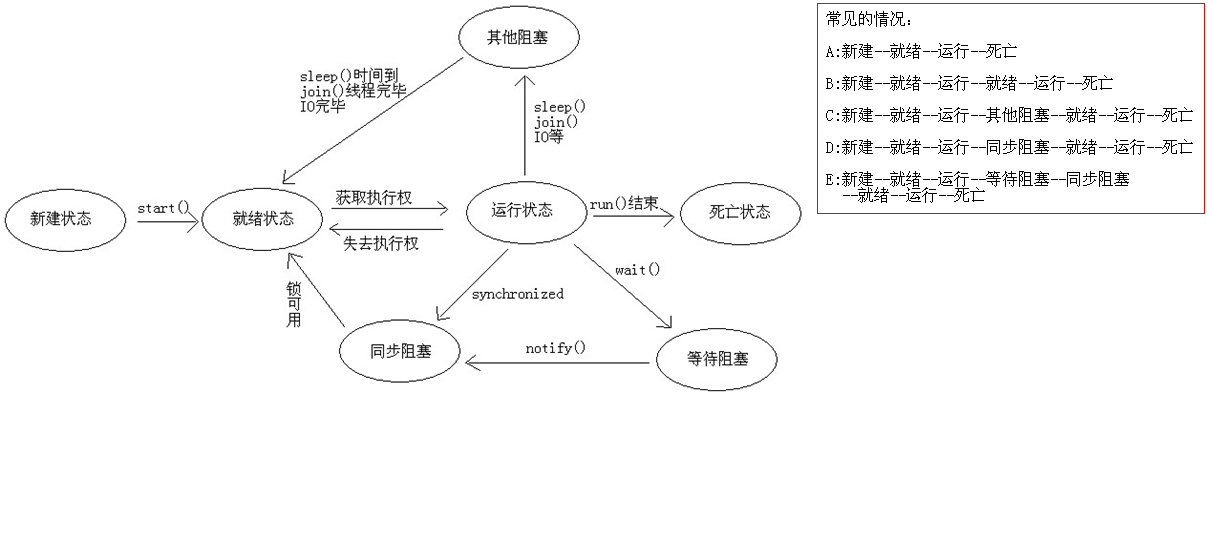
线程的状态转换图及常见执行情况:
上述代码的优化方案:
1 //创建对象的时候实现线程安全 2 public class Student { 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 private boolean flag; // 默认情况是没有数据,如果是true,说明有数据 6 7 public synchronized void set(String name, int age) { 8 // 如果有数据,就等待 9 if (this.flag) { 10 try { 11 this.wait(); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // 设置数据 18 this.name = name; 19 this.age = age; 20 21 // 修改标记 22 this.flag = true; 23 this.notify(); 24 } 25 26 public synchronized void get() { 27 // 如果没有数据,就等待 28 if (!this.flag) { 29 try { 30 this.wait(); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 36 // 获取数据 37 System.out.println(this.name + "---" + this.age); 38 39 // 修改标记 40 this.flag = false; 41 this.notify(); 42 } 43 } 44 45 public class GetThread implements Runnable { 46 private Student s; 47 48 public GetThread(Student s) { 49 this.s = s; 50 } 51 52 @Override 53 public void run() { 54 while (true) { 55 s.get(); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 public class SetThread implements Runnable { 61 62 private Student s; 63 private int x = 0; 64 65 public SetThread(Student s) { 66 this.s = s; 67 } 68 69 @Override 70 public void run() { 71 while (true) { 72 if (x % 2 == 0) { 73 s.set("林青霞", 27); 74 } else { 75 s.set("刘意", 30); 76 } 77 x++; 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 82 public class StudentDemo { 83 public static void main(String[] args) { 84 //创建资源 85 Student s = new Student(); 86 87 //设置和获取的类 88 SetThread st = new SetThread(s); 89 GetThread gt = new GetThread(s); 90 91 //线程类 92 Thread t1 = new Thread(st); 93 Thread t2 = new Thread(gt); 94 95 //启动线程 96 t1.start(); 97 t2.start(); 98 } 99 }