datanode的存储大体上可以分为两部分:
1.与Storage相关的类从宏观上刻画了每个存储目录的组织结构,管理由HDFS属性dfs.data.dir指定的目录,如current、previous、detach、tmp、storage等目录和文件,并定义了对整个存储的相关操作;
2.与Dataset相关的类描述了块文件及其元数据文件的组织方式,如current目录中的文件组织结构,以及对块文件的相关操作。
因为namenode也会用到Storage相关,而namenode并不存储块文件,因而将存储分成这两部分。
Storage类相关
先从一个datanode的配置看起,datanode的本地数据可以分配在多个磁盘上,具体配置就是如下
<property>
<name>dfs.data.dir</name>
<value>/data/hdfs/dfs/data,/data/hdfs/dfs/data2</value>
</property>
/data/hdfs/dfs/data,/data/hdfs/dfs/data2两个目录下存储的就是本datanode所能管理的所有数据.
进入其中一个目录,可能的目录结构是这样的
/current/VERSION
/blk_<id_1>
/blk_<id_1>.meta
/blk_<id_1>
/blk_<id_1>.meta
/...
/blk_<id_64>
/blk_<id_64>.meta
/subdir0/
/subdir1/
/...
/subdir63/
/previous/
/detach/
/tmp/
/in_use.lock
/storage
在这里粗略的概括下在datanode中的对应关系:
StorageDirectory对应的为每个本地存储路径,如/data/hdfs/dfs/data
FSDir对应的是current,以及他的子目录subdir*
DataStorage对所有的本地存储路径进行统一管理,也就是对StorageDirectory进行管理,并没有对存储路径中的具体数据文件进行管理
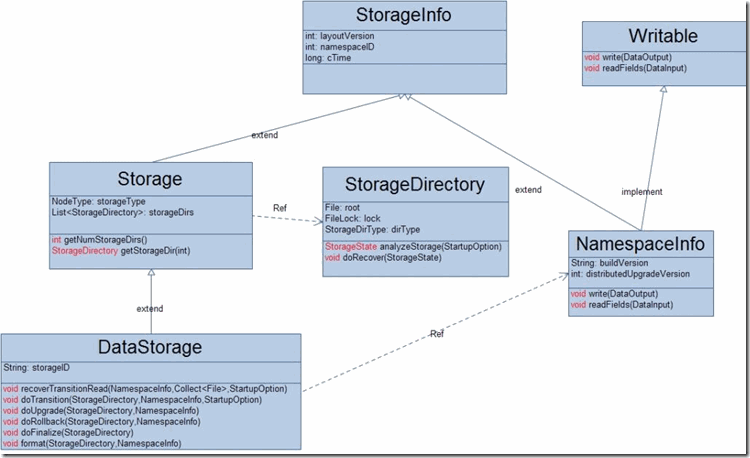
和DataStorage相关的类图
在上面的类图中,NamespaceInfo用来表示整个HDFS集群中命名空间的版本号,这个版本号在NameNode节点格式化时生成,DataNode每一次启动向NameNode节点注册时都会获取到这个命名空间的版本号,如果DataNode是第一次启动,则会持久保存这个版本号;否则,它会用自己第一次启动获取的版本号与这个版本号进行比较,如果不匹配则终止启动
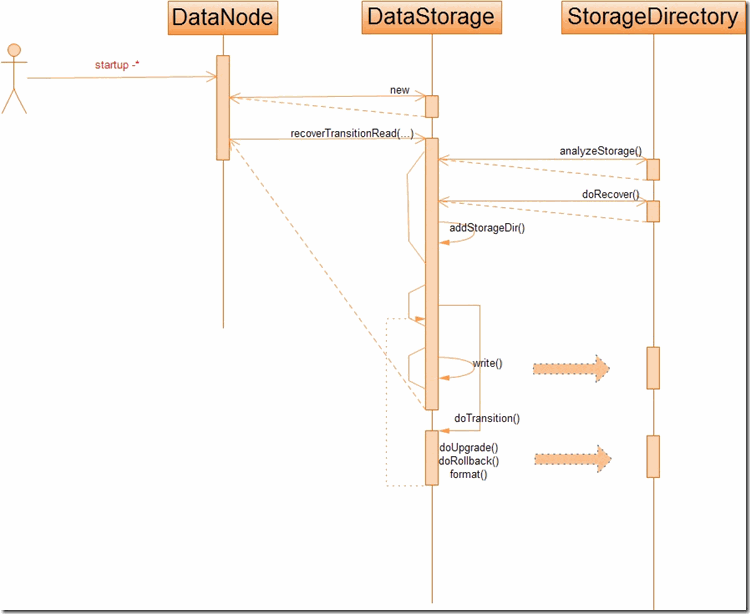
DataStorage主要在DataNode节点启动时扮演重要的角色.StorageDirectory提供了粗粒度的事务性操纵,对StorageDirectory的事务性操作都是由DataStorage完成的。下面是在datanode启动的时候所进行的操作
recoverTransitionRead函数所做的工作是,DataStorage对每一个存储路径构造成一个StorageDirectory,然后分析每一个存储路径当前的状态,对处于非正常状态的存储路径进行相应的操作;当所有的存储路径处于正确的状态之后,就要对每一个存储路径进行用户启动节点时的指定操作(备份/升级/回滚/恢复/提交);最后,如果所有的存储路径操作成功之后,就需要更新每一个存储路径下的storage版本信息,及对应的VERSION文件. recoverTransitionRead的主要流程如下
void recoverTransitionRead(NamespaceInfo nsInfo, Collection<File> dataDirs, StartupOption startOpt) throws IOException { // 1. For each data directory calculate its state and check whether all is consistent before transitioning.Format and recover. this.storageID = ""; this.storageDirs = new ArrayList<StorageDirectory>(dataDirs.size()); ArrayList<StorageState> dataDirStates = new ArrayList<StorageState>(dataDirs.size()); for (Iterator<File> it = dataDirs.iterator(); it.hasNext();)//对每一个本地存储路径 { File dataDir = it.next(); StorageDirectory sd = new StorageDirectory(dataDir); StorageState curState; try { curState = sd.analyzeStorage(startOpt);//分析本地存储路径的状态 // sd is locked but not opened switch (curState) { case NORMAL: break; case NON_EXISTENT: // ignore this storage LOG.info("Storage directory " + dataDir + " does not exist."); it.remove(); continue; case NOT_FORMATTED: // format LOG.info("Storage directory " + dataDir + " is not formatted."); LOG.info("Formatting ..."); format(sd, nsInfo);//初次启动的时候,格式化 break; default: // recovery part is common sd.doRecover(curState);//先回复正常状态 } } catch (IOException ioe) { sd.unlock(); throw ioe; } // add to the storage list addStorageDir(sd); dataDirStates.add(curState); } // 2. Do transitions Each storage directory is treated individually.During sturtup some of them can upgrade or rollback //while others could be uptodate for the regular startup. for (int idx = 0; idx < getNumStorageDirs(); idx++) { doTransition(getStorageDir(idx), nsInfo, startOpt);//对每个本地存储路径依次执行 升级 回滚 提交等操作 } // 3. Update all storages. Some of them might have just been formatted. this.writeAll(); }
4种操作:
format:创建VERSION文件
doUpgrade:升级系统
删除previous
current -> previous.tmp
previous.tmp做硬链接到current
写VERSION文件
previous.tmp -> previous
doRollback:回滚
current -> removed.tmp
previous -> current
删除removed.tmp
doFinalize:提交存储目录升级
previous -> finalized.tmp
删除finalized.tmp
参考url
http://blog.csdn.net/xhh198781/article/details/7170087
http://blog.jeoygin.org/2012/03/hdfs-source-analysis-3-datanode-storage.html