概述
mongodb 被用到越来越多的场景,本篇为入门篇。
monogodb 主要特点
- 高性能
- 丰富的查询条件
- 高可用
- 水平扩展
- 多种存储引擎
基本模型
基本数据模型
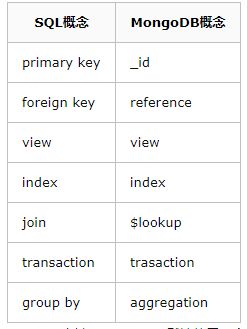
用两个图片来看一下和关系型数据库的对照
- _id 主键,MongoDB 默认使用一个_id 字段来保证文档的唯一性。
- reference 引用,勉强可以对应于 外键(foreign key) 的概念,之所以是勉强是因为 reference 并没有实现任何外键的约束,而只是由客户端(driver)自动进行关联查询、转换的一个特殊类型。
- view 视图,MongoDB 3.4 开始支持视图,和 SQL 的视图没有什么差异,视图是基于表/集合之上进行动态查询的一层对象,可以是虚拟的,也可以是物理的(物化视图)。
- index 索引,与SQL 的索引相同。
- $lookup,这是一个聚合操作符,可以用于实现类似 SQL-join 连接的功能
- transaction 事务,从 MongoDB 4.0 版本开始,提供了对于事务的支持
- aggregation 聚合,MongoDB 提供了强大的聚合计算框架,group by 是其中的一类聚合操作。
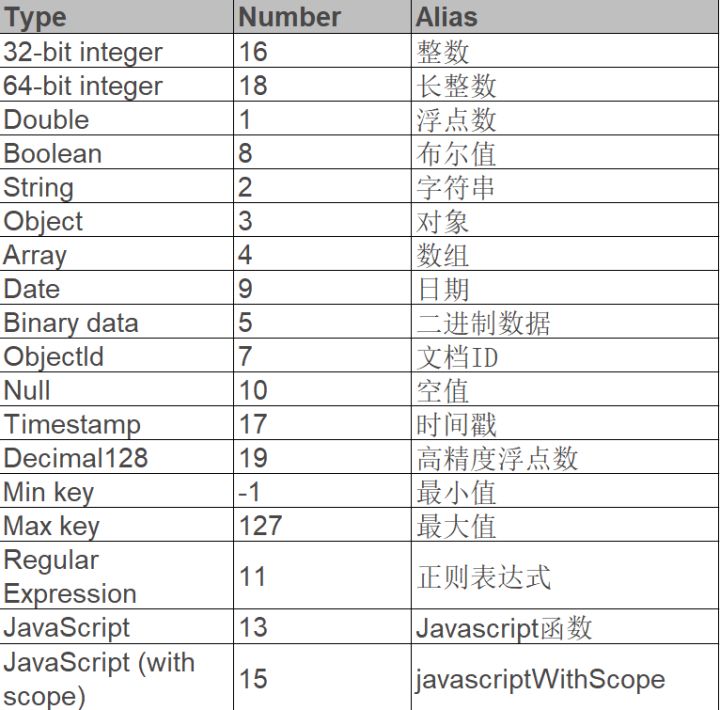
BSON
曾经,JSON 的出现及流行让 Web 2.0 的数据传输变得非常简单,所以使用 JSON 语法是非常容易让开发者接受的。
但是 JSON 也有自己的短板,比如无法支持像日期这样的特定数据类型,因此 MongoDB 实际上使用的是一种扩展式的JSON,叫 BSON(Binary JSON)。
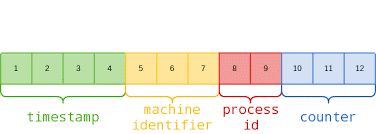
分布式ID
MongoDB 采用 ObjectId 来表示主键的类型,数据库中每个文档都拥有一个_id 字段表示主键。 _id 的生成规则如下:
需要注意的是默认的主键基于雪花算法,基于时间戳,假如回滚时间或是时间不准确会导致数据受到影响
mongodb 语句操作
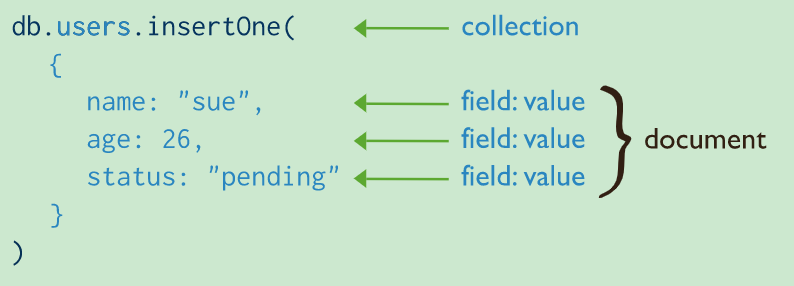
insert 操作
其中 users 为 collection ,另外一个例子 :
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }
]);
select 操作
db.inventory.find( {} )
我们前面也知道collection(上面例子中的 inventory )相当于数据库中的表,那么上面的语句就像
select * from inventory
我们需要查特定条件的记录呢,相当于加了 where 语句 。
db.inventory.find( { status: "D" } )
相当于
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "D"
其他条件的查询可见如下,其他复杂的查询可见 : https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/query-documents/
db.inventory.find( { $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] } )
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" OR qty < 30
db.inventory.find( {
status: "A",
$or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ]
} )
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND ( qty < 30 OR item LIKE "p%")
update 操作
mongodb 的 update 有两类 :
- update 更新
- replace 替代操作
// 这个是更新
db.inventory.updateOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "cm", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
// 这个 replace
db.inventory.replaceOne(
{ item: "paper" }, //被更新对象匹配的条件
{ item: "paper", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 40 } ] } //替代的新记录
)
delete 操作
删除也有删除一条记录和多条记录的不同操作方式
db.inventory.deleteMany({ status : "A" })
db.inventory.deleteOne( { status: "D" } )
后面索引这一节的内容来自 : https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/87722764 ,非原创
索引
mongodb 索引上使用 B+ 树的实现,下面是建立索引的例子 。
// author后面的数字 1 代表升序,如果是降序则是 -1
db.book.ensureIndex({author: 1})
//复合索引
db.book.ensureIndex({type: 1, published: 1})
//MongoDB 可以在复合索引上包含数组的字段,但最多只能包含一个
db.book.ensureIndex({tags: 1})
索引特性
在声明索引时,还可以通过一些参数化选项来为索引赋予一定的特性,包括:
- unique=true,表示一个唯一性索引
- expireAfterSeconds=3600,表示这是一个TTL索引,并且数据将在1小时后老化
- sparse=true,表示稀疏的索引,仅索引非空(non-null)字段的文档
- partialFilterExpression: { rating: { $gt: 5 },条件式索引,即满足计算条件的文档才进行索引
索引分类
除了普通索引之外,MongoDB 支持的类型还包括:
- 哈希(HASH)索引,哈希是另一种快速检索的数据结构,MongoDB 的 HASH 类型分片键会使用哈希索引。
- 地理空间索引,用于支持快速的地理空间查询,如寻找附近1公里的商家。 (这一个使我们想到一些使用场景)
- 文本索引,用于支持快速的全文检索
- 模糊索引(Wildcard Index),一种基于匹配规则的灵活式索引,在4.2版本开始引入。
索引评估、调优
mongodb 中也有 explain 语句 ,下面例子使用 explain() 命令可以用于查询计划分析,进一步评估索引的效果。 如下:
db.test.explain().find( { a : 5 } )
{ "queryPlanner" : { ... "winningPlan" : { "stage" : "FETCH", "inputStage" : { "stage" : "IXSCAN", "keyPattern" : { "a" : 5 }, "indexName" : "a_1", "isMultiKey" : false, "direction" : "forward", "indexBounds" : {"a" : ["[5.0, 5.0]"]} } }}, ... }
集群
这里就不深入集群的一些细节,本篇是入门篇,在后续的篇章中会介绍集群相关的。
总结
本篇介绍了 mongodb 一些基本的操作,在后续的文章中我们会更加深入地介绍
参考资料
学习 monogodb 入门可以先阅读以下几篇文章 :
- https://www.mongodb.com/document-databases(What is a Document Database?)
- https://www.mongodb.com/nosql-explained (关于 nosql 的介绍)
入门学习
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/87722764 (入门学习介绍)
mongodb 命令操作
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/crud/
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/query-documents/ (挺不错的,提供 shell 命令行界面)